About
-
Collaborator integrates with Git repositories hosted at dev.azure.com or visualstudio.com, as well as on on-premises Azure DevOps Servers in your network.
-
When you integrate Collaborator with a Azure DevOps Server repository, your Collaborator server creates reviews automatically for pull requests in the repo, as well as for push events that occur in that repo. For complete information on how the integration works, see Integration With Repository Hosting Services.
-
To inform Collaborator about changes, Azure DevOps Server uses a webhook that sends notification messages to your Collaborator server.
-
To set up the webhook and other integration parameters, you need to set up some options in Collaborator and in Azure DevOps Server. See the rest of this topic for details.
 |
Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) repositories are not supported. |
Supported Hosting Services
-
Azure DevOps Services (cloud hosting at dev.azure.com),
-
Azure DevOps Services (cloud hosting at visualstudio.com) formerly named Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS),
-
Azure DevOps Server (on-premises hosting) formerly named Team Foundation Server (TFS).
Requirements
-
Your Collaborator server must be accessible to Azure DevOps Server and vice versa. You may need to configure your firewall or enable tunneled connections to expose the server’s External URL to the Web. If needed, ask your system administrator for help.
-
To configure integration settings in Collaborator, you need Administrator privileges.
1. Get Azure DevOps Server Tokens
To integrate with Azure DevOps Server/Services, you need a personal access token that will be used to access your repositories.
For detailed information on generating a personal access token, follow instructions on this page of Azure DevOps Server documentation:
 Notes:
Notes:
-
When setting up the token parameters, make sure to enable the following scopes for the token:
Code: FullCode: StatusWork Items: Read, write, & manage
-
After Azure DevOps Server generated the token, save it somewhere or write it down. We will need the token later, when we will configure the integration between Collaborator and Azure DevOps Server.
2. Set Up Integration
Collaborator offers two groups of settings for configuring integration with remote repositories:
| Settings | When to use |
|---|---|
| Easy Add Repository tab | We recommend using these settings to set up new connections to your repositories quickly. |
| Use these settings to configure existing connections. Though you can use these settings to set up integration, the settings on the “Easy Add Repository” tab will help you do this faster. |
Additionally, you can create auto-polling configuration to periodically look for new repositories on the specified server and suggest creating integrations for them.
Easy Add Repository tab (recommended)
-
Log in to Collaborator as administrator. (To integrate with Azure DevOps Server repositories, you need administrator privileges in Collaborator).
-
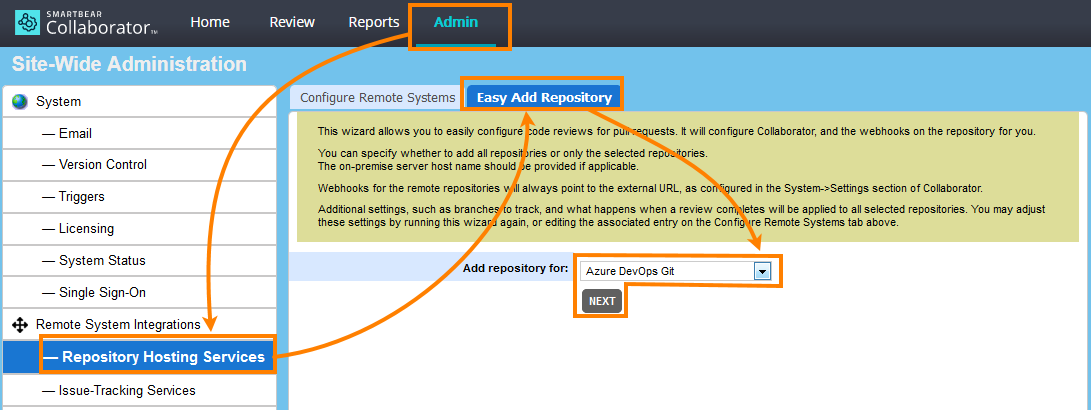
On the Collaborator main toolbar, click ADMIN, and then select Repository Hosting Services from the tree on the left. Then switch to the Easy Add Repository tab.
-
On the tab, select Azure DevOps Git in the Add repository for box and click Next:
-
Collaborator will displays a page with connection details.
