About
-
Collaborator integrates with Git repositories hosted at GitHub.com, as well as on GitHub Enterprise servers in your network.
-
When you integrate Collaborator with a GitHub repository, your Collaborator server creates reviews automatically for pull requests in the repo, as well as for push events that occur in that repo. For complete information on how the integration works, see Integration With Repository Hosting Services.
-
To inform Collaborator about changes, GitHub uses a webhook that sends notification messages to your Collaborator server.
-
To set up the webhook and other integration parameters, you need to set up some options in Collaborator and in GitHub. See the rest of this topic for details.
Supported Hosting Services
-
GitHub (github.com)
-
GitHub Enterprise
Requirements
-
Your Collaborator server must be accessible to GitHub and vice versa. You may need to configure your firewall or enable tunneled connections to expose the server’s External URL to the Web. If needed, ask your system administrator for help.
-
To configure integration settings in Collaborator, you need Administrator privileges.
1. Get GitHub Tokens
To integrate with GitHub, you need a personal access token that will be used to access your repositories.
For detailed information on generating a personal access token, follow instructions on this page of GitHub documentation:
 https://help.github.com/articles/creating-an-access-token-for-command-line-use/
https://help.github.com/articles/creating-an-access-token-for-command-line-use/
 Notes:
Notes:
-
When setting up the token parameters, make sure to enable the following scopes for the token:
repoadmin:orgadmin:repo_hook, andadmin:org_hook
-
After GitHub generated the token, save it somewhere or write it down. We will need the token later, when we will configure the integration between Collaborator and GitHub.
2. Set Up Integration
Collaborator offers two groups of settings for configuring integration with remote repositories:
| Settings | When to use |
|---|---|
| Easy Add Repository tab | We recommend using these settings to set up new connections to your repositories quickly. |
| Use these settings to configure existing connections. Though you can use these settings to set up integration, the settings on the “Easy Add Repository” tab will help you do this faster. |
Easy Add Repository tab (recommended)
-
Log in to Collaborator as administrator. (To integrate with GitHub repositories, you need administrator privileges in Collaborator).
-
On the Collaborator main toolbar, click ADMIN, and then select Remote System Integration from the tree on the left. Then switch to the Easy Add Repository tab.
-
On the tab, select GitHub in the Add repository for box and click Next:
-
Collaborator will displays a page with connection details.
Fill in the edit boxes:
Setting Description Personal access token
Required. The personal access token for a GitHub account that has access to your remote repository.
This is the token that we generated in GitHub earlier.
Organization
Required only for organization owned repositories (https://github.com/OrganizationName/RepoName). Specifies the name of your GitHub organization account (OrganizationName).
GitHub Enterprise host name
Required for repositories hosted on GitHub Enterprise servers. Specifies the host name of your GitHub Enterprise server.
Webhook secret token
Optional. The secret token for webhook events. If provided, must be at least 8 characters long.
To learn more about webhook settings on the GitHub side, see GitHub documentation:
Scopes for user
Optional. Defines which types of repositories to track.
Scope Description Owner (default) Repositories that are owned by the specified user Collaborator Repositories that the user has been added to as a collaborator.
Webhooks will be created for those repositories where allowed by the repository permissions for the specified user.Organization member Repositories that the user has access to through being a member of an organization. This includes every repository on every team that the user is on.
Webhooks will be created for those repositories where allowed by the repository permissions for the specified user.Override existing configurations
Optional. Specifies whether to override existing configurations that track the same repository URI.
Branches to track
Optional. The names of branches to track changes and create reviews on pull requests and direct pushes. Separate multiple branch names with commas.
You can use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches. Note that wildcards and regular expressions cannot be used if you enable the Status check required setting (see below).If this edit box is empty, the branch master will be tracked.
Ignore pushes for branches
Optional. Specifies branches for which Collaborator will not create reviews on direct pushes.
You can enter one or several branch names. Separate multiple branch names with commas. You can also use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches. Note that wildcards and regular expressions cannot be used if you enable the Status check required setting (see below).Status check required
Specifies if Collaborator should enforce status checks for the tracked branches before merging pull requests.
If this option is enabled, you cannot use regular expressions in the Branches to track setting, since this option requires exact name match.
