TestComplete provides you with access to individual objects of Visual C++ applications, their internal properties and methods. The following sections describe how you can access these native properties and methods from your tests:
 About Accessing Native Properties and Methods
About Accessing Native Properties and Methods
 Getting Access to Visual C++ Applications’ Native Properties and Methods
Getting Access to Visual C++ Applications’ Native Properties and Methods
About Accessing Native Properties and Methods
TestComplete identifies individual GUI objects in unmanaged Visual C++ applications and provides specialized methods and properties for automating various operations on these objects, getting object data, checking state and so on. However, if these predefined properties and methods are insufficient for your testing needs, you can use native properties and methods of Visual C++ objects to complete the desired tasks. These are the same properties and methods that are available for use in the tested application’s source code as well as custom properties and methods implemented by the application developers. This way, you can perform almost any operation in the tested Visual C++ application, even those that cannot be performed via the application’s GUI.
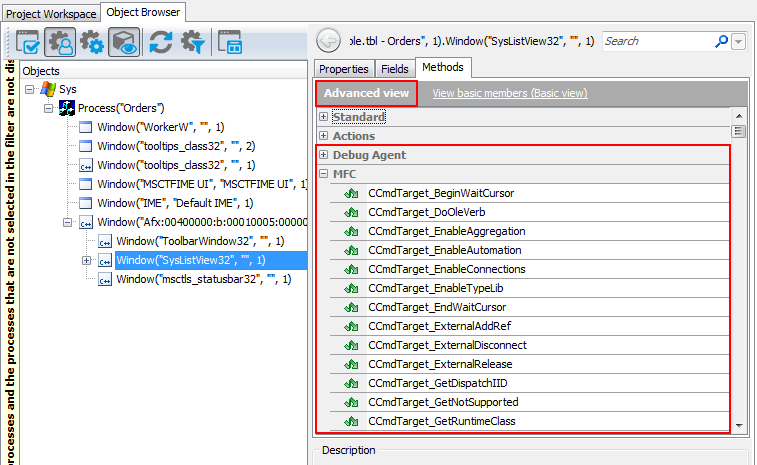
The Object Browser marks objects of Visual C++ applications with the  glyph. To view native members available for a Visual C++ object, use the Object Spy or Object Browser in the Advanced view mode. In the Object Browser, native properties, fields and methods of Visual C++ objects are displayed under the MSVC and Debug Agent categories (see Important Notes for details).
glyph. To view native members available for a Visual C++ object, use the Object Spy or Object Browser in the Advanced view mode. In the Object Browser, native properties, fields and methods of Visual C++ objects are displayed under the MSVC and Debug Agent categories (see Important Notes for details).
For more information on how to refer to objects in Visual C++ applications, see Addressing Objects in Visual C++ Applications.
Getting Access to Visual C++ Applications’ Native Properties and Methods
If your application is compiled with runtime type information, TestComplete provides you with access to Visual C++ applications' public methods and properties. If you need to get access to an application’s public, protected and private members, you need to compile your application with external debug information.
For detailed instructions on how to configure your Visual C++ compiler to enable compiling with runtime type information and debug information, see Preparing Visual C++ Applications for Testing.
Getting and Setting Native Object Properties
To access an object’s property in script code, you specify the property name after the object name using the dot operator "." (in VBScript, JScript, Python and DelphiScript projects) or the square bracket notation [" "] (in C++Script and C#Script projects).
