Collaborator integrates with popular repository hosting services like GitHub, GitLab or Bitbucket. It automatically creates and updates reviews when changes occur in repositories hosted in these systems. This simplifies the process of review creation and help you make reviewing an integral part of your workflow.
This topic describes how the integration works.
Supported Hosting Services
Collaborator integrates with the following repository hosting services. It supports both online and installable editions:
-
GitHub (github.com and GitHub Enterprise)
-
GitLab (gitlab.com, GitLab Community, and GitLab Enterprise editions)
-
Bitbucket (bitbucket.org and Bitbucket Server)
Set Up Integration Settings
To integrate Collaborator with repository hosting services, you need to configure settings of Collaborator and set certain options on the hosting service side. For complete information, follow these links:
How Integration Works
The integration works similarly for all the supported hosting services:
-
When you integrate Collaborator with a repo, Collaborator creates a webhook on the repo side.
-
When changes occur in the repo, the webhook sends notifications to Collaborator, and the latter automatically creates reviews for these changes, and attaches the changed files to it.
-
Collaborator tracks further changes in the repository and uploads newer file versions to the review until the corresponding pull request is closed. It can also close the pull request automatically, if you complete the review.
See below for detailed information on all these actions.
When a review is created
After you configured integration settings, Collaborator tracks changes in one or several branches of your repository (you specify the branches to track and to ignore when configuring integration settings in Collaborator).
Collaborator automatically creates reviews in the following cases:
-
When it detects a pull request to the tracked branch (in some systems, pull requests are called merge requests).
-
When it detects push events (commits, not pull requests) to the tracked branch.
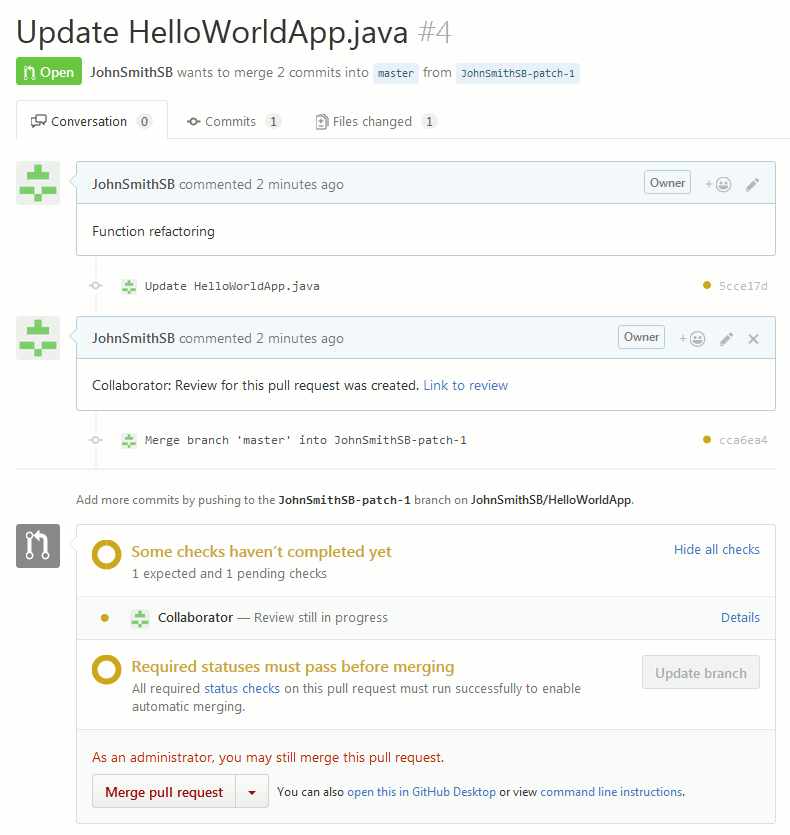
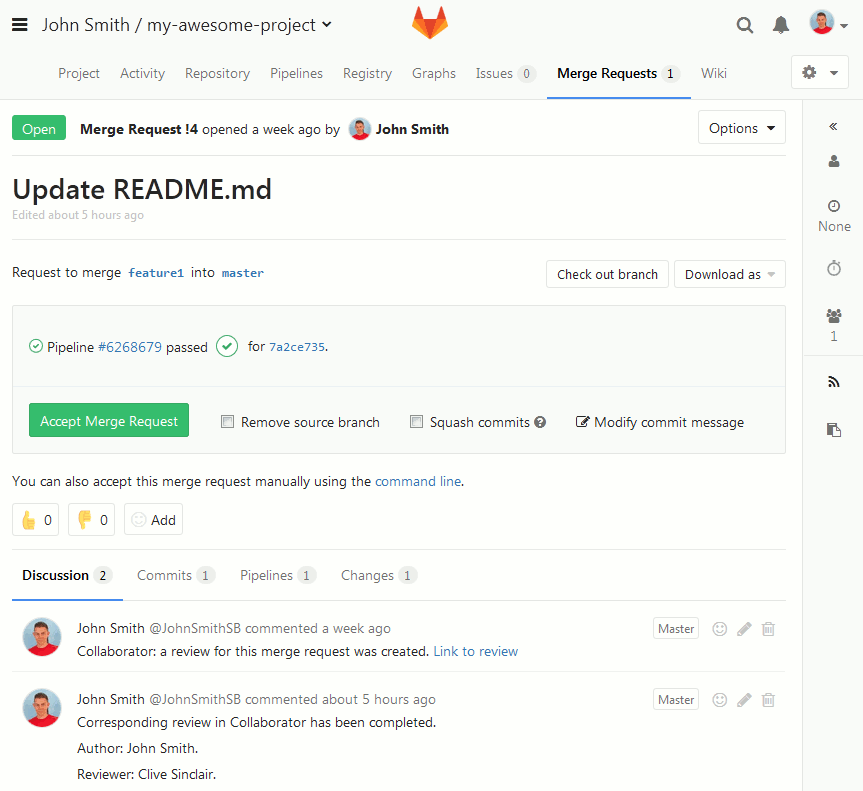
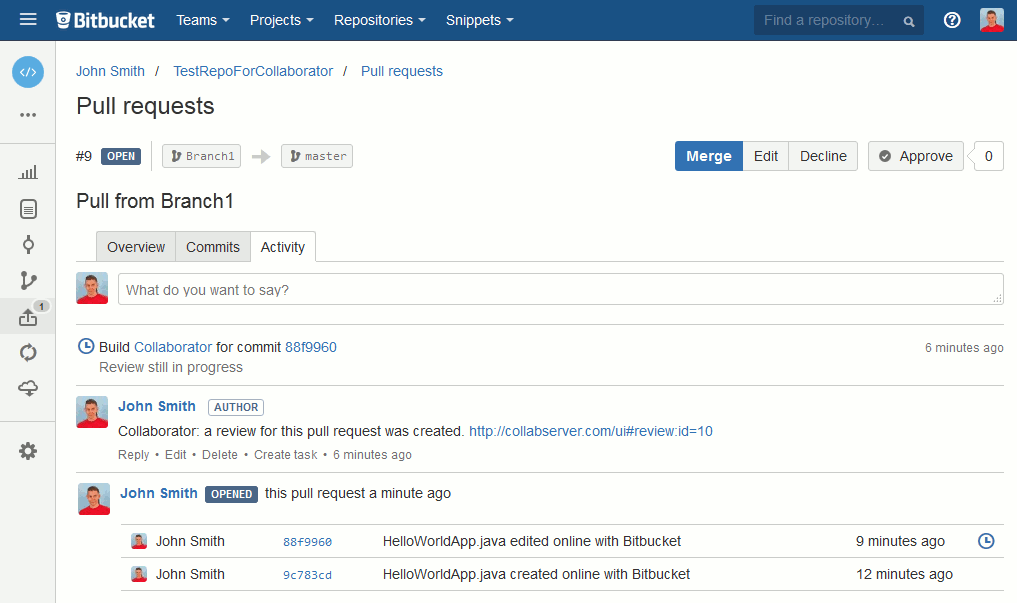
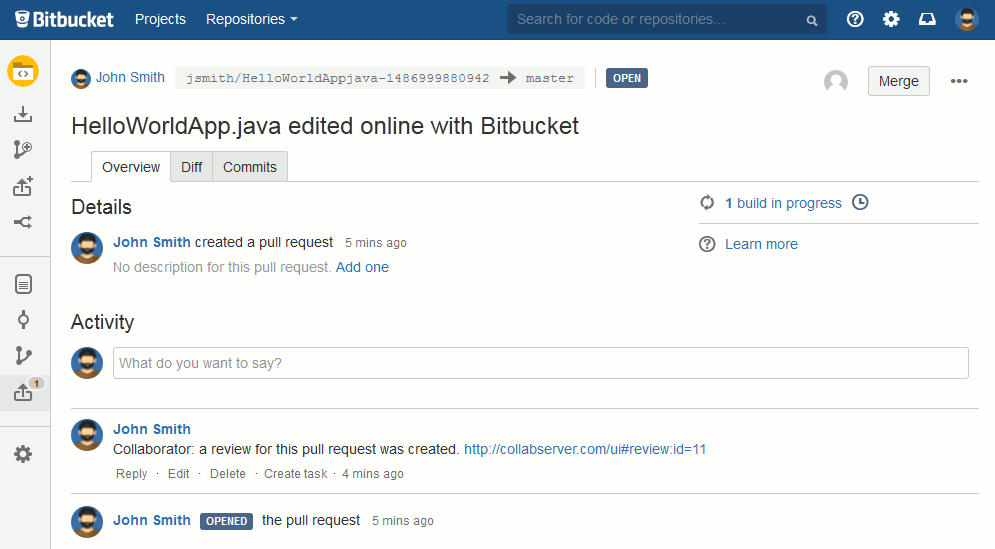
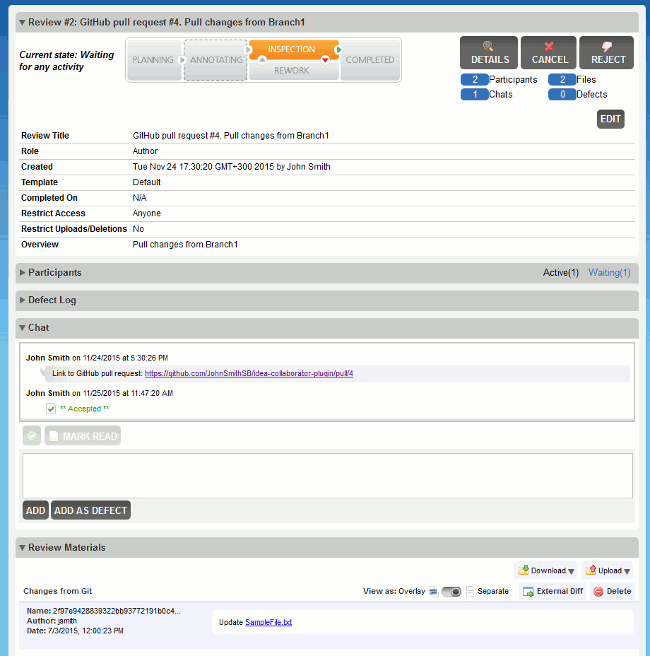
Collaborator uploads the copies of changes files to the review and assigns the review to the respective user. On the repository side, it registers the review as a CI test for the pull request (in GitHub terms, these are called status checks, in GitLab — pipelines, in Bitbucket and Bitbucket Server — builds). So, you can see the status of the created review in the pull request details:
 For protected branches, you have to complete Collaborator reviews before closing the pull request.
For protected branches, you have to complete Collaborator reviews before closing the pull request.
Collaborator also automatically creates reviews for changes in submodules (or subrepositories). See below.
What data the review contains
The new review includes changes made to the remote repository. Namely —
-
When creating a new review, Collaborator automatically uploads copies of the pull request’s or commit’s files to the review. That is, the review contains the modified files, not the file links or commit IDs. You can see these files in the Review Materials section of the review.
-
The Remote System Links section contains the links to pull requests or commits, as well as their current statuses.
-
The Chat section contains a link to the remote repository.
Reviews do not include comments that users make to pull requests in repository hosting services. Similarly, comments of review participants are not added to pull requests.
Whom the review is assigned to
When Collaborator gets a notification about changes in a repository, it also gets information about the source-control user, who made these changes. So, it attempts to find a corresponding user in Collaborator to assign the new review to that user. In order for the search to be successful, you and your teammates need to link their Collaborator and source-control accounts in Collaborator settings. See Link User Accounts for details.
If Collaborator finds a Collaborator user that matches the source-control user, it assigns the new review to that Collaborator user and logs that user as a review creator. If Collaborator does not find a matching user, it assigns the review to the Collaborator administrator and logs the administrator as a review creator.
When further commits are made
-
If a review was created for a pull request
If your teammates make more changes to the branch after a review was created, and if the pull request is not closed, Collaborator uploads new file versions to the created review. This works until the pull request is closed. If the review remains open after the pull request is closed, then Collaborator will not upload files from subsequent commits to the review.
