This topic explains the concept and specifics of the Tree model of web test objects. For the general principles of web object identification, see About Web Object Identification and Object Models.
About the Tree Model
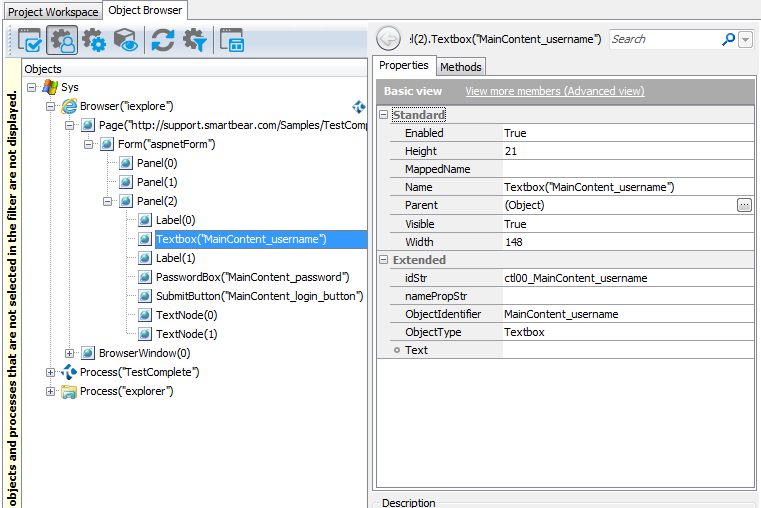
The Tree model represents web page objects in a tree-like structure that reflects the nesting of HTML elements in the page markup. For example, suppose a web page contains a table with an input field. In the Tree model, it is represented as a Table object that has a child Cell object with a child TextBox object.
The Tree model is recommended for web testing and is used by default in all new TestComplete projects. It is also more full-featured than other models. For example, the cross-browser contentText property for getting the element contents is supported only in the Tree model.
How Object Names Are Formed
If you use Name Mapping, the names used to refer to web page objects from tests are specified in Name Mapping. For example, the full name of a user name input field on a web page titled “Example” can be as follows:
Aliases.browser.pageExample.formAspnetform.panelContainer.inputUsername
You can modify the default generated names to make them more descriptive. For more information, see Addressing Web Objects Using Name Mapping and Aliases.
In the Object Browser and in tests where Name Mapping is not used, object names are formed in accordance with the following rules:
-
Most object names have the following format:
ObjectType(ObjectIdentifier). They are formed by using the corresponding object properties -ObjectTypeandObjectIdentifier.Names of objects that correspond to custom elements have the following format:
CustomObjectType(ObjectIdentifier). They are formed by theCustomObjectTypeandObjectIdentifierproperties.ObjectTypetakes one of the values listed in the Object Types Used in the Tree Model topic. Note that they are not the same as the tag names. For example, the A elements (links) haveObjectTypeof Link.The
CustomObjectTypevalue is based on the name under which the custom element is registered in the web application. To learn more, see About Support for Web Components.ObjectIdentifierhas of the following values (in the order of precedence):-
For Image objects (
<img>elements) - the object’snamePropStrproperty value which holds the last component of the src URL (typically the file name). -
For Button (
<button>and<input type="button">), ResetButton (<input type="reset">) and SubmitButton (<input type="submit">) - thevalueattribute. -
For Area objects (
<area>elements) - the area’stitleattribute value. -
For other objects - the object’s
idornamein the HTML code, changed as follows:- processed according to the dynamic identifier patterns specified in the project’s Object Identification properties,
- all characters other than Latin letters (A..Z a..z) and digits replaced with underscores ( _ ),
- subsequent underscores replaced with a single underscore,
- leading underscores stripped.
The project’s Identification attribute setting specifies which attribute -
idorname- is used first. -
The object’s zero-based index among the sibling objects of the same type.
Examples:
Panel(0)
Image("logo")
Link("firstTab")
CustomElement(0) -
-
The names of table cells have the following format:
Cell(RowIndex, ColumnIndex), where RowIndex and ColumnIndex are the cell’s row and column numbers (zero-based) in the table. -
The
Alert,Confirm,PromptandLogintest objects are named by their name without any parameters. For example,Alert. -
Some elements (for example hidden INPUT fields) are not displayed. See Web Elements Included in and Excluded From the Tree Model for a full list.
Dealing With Long Object Names
Since the Tree model reflects logical nesting of web page elements, the fully-qualified names of objects on web pages with complex markup can be quite long. For example:
// Using Name Mapping
Aliases.browser.pageSmartBear.formAspnetform.panelContainer.panelMain.panelHome.panelTools.panelColWrap.panelCol1.panel.linkViewAll
// Not using Name Mapping
Sys.Browser("*").Page("http://smartbear.com/").Form("aspnetForm").Panel("container").Panel("main").Panel("home").Panel("tools").Panel(0).Panel(0).Panel(0).Link(0)
Such long object names can make your tests difficult to read.
There are several ways to avoid long object names in tests:
-
If you use Name Mapping, you can use the Extended Find feature to identify target objects while skipping intermediate hierarchy objects. TestComplete automatically uses Extended Find for new web objects added to Name Mapping if the Use extended find when possible option is enabled. For more information, see Extended Search.
-
You can locate target objects using search functions, such as
FindChildorEvaluateXPath. For more information, see About Finding Web Objects. -
If you use keyword tests, you can use the Maximum depth option to control the number of displayed hierarchy levels (that is, intermediate levels will not be displayed). Note that when editing keyword test operations, you see the full object hierarchy.
See Also
Testing Web Applications
About Web Object Identification and Object Models
Web Object Types Used by the Tree Model and Hybrid Mobile Applications
DOM Model
Tag Model
Hybrid Model
Accessing DOM document Object

 About the Tree Model
About the Tree Model