You can run the entire test project or project suite, or individual automated tests. This topic explains how you can run automated tests from the TestComplete IDE. For other ways to run automated tests, see Running Tests.
Before Running Tests
You should run automated tests in an environment with proper initial conditions to avoid possible errors due to environment inconsistencies. For example:
-
If a test runs the application, make sure that the application is not already running.
-
If a test works with an already running application, make sure the application is in the right state for the test.
-
If a test creates files, make sure these files do not already exist.
-
And so on.
If needed, add the appropriate commands at the beginning of the test to create proper initial conditions.
Running Tests
To run the entire project or project suite
-
Configure the test run order on the Test Items page of the project editor or project suite editor.
-
Select
 Run Project or
Run Project or  Run Project Suite from the Test menu.
Run Project Suite from the Test menu.– or –
Select Run > Run Project or Run > Run Project Suite from the Test Engine toolbar.
Notes:
-
If a project does not have project items, the test engine is unable to run it and shows the The project_name project cannot be run because there are no test items in it message. You can add test items to the project or select a test to run.
-
If the project suite does not contain projects or if all of the projects are excluded from the suite run, the test engine is unable to run the project suite and shows the The project suite cannot be run because there are no selected projects to be run message.
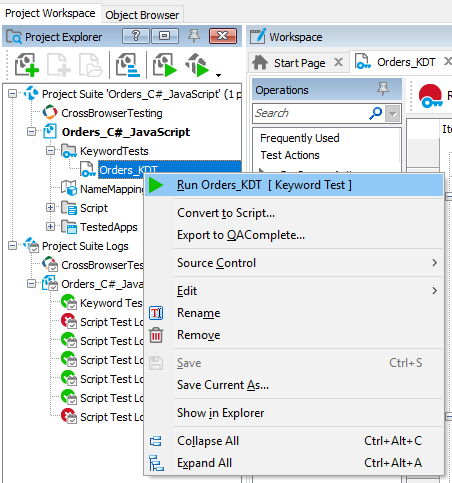
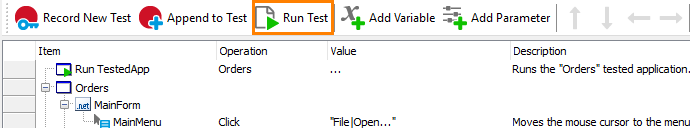
To run a keyword test
-
Right-click the needed script unit in the Project Explorer and select Run from the context menu.
– or –
-
Open the test in the Keyword Test editor and then click
 Run Test on the editor’s toolbar.
Run Test on the editor’s toolbar.
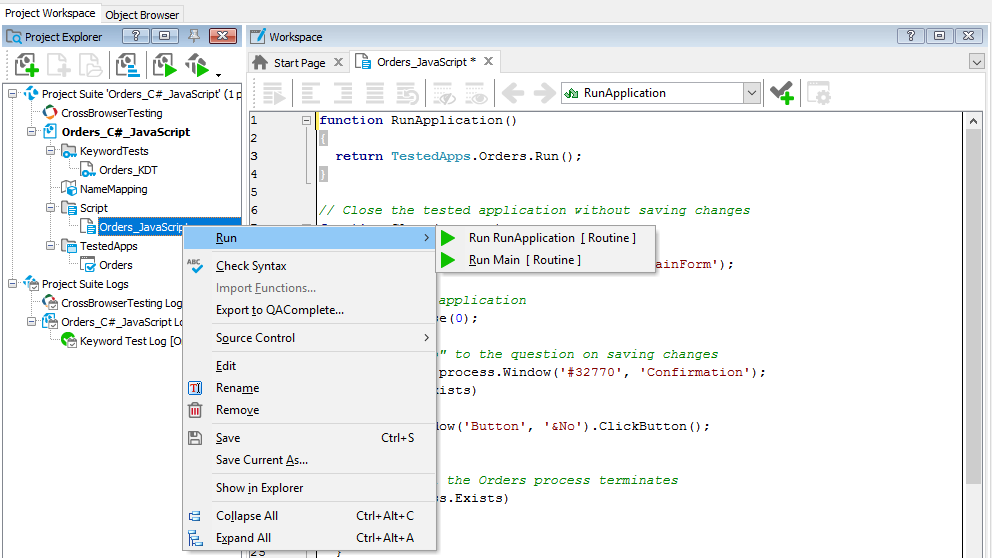
To run a script routine
-
Right-click the needed script unit in the Project Explorer and select Run | Run RoutineName from the context menu.
– or –
-
In the Code Editor, place an insertion point inside the routine code and then click
 Run This Routine on the Code Editor’s toolbar.
Run This Routine on the Code Editor’s toolbar.
| Note: | This works only for script routines that have no parameters. Routines with parameters can be called only from other tests, because you need to specify parameter values. |
To run a runnable project item (a low-level procedure, unit test and so on)
-
Right-click the item in the Project Explorer and select
 Run from the context menu.
Run from the context menu.
To run a test that was launched last
-
Select Run > Repeat Last Run on the Test Engine toolbar.
Pausing Tests
To pause a running automated test, do one of the following:
-
Click the
 button on the TestComplete indicator.
button on the TestComplete indicator. -
Press Shift+F10 (the shortcut can be changed in the Global Shortcuts dialog).
-
Click
 Pause on the Debug toolbar.
Pause on the Debug toolbar.
| Note: | You cannot pause network suites (distributed tests) and low-level procedures. |
When a test is paused you can:
-
Debug the test: step through it, view variable values and so on.
-
View the current test log (if the Show Log on pause option is enabled).
Resuming Tests
To resume a paused test, do any of the following:
-
Click the
 button on the TestComplete indicator.
button on the TestComplete indicator. -
Press Shift+F3 (the shortcut can be changed in the Global Shortcuts dialog).
-
Click
 Run on the Test Engine toolbar.
Run on the Test Engine toolbar. -
(For keyword tests only) Right-click within the Keyword Test editor and choose
 Continue from the context menu.
Continue from the context menu.
Stopping Tests
To stop the test before it completes, do any of the following:
-
Click the
 button on the TestComplete indicator.
button on the TestComplete indicator. -
Press Shift+F2 (the shortcut can be changed in the in the Global Shortcuts dialog).
-
Click
 Stop on the Test Engine toolbar.
Stop on the Test Engine toolbar.
TestComplete lets you stop tests on timeout and on errors. For more information, see Controlling Test Execution Flow.
You can also stop the test run from the test itself:
-
in keyword tests - using the Stop Execution operation,
-
in scripts - using the
Runner.StoporRunner.Haltmethod (the difference is thatStopdoes not log an error).
Stopping Tests on Errors and Exceptions
By default, if an error occurs during the test run (for example, a tested object is not found), TestComplete posts information about it to the test log and stops the test run. Also, if an unhandled exception occurs in your script test (for example, the list index is out of bounds), TestComplete shows an error message and stops the test run. You can change this behavior to handle errors in the way you need. You can configure TestComplete to do the following:
-
Ignore any errors and continue the test run.
-
Stop the current test and proceed with the next test (applicable, for example, when running a project).
-
Stop the test run when an error limit is reached.
-
Stop the test run only when a specific error occurs.
To learn how to do this, see Controlling Test Execution Flow.
Test Playback Options
You can change the mouse movement and text input speed, default object waiting timeout and other playback options in your TestComplete project properties. For a description of available options, see:
See Also
Running Tests
Running Tests - Specifics
Specifics of Using TestComplete on Various Windows Operating Systems

 Before Running Tests
Before Running Tests