-
If a review was created for a commit (push event)
Collaborator will not upload new file versions to the review automatically.
When files conflict
If a file conflict can be resolved automatically, Collaborator will not add any new file copies to the review. If a file conflict needs to be resolved manually (that is, if some files are to be changed to complete the merge request), then Collaborator will update the review with newer file versions.
| Note: | If Collaborator’s User Preferences > Default Revision Comparison of Diff Viewer option is set to “Branch Only”, changes from merge commits will not be displayed in Diff Viewer. |
When merge commit was added
... file changes made by merge commits will only be displayed in Separate view of the Review Materials section of the review. They will not be displayed in Overlay view. Besides, file changes made by merge commits are not taken into account when calculating overall LOC metrics and they do not affect the overall rework count of a file.
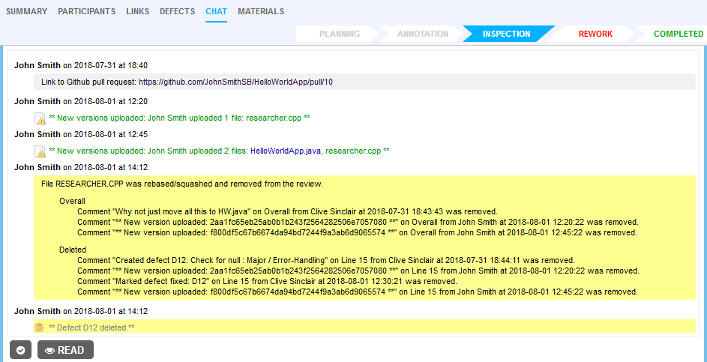
When commit history is modified (rebasing or squashing commits) ...
... Collaborator will process the outdated commits and will reorder the list of file revisions to keep it up-to-date.
- If some file revisions have been removed, the comments or defects addressing that file revision will be promoted to resulting revision and will display a special icon
 indicating that the comment/defect could be outdated.
indicating that the comment/defect could be outdated.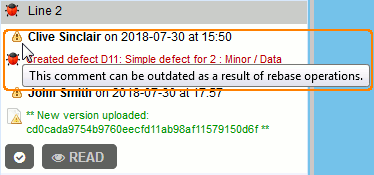
- If some files have been removed, they will also be removed from the review materials. For audit purposes, comments and defects for removed files will be copied to the review's general chat.
When the review is completed ...
... Collaborator can automatically merge or close the appropriate pull request. This behavior is controlled by the When review completed option that you set when integrating Collaborator with your repository.
When a review is completed and pull request is updated ...
... the review can be reopened. The Reopen a review when option allows selecting what events should reopen the review.
When the review is canceled, deleted or rejected ...
... Collaborator can automatically close the corresponding pull request. Additionally, it can automatically delete the corresponding branch. This behavior is controlled by the When Review Cancelled/Deleted/Rejected option that you set when integrating Collaborator with your repository.
When the pull request is closed ...
... Collaborator posts a comment to the corresponding review.
When the pull request is reopened
It is quite possible, that the pull request, for which a review was created, is reopened after that review was completed. In this case, Collaborator will reopen the review.
If review was canceled, deleted or rejected and if the pull request is reopened, Collaborator creates a new review.
Notes
-
By default, webhooks do not use SSL. This is done intentionally, in order to avoid handshake issues with self-signed or untrusted certificate authority (CA) root certificates on the Collaborator side. To enable SSL verification for existing webhooks, modify them on the repository server side (for more information on this, see your hosting service documentation). To enable SSL verification for all new webhooks, use the
-Dcom.smartbear.collab.datamodel.remotesystem.webhooks.ssl.enable=trueJava VM Options. -
Collaborator creates reviews for any pull requests, including those that came from forked repositories.
-
If your repo contains a Git submodule, Collaborator will also create review for changes in submodule files.
At that, the commits that add a new submodule, or remove an existing submodule will be represented as changes in the
.gitmodulesfile. Other changes in the submodule folder will be ignored in this commit. Once submodule has been added, further changes in its files will be displayed as file changes in the submodule folder.Submodules must belong to the same owner/project/organization.
-
Currently, Collaborator incorrectly displays non-Latin characters in pull request names, branch names, and in pull request descriptions.

 See examples
See examples