User groups is an optional feature that allows you to define groups of users within your organization, so reviews can be associated with a group. Groups can be used to model the hierarchy and project assignments of your organization. Each group can contain multiple users and can also contain other groups. Each user can be in more than one group. You can specify group administrators who are able to maintain individual groups.
The word Group is configurable in the General Settings, so you could change it to Team, or Project, or whatever else.
| Note: | User groups are only supported in Collaborator Enterprise. For a complete list of differences between Collaborator editions, see Collaborator Editions. |
Associate Groups With Reviews
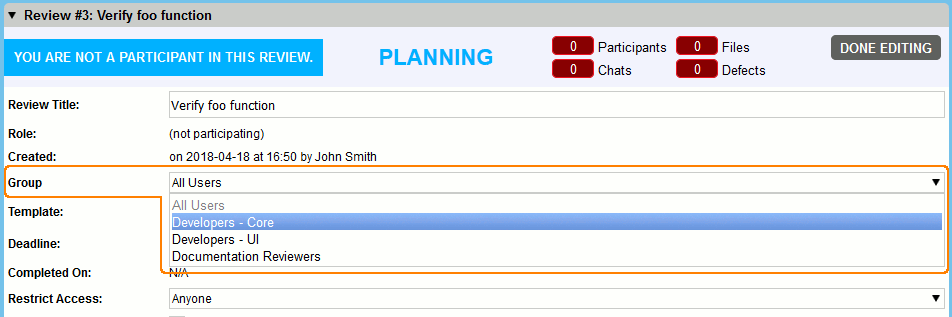
If a user is a member of a single group that can be associated with a review, reviews created by that user are automatically associated with that group. If a user is a member of more than one group that can be associated with a review, an additional field is displayed when creating a review:
The list of groups to select from is calculated by first creating a list of all groups that contain the review creator as a member. All groups in that list are then checked to see if they are a child group of any other group or groups. Parent groups are added to the list recursively.
In the settings for a group there is an option to disallow associating that group with reviews. This is useful for creating groups that are used for reporting or filtering only. When a group and all its sub-groups cannot be associated with reviews, then this group is not displayed in the group list. When a group cannot be associated with reviews, but some of its sub-groups can be associated with reviews, then the parent group is displayed in the group list, but cannot be selected.
Associating a group with a review makes it easier to select participants for that review because the Person list can optionally be filtered by group. The filter is calculated by starting with the users that are members of the selected group. If the selected group also contains child groups, then the users that are members of those child groups will also be added. The search for child groups is done recursively.
Change Review Group
We do not recommend changing a group on phases other than Planning phase.
- Changing a group will remove existing participants that do not belong to a new group. If participants belong both to existing group and to new group, they will be retained.
- Changing a group clears the current template, unless the template is available for both groups.
- Changing a group clears currently filled-in checklist items, unless the checklist is available for both groups.
Restrict Access
You can use groups to limit access to reviews by setting Restrict Access to Review Content in the General settings. When the group access restriction feature is used, the list of users who have access to the review is calculated by starting with the users that are members of the group that is associated with the review. If that group also contains child groups, then the users that are members of those child groups will also be added. The search for child groups is done recursively. Finally, if the group associated with the review is a child of any other group or groups, then the users that are members of those parent groups will also be added. The search for parent groups is done recursively.
Group Hierarchies
It may be difficult to understand how best to use groups based on the rules given above. We have provided a few examples of how they are usually used:
Maintain Groups
Groups can be created and modified in one of two ways: manually (with the web user interface – see the sections below, starting with Create New Groups, or with the command-line scripting command ccollab admin group create) or automatically via the command-line scripting ccollab admin group sync command.
If you have only a few groups, it will be easier to manage them manually. If you have many groups or if you are mirroring them from an external system like LDAP, it is best to manage them automatically using the sync command.
The command-line sync command interface is provided to make it easy to mirror group definitions in to Collaborator from an external system. The ccollab admin group sync command uses the contents of the group-sync-xml.xsd XML file to update the Collaborator group definitions. See Synchronize Groups and Members for more information.
Collaborator tracks which groups were created manually and which were defined via ccollab admin group sync. Groups that were defined manually are not overwritten as a result of using ccollab admin group sync. See the Use Groups for Organizational Hierarchy and Projects example to see how this can be useful.
Create New Groups
To create a new user group, first specify its display name, then click Create Group.
Once a group is created, the group will appear in the Group List. Group administrators will only see groups listed that they can administer.