When review completed
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to a pull request was accomplished:
Value Description Do nothing Do not perform any action. Merge pull request Merge pull request that matches the review. Merge pull request and delete its branch Merge pull request that matches the review and delete the corresponding branch. Close pull request Close pull request that matches the review. Close pull request and delete its branch Close pull request that matches the review and delete the corresponding branch. When review cancelled/deleted/rejected
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to a pull request was cancelled, deleted or rejected:
Value Description Do nothing Do not perform any action. Close pull request Close pull request that matches the review. Close pull request and delete its branch Close pull request that matches the review and delete the corresponding branch. Reopen a review when
Optional. Specifies in what cases Collaborator should reopen completed reviews. May include any combination of the following:
- when a push to a pull request is made,
- when a comment is added to a pull request,
- when a comment is added to commit which is a part of a pull request
-
After you specified the settings, click Load repositories. This will display a list of repositories available for the specified user account or organization in GitHub. Select the repositories to track and click Create for selected.
Alternatively, you can click Create for all and use the settings for all repositories that are available for the specified user account or organization in GitHub. Collaborator will create an individual configuration for each repository, and, if needed, will create a webhook for each repo in GitHub.
Configure Remote Systems tab
-
Log in to Collaborator as an administrator. (To configure integration settings, you need administrator privileges in Collaborator).
-
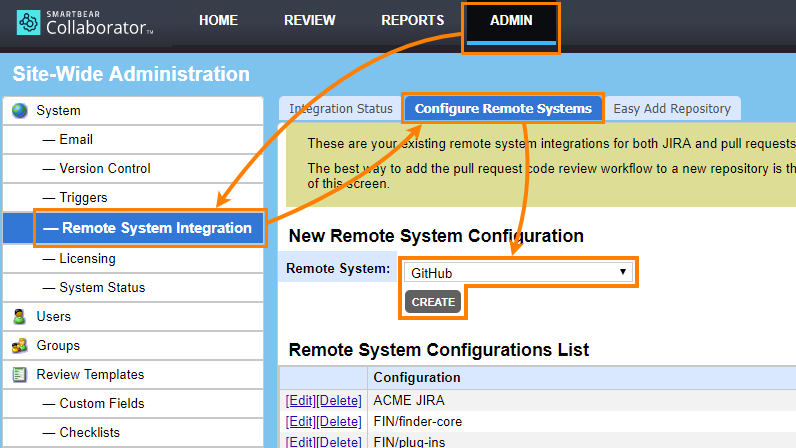
On the Collaborator main toolbar, click ADMIN, and then select Remote System Integration from the tree on the left. Then switch to the Configure Remote Systems tab.
-
In the New Remote System Configuration section, select GitHub and click Create:
-
Collaborator will display a page with configuration settings. Specify the setting values:
Setting Description Title
Required. The configuration name as it will be displayed in Collaborator user interface.
GitHub repo URI
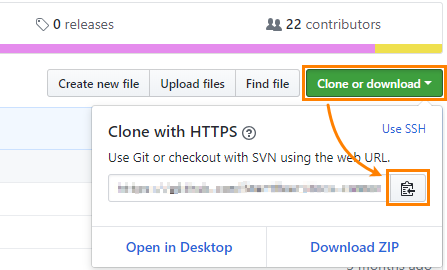
Required. The URI of the GitHub repository to be tracked, for example,
https://github.com/torvalds/linux.git.You can copy the URI from the repository page in GitHub:
GitHub API token
Required. The personal access token for the GitHub account that has access to remote repository.
This is the token that we generated in GitHub earlier.
Webhooks secret token
Optional. The secret token for webhook events. If provided, must be at least 8 characters long.
To learn more about webhook settings on the GitHub side, see GitHub documentation:
Branches to track
Optional. The names of branches to track changes and create reviews on pull requests and direct pushes. Separate multiple branch names with commas.
You can use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches. Note that wildcards and regular expressions cannot be used if you enable the Status check required setting (see below).If this edit box is empty, the branch master will be tracked.
Ignore pushes for branches
Optional. Specifies branches for which Collaborator will not create reviews on direct pushes.
You can enter one or several branch names. Separate multiple branch names with commas. You can also use Java-style regular expressions to match specific branch names, or you can use the
*wildcard (alone, or separated by commas) to match all branches. Note that wildcards and regular expressions cannot be used if you enable the Status check required setting (see below).Status check required
Specifies if the integration should enforce status checks for the tracked branches before merging pull request.
If this option is enabled, you cannot use regular expressions in the "Branches to track" setting, since this option requires exact name match.
When review completed
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to a pull request was accomplished:
Value Description Do nothing Do not perform any action. Merge pull request Merge pull request that matches the review. Merge pull request and delete its branch Merge pull request that matches the review and delete the corresponding branch. Close pull request Close pull request that matches the review. Close pull request and delete its branch Close pull request that matches the review and delete the corresponding branch. When Review cancelled/deleted/rejected
Optional. Specifies an action to perform when a review corresponding to a pull request was cancelled, deleted or rejected:
Value Description Do nothing Do not perform any action. Close pull request Close pull request that matches the review. Close pull request and delete its branch Close pull request that matches the review and delete the corresponding branch. Reopen a review when
Optional. Specifies in what cases Collaborator should reopen completed reviews. May include any combination of the following:
- when a push to a pull request is made,
- when a comment is added to a pull request,
- when a comment is added to commit which is a part of a pull request
Webhook status
Indicates the current status of the webhook:
Status Description Webhook is absent The webhook has not been created yet. Webhook isn't active The webhook has been created, but is inactive. Up and running The webhook is active. -
To create or activate a webhook, click Update webhook.