Specify settings in the the following sections of the wizard:
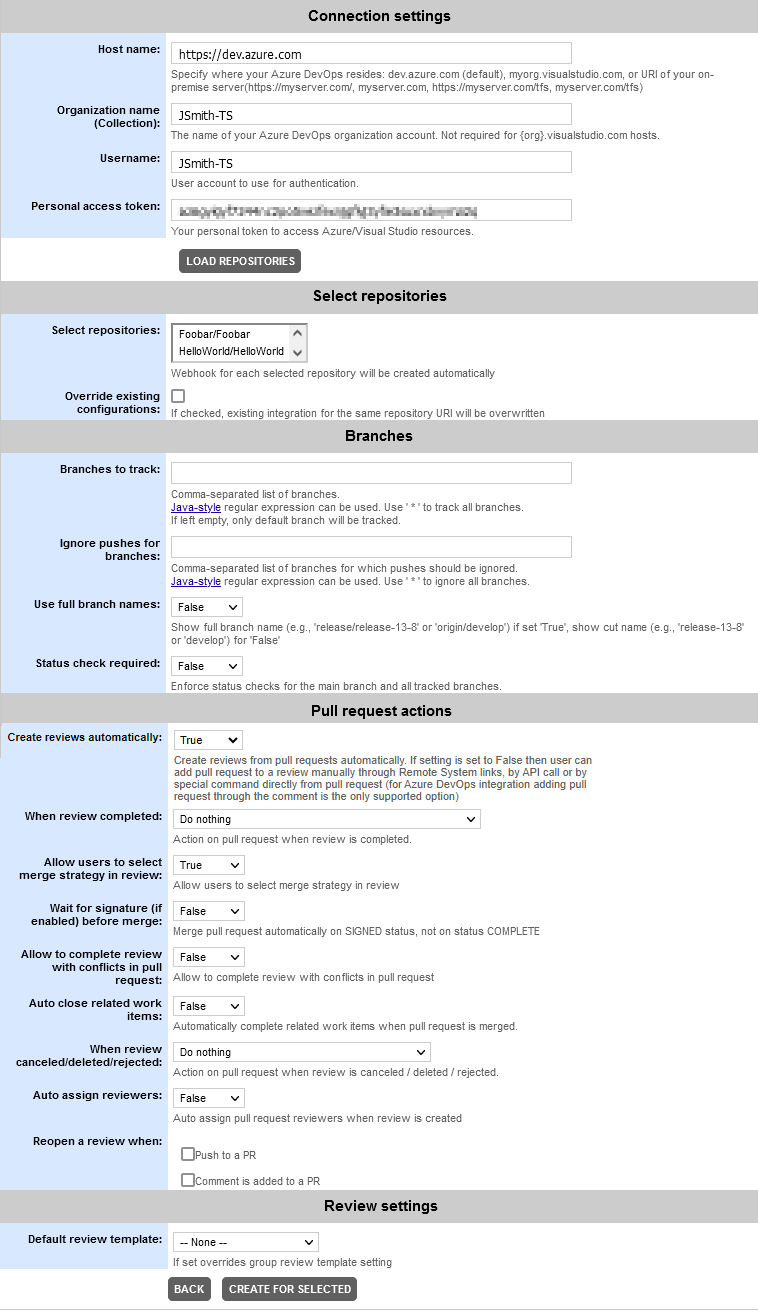
Connection settings
Setting Description Host name
Optional. Specifies the host name where your Azure DevOps Server resides. For example
dev.azure.com,myorg.visualstudio.com, or URI of your on-premise server.If host name is omitted,
dev.azure.comwill be used.Organization name (Collection)
Specifies the name of your organization account. Required for
dev.azure.comand on-premise hosts.Username
Required. Specifies the account name to use for authentication.
Personal access token
Required. The personal access token for a Azure DevOps Server account that has access to your remote repository.
This is the token that we generated in Azure DevOps Server earlier.
After specifying connection settings, you can click Load repositories to retrieve a list of repositories available for the specified user or organization.
Select repositories
Select repositories
Optional. Displays a list of repositories available for the specified user or organization.
