This topic describes the changes made to LoadComplete 4.40. For information on the changes made to other versions of the product, see Version History.
Improved Runtime Graphs
-
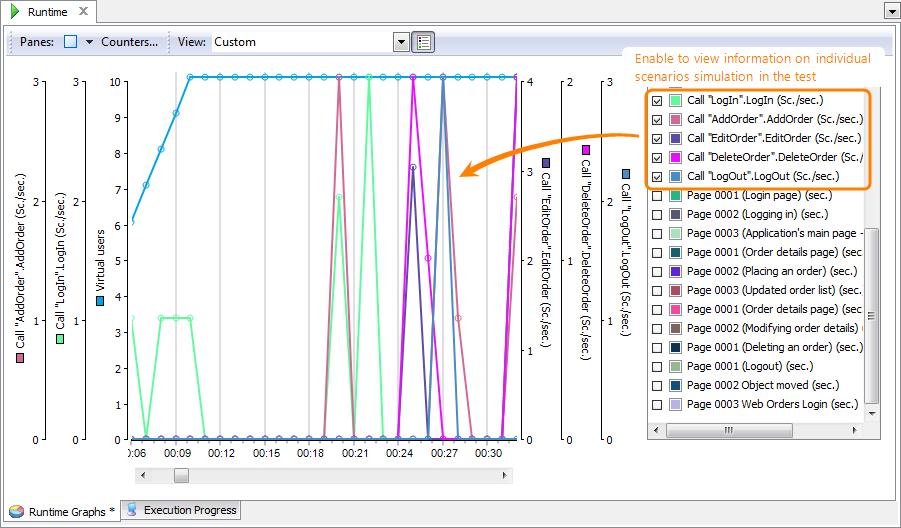
The Runtime graphs panel now displays the number of accomplished scenarios in your test:
-
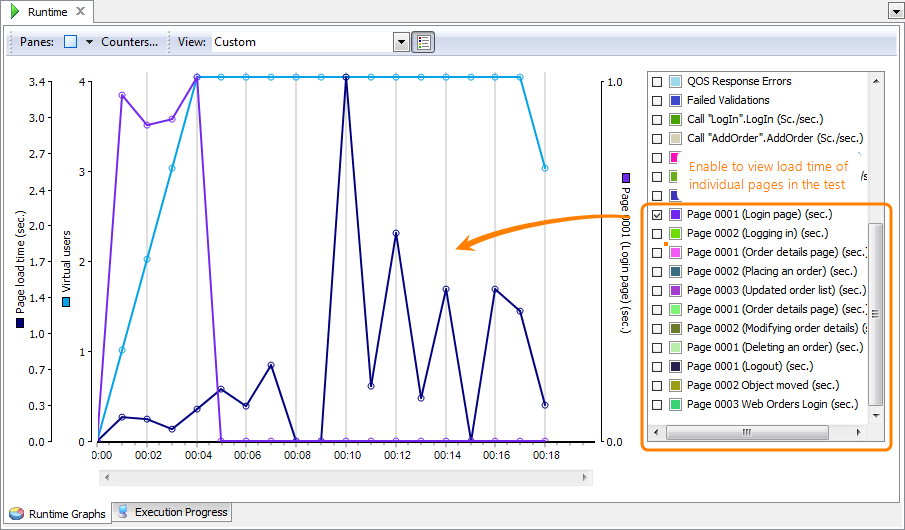
In addition to the average load time that LoadComplete calculates for all pages during the test run, the Runtime Graphs page now shows the load time of individual pages:
Improved Reports
-
A new metric in the Summary report –“90% Response Time”. It indicates the load time that covers 90% of simulated requests. This value provides more reliable estimation for the page load time in comparison with the average load time in situations when the minimum and maximum load time values differ a lot.
-
The new Response Throughput metric in custom charts after the test run is over. In previous versions, this metric was available only on the Runtime graph during test runs.
-
Before printing reports or exporting them to a PDF file, you can now specify your name and organization to include that data in the report.
Overall Improvements
-
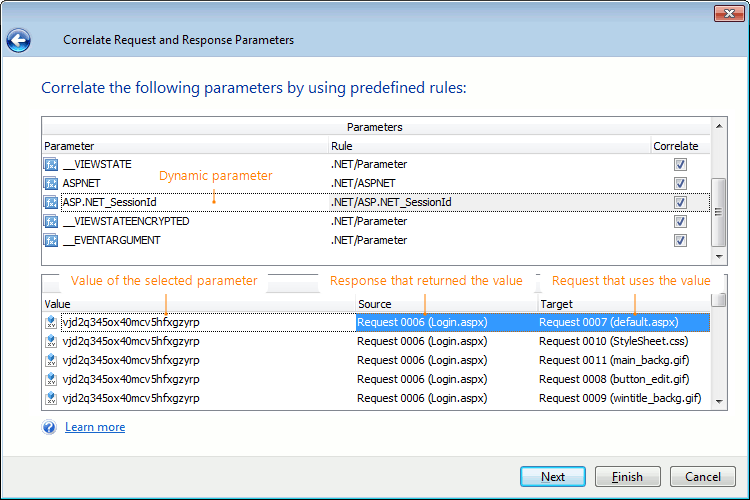
The Correlate Requests and Responses wizard has been improved. Now it displays the value of each parameter you correlate, as well as a list of requests and responses that use that value. This makes the correlation process clearer and easier to understand:
-
Exporting test results in the new XML tree format. In this format, test results are hierarchically organized by workstations, users, iterations, scenarios and pages. Thus, it is much easier to combine load test results obtained from multiple workstations.
-
The Simulating | General | Logging options have been renamed to make them more descriptive and easier to understand.
-
A number of bugs reported by our customers have been fixed.
Discontinued Support
The non-proxy recording mode is deprecated. It will be removed from the product in one of the future releases.
We recommend that you record traffic in proxy mode: it is more stable than the non-proxy mode and allows recording traffic in browsers and applications which the non-proxy mode does not support, for example, in Microsoft Edge.