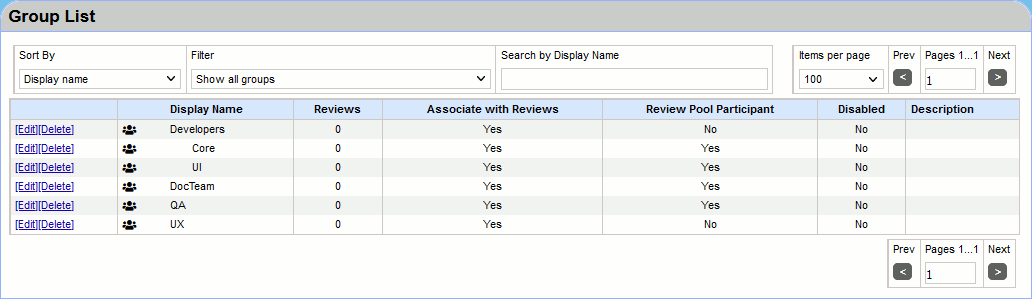
You can sort and filter group list, also, you can search for groups that contain the specified letters.
When your server has multiple groups, the Group List is divided into several pages. The controls above and below the list allow to select how many items will be displayed per page and navigate to next and previous pages.
In the group list, you can edit the configuration details or delete the group by clicking the appropriate link. The group list also shows the number of reviews associated with the group, whether or not the group can be associated with reviews, whether or not the group is enabled, and any descriptions given to the group.
Delete Groups
To delete a group, click Delete next to the title of the group in the group list. You can only delete a group if it is not associated with reviews. If the group is associated with reviews, you must first associate those reviews with a different group before deleting it. Alternatively, you could instead disable the group in order to prevent future reviews from being associated with it.
Group administrators are further restricted to only being able to delete groups that they are group administrators of and that have no child groups. This restriction exists to prevent group administrators from indirectly creating top-level groups.
Edit Group Properties
To edit a group, click Edit next to the title of the group in the group list. You will be directed to the Edit Group form.
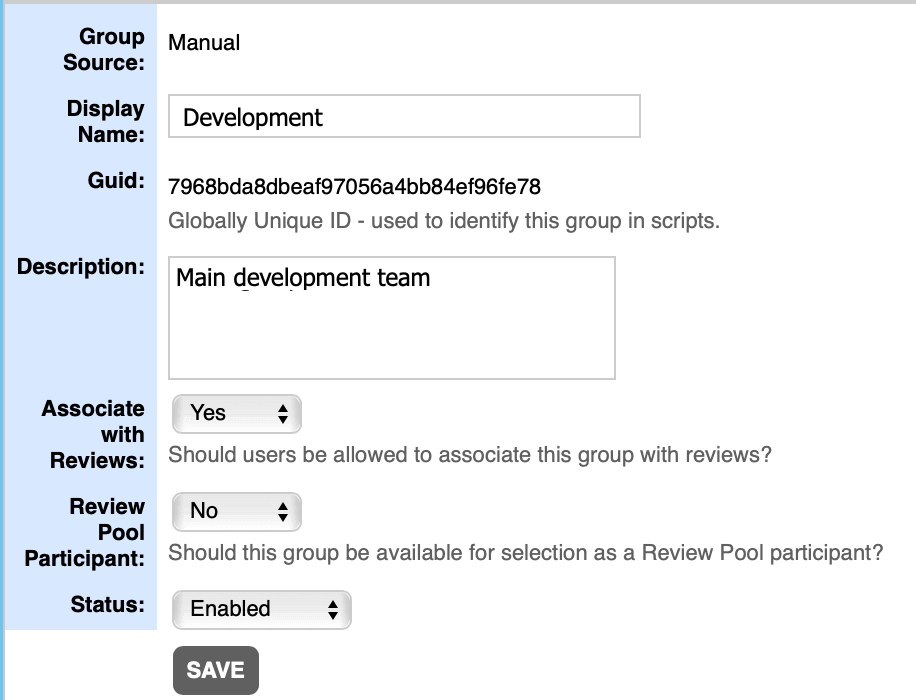
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Group Source | Specifies source where/how the group was created. Possible values: Manual, Crowd, SAML, LDAP, remote system. |
| Display Name | Human-readable title for the group, used in drop-down menus and other UI elements. This does not have to be unique across all groups |
| GUID | Machine-readable ID for group, unique across all groups. If the group was created using the Web Client, this is generated automatically. If the group was created using the sync command, this ID is supplied in the XML file. |
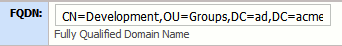
| FQDN |
Fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the group. This name is used when synchronizing groups with LDAP or AD.
 |
| Description | Human-readable description for the group. This is displayed on the General Information page when associating a group with a review. |
| Associate with Reviews | If this is set to Yes, this group is selectable from the Group drop-down list when associating a group with a review. If No, this group will be hidden or disabled in the group list. For an example, see Use Groups for Organizational Hierarchy and Projects. |
| Review Pool Participant | Specifies whether this group is a Review Pool, that is it could be selected as a participant of a review. |
| Status | Specifies whether the group is enabled or disabled. Groups can be disabled when they are no longer in use. Disabled groups still show up in reports because reviews may be associated with them. |
Group administrators are regular (not full administrator) users who are allowed to administer this group. Group administrators can edit all of the fields of the group.