Select which repositories you need to track. Use Ctrl+click or Shift+click for multi-selection.
If any of the repositories were chosen, the wizard will display the Create for selected button below the settings section.
If none of the repositories were chosen, the wizard will display the Create for all button below the settings section.
Override existing configurations
Optional. Specifies whether to override existing configurations that track the same repository URI.
Branches
Branches to track
Optional. The names of branches to track changes and create reviews on pull requests and direct pushes. Separate multiple branch names with commas.
You can use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches. Note that wildcards and regular expressions cannot be used if you enable the Status check required setting (see below).If this edit box is empty, the branch main will be tracked.
Ignore pushes for branches
Optional. Specifies branches for which Collaborator will not create reviews on direct pushes.
You can enter one or several branch names. Separate multiple branch names with commas. You can also use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches.Use full branch names
Specifies whether to display full or shortened names for branches in the Review Screen. For example, release/release-13-8 or origin/develop instead of release-13-8 or develop.
This setting affects newly created reviews, for existing reviews branch names remain unchanged.
Status check required
Specifies if Collaborator should enforce status checks for the tracked branches before merging pull requests.
If this option is enabled, you cannot use regular expressions in the Branches to track setting, since this option requires exact name match.
Pull request actions
Create review automatically
If enabled, reviews for pull request are created automatically.
If disabled, user can add pull request to a review manually only by special command directly from pull request.
When review completed
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to the pull request was accomplished:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Merge pull request: Merge pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Merge pull request and delete its branch: Merge pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
- Squash and merge pull request: Squash and merge pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Squash and merge pull request and delete its branch: Squash and merge pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
- Rebase and fast-forward pull request: Rebase and fast-forward pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Rebase and fast-forward pull request and delete its branch: Rebase and fast-forward pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
- Semi-linear merge pull request: Semi-linear merge pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Semi-linear merge pull request and delete its branch: Semi-linear merge pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
To learn more about pull request merge strategies, see Azure DevOps documentation.
Allow users to select merge strategy in review
If enabled, regular users would be able to choose pull request merge strategies in each separate review.
If disabled, all pull requests would behave as specified by the When review completed setting.
Wait for signature (if enabled) before merge
Optional. Effective, if any of merge actions (merge, squash and merge, rebase) was selected in When review completed setting.
If enabled Collaborator will wait for the completed review to be signed off before merging the respective pull request. Otherwise, pull request will be merged immediately, even if the review have not been signed yet.
Allow to complete review with conflicts in pull request
Should it be possible to complete a review if there are conflicts in the respective pull request.
When review cancelled/deleted/rejected
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to a pull request was cancelled, deleted or rejected:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Abandon pull request: Abandon pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Abandon pull request and delete its branch: Abandon pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
Auto assign reviewers
Whether to assign Collaborator reviewers when some specific users were added as pull request reviewers on the Azure DevOps side and integration can match those Azure DevOps users with Collaborator users.
Reopen a review when
Optional. Specifies in what cases Collaborator should reopen completed reviews. May include any combination of the following:
- when a push to a pull request is made,
- when a comment is added to a pull request.
When PR is merged
Optional. Specifies an action to perform on review when pull request is merged:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Cancelled: If the review is in the Planning phase, the review is deleted; if the review is in the Annotate, Inspection, or Rework phase, the review is cancelled (moved to the Cancelled state).
When PR is declined
Optional. Specifies an action to perform on review when pull request is declined:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Cancelled: If the review is in the Planning phase, the review is deleted; if the review is in the Annotate, Inspection, or Rework phase, the review is cancelled (moved to the Cancelled state).
Review settings
Default review template
Optional. Specifies the initial template that will be chosen when creating review (if set to "None", the first template in the list will be chosen).
The value of this setting overrides the value of Default review template setting specified on group level.
-
Click the Create for selected button or the Create for all button to create repository integrations and automatically create webhooks for each repository in Azure DevOps. To stop suggesting integrations for some specific repositories, select these repositories in the list and click Ignore selected.
For every repository a separate configuration will be created in Collaborator and a webhook will be automatically added in Azure DevOps.