 Important: Click this button, when you set up integration with your repository for the first time.
Important: Click this button, when you set up integration with your repository for the first time.To learn more about webhook settings on the GitHub side, see GitHub documentation:
-
Click Test Connection to verify if you entered data correctly.
Click Save to store the settings.
3. Enable Configuration
After you finished configuring integration settings, you need to enable the integration:
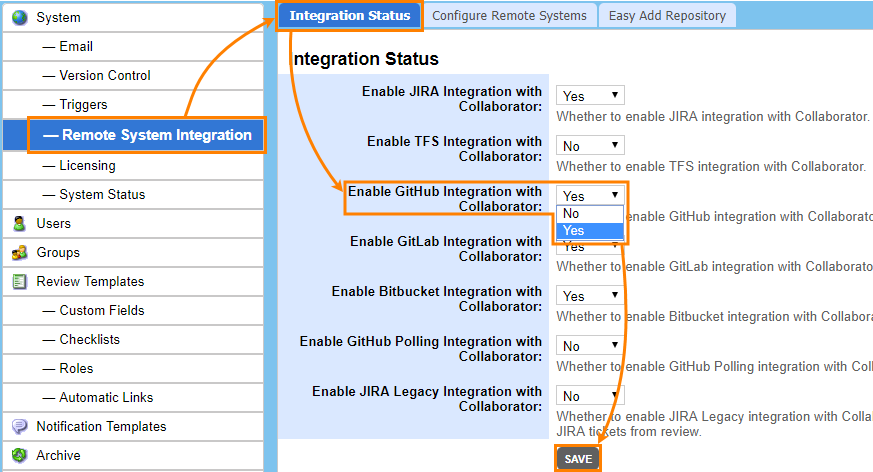
- In Collaborator, go to ADMIN > Remote System Integration.
- Switch to the Integration Status tab. Here you can enable or disable integrations quickly.
- Find the Enable GitHub Integration setting and change it to Yes.
Now the integration between Collaborator and GitHub is configured and running.
4. Link Collaborator User Account to GitHub Account
The last step is to link Collaborator user accounts to the GitHub accounts. See —
Configure SSL Connection for GitHub Enterprise
If your GitHub Enterprise server is using SSL connection, it is possible that Collaborator will not trust this server’s certificates. To establish trust, you need to create a keystore and import the public key of the GitHub Enterprise server as a trusted certificate in it:
-
Get the certificate file from your GitHub Enterprise or network administrator.
-
Use Java’s
keytoolutility to create the keystore and to import the certificate in it. You can findkeytoolin the $JAVA_HOME/bin directory:keytool -import -alias github -keystore <Collaborator Server>/tomcat/conf/collab.ks -trustcacerts -file <certificate-file-name>
For more information on command-like arguments of the keytool utility, see keytool documentation.
-
 Most likely you will be prompted to confirm the validity of the certificate. It is imperative for the security of the overall system that you verify the key matches the trusted material. Before accepting the certificate, you should contact the administrator that sent you the certificates and verify that the certificate fingerprints that you see match the certificate fingerprints that they intended to send you.
Most likely you will be prompted to confirm the validity of the certificate. It is imperative for the security of the overall system that you verify the key matches the trusted material. Before accepting the certificate, you should contact the administrator that sent you the certificates and verify that the certificate fingerprints that you see match the certificate fingerprints that they intended to send you.For more information on why this step is important, see the note in the keytool documentation.
-
The final step is to configure Collaborator to use the newly created keystore. Open the <Collaborator Server>/ccollab-server.vmoptions file in a text editor, and add the following lines to it:
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore=<Collaborator Server>/tomcat/conf/collab.ks
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword=<the password>
-
Restart the Collaborator Server.
Known Issues and Specifics
-
You can secure webhook calls by providing a secret token when you are creating or modifying a webhook and integration settings in GitHub and in Collaborator. This token will be used as server signature for verifying webhook events. The webhook token is optional and is absent by default.
-
To avoid creating reviews for merge commits, keep their messages default or start them with the Merge pull request # substring.
-
Right after you set up integration with some GitHub repo, the very first push or pull request to this repo will not be tracked. Subsequent requests will be tracked as they should.