Group administrators can add or remove group administrators for the group, even themselves, but they can not remove the last group administrator from the group.
Group administrators can add or remove user members of the group. Users that are group administrators may or may not also be regular members of the group.
Group administrators are not allowed to directly edit the list of child groups of the group, also they cannot create top-level groups. If the Can Create Child Groups option is enabled for the respective user, group administrator can create new child groups of the group. The group administrator that has created a child group automatically becomes a group administrator of that child group.
You can add multiple groups to be children of the group. This may be helpful if a group is constituted by a number of subgroups. The group hierarchy created by Group -> Child Group relationships is important for the associate with review and access control algorithms.
Groups can have specifically named member users, or they can automatically contain all users as members, if All Users drop-down is set to Yes. Group membership is important for the associate with review and access control algorithms.
You can also configure which review templates can be used by this group. That is, specify which workflows, sets of roles, rules will become available to group members when creating reviews. To make all review templates available to the group, set the All Review Templates option to Yes. To define a specific list of templates that should be available to the group, set the All Review Templates option to No and move the desired templates to the Current Review Templates list. The Default Review Template setting specifies the initial template that will be chosen when creating review (if set to None, the first template in the list will be chosen).
Besides, on this page you can create child groups of the selected group.
Use Groups as Review Pools
Review pools are groups that can be selected as participants in a review. You can configure groups for review pools specifically for use as review pools, or select review pools from an existing group hierarchy.
To learn more, see the corresponding topic.
Review Pool Subscriptions
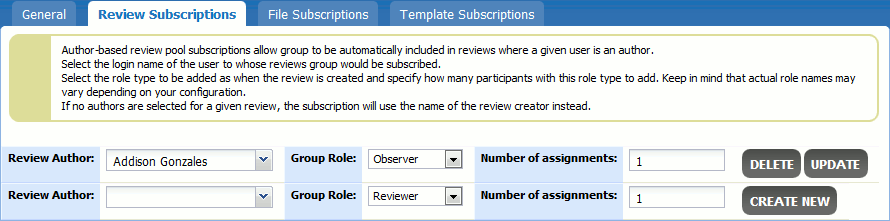
When the group could be selected as a participant of a review (that is, when the Review Pool Participant option is set to Yes), administrators can also set-up review pool subscriptions. Once a review of particular author is created, or a review contains some particular files, or a review uses some particular template, Collaborator will automatically add a group to this review as participant.
Author Subscriptions
File Subscriptions
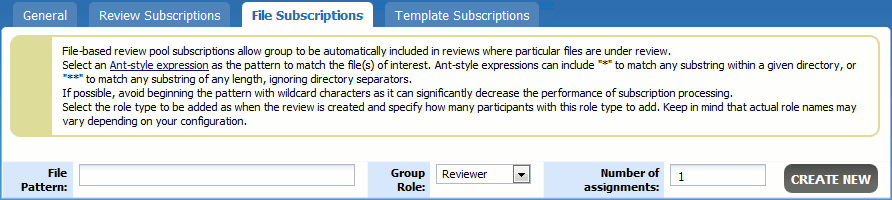
File pattern subscriptions allow a group to be automatically included in reviews where particular files are under a review.
Select an Ant-style expression as the pattern to match the file or files of interest. The expression will be matched to the file path and repository name; it will not look for matches in the complete repository path with URL and other server descriptions. Ant-style expressions can include * to match any substring within a given directory, or ** to match any substring of any length, ignoring directory separators. If possible, avoid beginning the pattern with wildcard characters as it can significantly decrease the performance of subscription processing.
Select the desired role type of group members (Reviewer, Observer, or Moderator) and specify how many participants with this role type to add to the the review. Keep in mind that actual role names may vary depending on your role configuration.
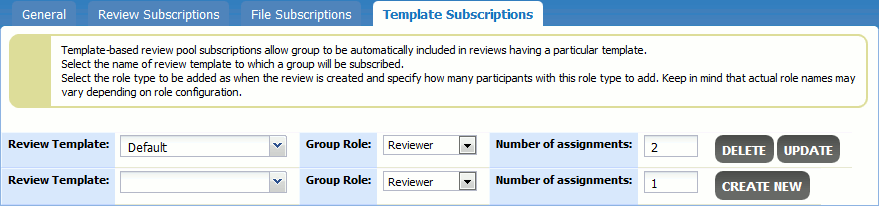
Template Subscriptions
Template subscriptions allow a group to be automatically included in reviews that use particular templates.
Under the Review Template field, select the name of the template to which the group would be subscribed.
Select the desired role type of group members (Reviewer, Observer, or Moderator) and specify how many participants with this role type to add to the the review. Keep in mind that actual role names may vary depending on your role configuration.