Configure Remote Systems tab
-
Log in to Collaborator as an administrator. (To configure integration settings, you need administrator privileges in Collaborator).
-
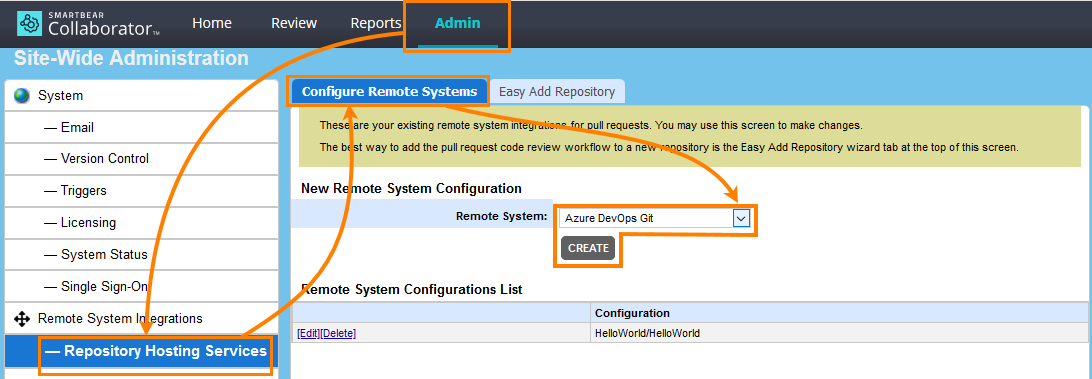
On the Collaborator main toolbar, click ADMIN, and then select Repository Hosting Services from the tree on the left. Then switch to the Configure Remote Systems tab.
-
In the New Remote System Configuration section, select Azure DevOps Git and click Create:
-
Collaborator will display a page with configuration settings. Specify settings in the following sections:
Azure Git settings settings
Setting Description Title
Required. The configuration name as it will be displayed in Collaborator user interface.
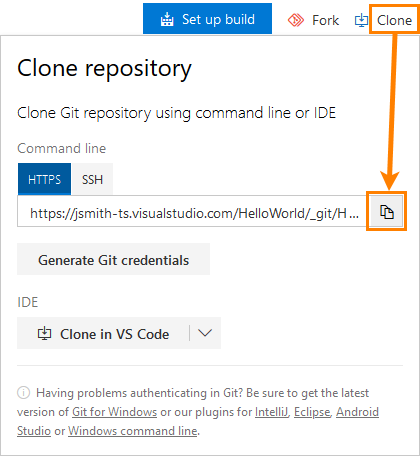
Azure DevOps repository URI
Required. The URI of the Azure DevOps repository to be tracked, for example,
https://dev.azure.com/myorg/myproject/_git/myrepoorhttps://myorg.visualstudio.com/myproject/_git/myrepo.You can copy the URI from the repository page in Azure DevOps Server:
Username
Required. Specifies the account name to use for authentication.
Personal access token
Required. The personal access token for a Azure DevOps Server account that has access to your remote repository.
This is the token that we generated in Azure DevOps Server earlier.
Webhook status
Indicates the current status of the webhook:
- Webhook is absent: The webhook has not been created yet.
- Webhook isn't active: The webhook has been created, but is inactive.
- Up and running: The webhook is active.
To create or activate a webhook, click Update webhook.
 Important: Click this button, when you set up integration with your repository for the first time.
Important: Click this button, when you set up integration with your repository for the first time.Branches
Branches to track
Optional. The names of branches to track changes and create reviews on pull requests and direct pushes. Separate multiple branch names with commas.
You can use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches. Note that wildcards and regular expressions cannot be used if you enable the Status check required setting (see below).If this edit box is empty, the branch main will be tracked.
Ignore pushes for branches
Optional. Specifies branches for which Collaborator will not create reviews on direct pushes.
You can enter one or several branch names. Separate multiple branch names with commas. You can also use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches.Use full branch names
Specifies whether to display full or shortened names for branches in the Review Screen. For example, release/release-13-8 or origin/develop instead of release-13-8 or develop.
This setting affects newly created reviews, for existing reviews branch names remain unchanged.