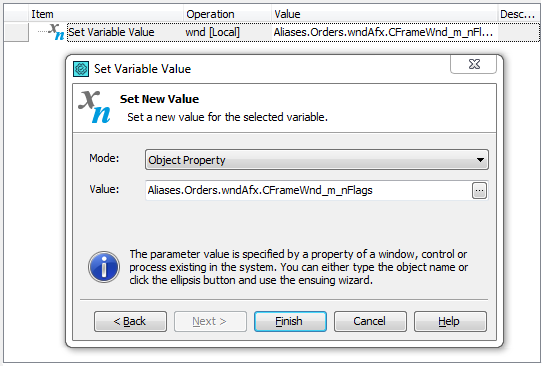
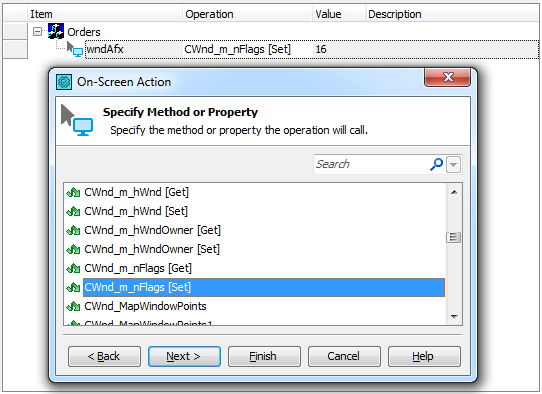
For example, you can get or set the value of the native CWnd_m_nFlags property of a Visual C++ form in the following way:
JavaScript, JScript
var wnd = Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags;
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags = 16;
Python
wnd = Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags;
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags = 16;
VBScript
Dim wnd
wnd = Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags = 16
DelphiScript
procedure Test;
var wnd;
begin
…
wnd := Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags;
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.CWnd_m_nFlags := 16;
…
end;
C++Script, C#Script
var wnd = Aliases["Orders"]["wndAfx"]["CWnd_m_nFlags"];
Aliases["Orders"]["wndAfx"]["CWnd_m_nFlags"] = 16;
In keyword tests, you can retrieve an object’s property value and save it to a test variable using the Set Variable Value operation. To change a property value, you can use the On-Screen Action operation to call the property’s [Set] method. For more information, see Getting and Setting Object Property Values.
You can also create checkpoints to verify the values of native object properties.
Calling Native Object Methods
To call an object’s method from script code, you use the dot operator "." (in VBScript, JScript, Python and DelphiScript projects) or the square bracket notation [" "] (in C++Script and C#Script projects) to specify the method name after the object name.
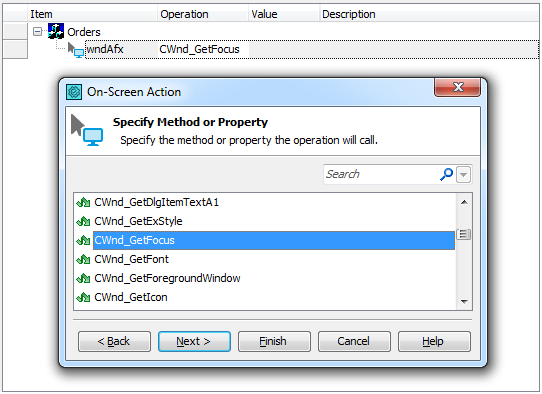
For example, in script code you can call the native GetFocus method of a Visual C++ form as follows:
JavaScript, JScript
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.GetFocus();
Python
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.GetFocus();
VBScript
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.GetFocus
DelphiScript
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.GetFocus();
C++Script, C#Script
Aliases["Orders"]["wndAfx"]["GetFocus"]();
In keyword tests, you can use the On-Screen Action operation to call an object’s native method. For more information, see Calling Object Methods.
Important Notes
-
In the Object Spy or Object Browser, native properties and methods of Visual C++ objects are displayed only in the Advanced view mode.
-
Hidden properties, fields and methods are not displayed by default. If you need to view hidden properties, enable the Show hidden properties option in the TestComplete Options dialog.
-
If a native property or method has the same name as the test object property or method provided by TestComplete, the native property or method can be accessed via the
NativeCPPObjectproperty. For example, you can access the nativeSetFocusmethod of a Visual C++ application’s form as follows:JavaScript, JScript
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.NativeCPPObject.SetFocus();
Python
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.NativeCPPObject.SetFocus();
VBScript
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.NativeCPPObject.SetFocus
DelphiScript
Aliases.Orders.wndAfx.NativeCPPObject.SetFocus();
C++Script, C#Script
Aliases["Orders"]["wndAfx"]["NativeCPPObject"]["SetFocus"]();
-
The leading underscore ( _ ) in property and method names is replaced with the character z. For example, a property named
_flagis accessed aszflag, a method named__reset()is accessed asz_reset(), and so on. -
If the object contains overloaded methods (methods with the same name but different parameters and they return value types), TestComplete appends indexes to method names in order to distinguish them. For example,
ChildWindowFromPoint()andChildWindowFromPoint_2(). To determine which index-suffixed method name corresponds to which overloaded method, examine the method’s parameter list in the Object Spy, Object Browser or Code Completion. -
Some native properties and methods of Visual C++ objects are unavailable to TestComplete. For more information, see Object Properties, Fields and Methods That Are Unavailable to TestComplete.
See Also
Testing Visual C++ Applications
Testing Visual C++ Applications - Overview