Status check required
Specifies if Collaborator should enforce status checks for the tracked branches before merging pull requests.
If this option is enabled, you cannot use regular expressions in the Branches to track setting, since this option requires exact name match.
Pull request actions
Create review automatically
If enabled, reviews for pull request are created automatically.
If disabled, user can add pull request to a review manually only by special command directly from pull request.
When review completed
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to the pull request was accomplished:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Merge pull request: Merge pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Merge pull request and delete its branch: Merge pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
- Squash and merge pull request: Squash and merge pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Squash and merge pull request and delete its branch: Squash and merge pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
- Rebase and fast-forward pull request: Rebase and fast-forward pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Rebase and fast-forward pull request and delete its branch: Rebase and fast-forward pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
- Semi-linear merge pull request: Semi-linear merge pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Semi-linear merge pull request and delete its branch: Semi-linear merge pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
To learn more about pull request merge strategies, see Azure DevOps documentation.
Allow users to select merge strategy in review
If enabled, regular users would be able to choose pull request merge strategies in each separate review.
If disabled, all pull requests would behave as specified by the When review completed setting.
Wait for signature (if enabled) before merge
Optional. Effective, if any of merge actions (merge, squash and merge, rebase) was selected in When review completed setting.
If enabled Collaborator will wait for the completed review to be signed off before merging the respective pull request. Otherwise, pull request will be merged immediately, even if the review have not been signed yet.
Allow to complete review with conflicts in pull request
Should it be possible to complete a review if there are conflicts in the respective pull request.
When review cancelled/deleted/rejected
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to a pull request was cancelled, deleted or rejected:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Abandon pull request: Abandon pull request that corresponds to a review.
- Abandon pull request and delete its branch: Abandon pull request that corresponds to a review and then delete the respective branch.
Auto assign reviewers
Whether to assign Collaborator reviewers when some specific users were added as pull request reviewers on the Azure DevOps side and integration can match those Azure DevOps users with Collaborator users.
Reopen a review when
Optional. Specifies in what cases Collaborator should reopen completed reviews. May include any combination of the following:
- when a push to a pull request is made,
- when a comment is added to a pull request.
When PR is merged
Optional. Specifies an action to perform on review when pull request is merged:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Cancelled: If the review is in the Planning phase, the review is deleted; if the review is in the Annotate, Inspection, or Rework phase, the review is cancelled (moved to the Cancelled state).
When PR is declined
Optional. Specifies an action to perform on review when pull request is declined:
- Do nothing: Do not perform any action.
- Cancelled: If the review is in the Planning phase, the review is deleted; if the review is in the Annotate, Inspection, or Rework phase, the review is cancelled (moved to the Cancelled state).
Review settings
Default review template
Optional. Specifies the initial template that will be chosen when creating review (if set to "None", the first template in the list will be chosen).
The value of this setting overrides the value of Default review template setting specified on group level.
-
Click Test Connection to verify if you entered data correctly.
Click Save to store the settings.
Click on Update Webhook button to add webhook for the repository on the remote system's side.
Creating Azure DevOps auto-polling configuration
Sections above describe how to add integrations for existing repositories. When some new repositories are created on a server, you may integrate them manually. Alternatively, you can setup Azure DevOps auto-polling configuration that will periodically look for new repositories on the specified server, user or project and suggest creating integrations for them.
-
Log in to Collaborator as administrator. (To integrate with Azure DevOps repositories, you need administrator privileges in Collaborator).
-
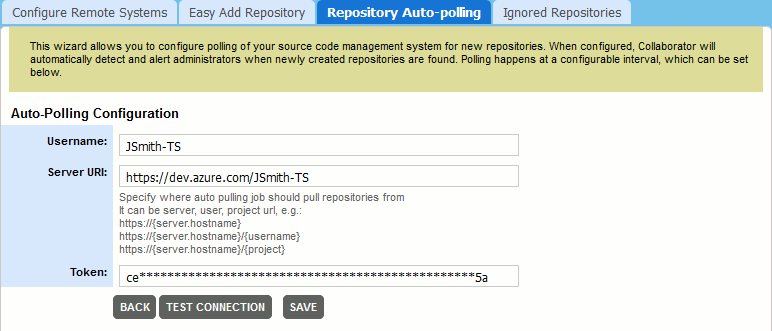
On the Collaborator main toolbar, click ADMIN, and then select Repository Hosting Services from the tree on the left. Then switch to the Repository Auto-Polling tab.
-
On the tab, select Azure DevOps in the Add configuration box and click Next.
-
Collaborator will displays a page with connection details.
Fill in the edit boxes:
Setting Description Username Required. Specifies the account name to use for authentication. Server URI Required. The URI of Azure DevOps server, user or project to be polled for new repositories. Token
Required. The personal access token for a Azure DevOps Server account.
This is the token that we generated in Azure DevOps Server earlier.
After specifying these values, you can click Test connection to verify if you entered data correctly.
- After you specified the values, click Save. This will create an auto-polling configuration and display it in the Auto-Polling Configurations List.
- Scroll down the Repository Auto-Polling tab and check that the Enable Auto-Polling setting is on and optionally change the Auto-Polling Interval setting.
Now Collaborator will automatically check if any new repositories were found on the specified server. Once found, it will notify administrators and suggest creating integrations with these newly created repositories via the Easy Add Repository wizard.
3. Link Collaborator User Account to Azure DevOps Server Account
The last step is to link Collaborator user accounts to the Azure DevOps Server accounts. See —
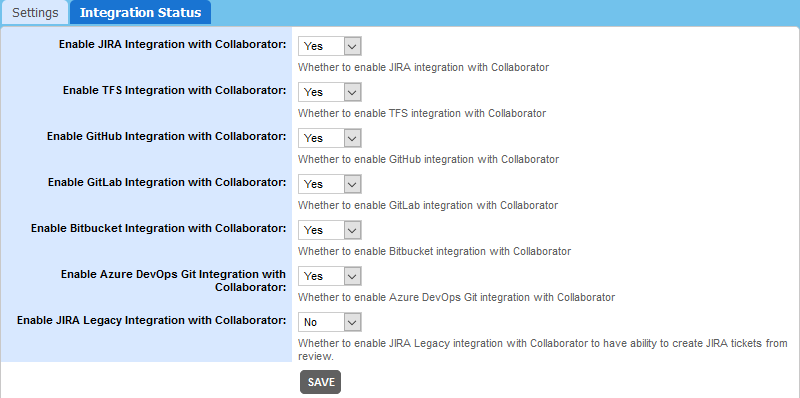
Enable/Disable configuration
Once a new repository configuration is created, it is enabled automatically. However, you can enable and disable integration with Azure DevOps Server manually. To do this:
- In Collaborator, go to ADMIN > Integrations.
- In the Integration Status section find the Enable Azure DevOps Git Integration setting and change it to Yes or No, respectively.
Known Issues and Specifics
-
Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) repositories of Azure DevOps are not supported.
-
If a pull request is associated with some work item on Azure DevOps side, the link to work item will be added to the review's Remote System Links section. Moreover, if the integration's Auto close related work items option is enabled, the respective work item will be automatically closed when pull request is merged.
-
You can specify Azure DevOps users as reviewers when you are creating a pull request. If your teammates link their Azure DevOps accounts with their Collaborator accounts correctly, and the Auto assign reviewers option is on, then Collaborator will automatically add those users as reviewers to the created review on the Collaborator side.
-
Collaborator will not create reviews on merge commits of pull requests when their merge commit message starts with the Merge pull request # substring or when merge commit message was specified in the Pull Request Merge Info section.
-
If the remote repository server is not accessible, Collaborator will retry connecting after a certain time period and will perform several retry attempts. Wait time is increased with each attempt: wait_time*1, wait_time*2, wait_time*3 and so on. Default wait time is 1 second and Collaborator will perform 3 retries. Wait time and maximal number of attempts could be configured via Java VM Options. If the server did not respond after all attempts, Collaborator will mark the respective webhook as inactive and put an exception to the remoteSystem.log
-
Currently, Azure DevOps Server (on-premises version of Azure DevOps) does not trigger webhook on comments made in pull requests. Therefore, these comments could not be copied into Collaborator reviews.