In TestComplete, file checkpoints verify the actual contents of specified files comparing them with baseline files stored in the project’s Stores > Files collection.
File checkpoints in TestComplete take two parameters:
-
The name (with the full path) of the file you want to verify.
-
The allowed difference value (in bytes).
File checkpoints you create by using the File Checkpoint wizard use hard-coded values to indicate the file to verify and the allowed difference.
You may want to parameterize your file checkpoints in your tests, that is, to replace file checkpoints’ hard-coded values with variable values.
For example, if a name of the file you want to verify changes between test runs, you can replace the checkpoint’s hard-coded file name with a parameter that obtains the required file name before each test run.
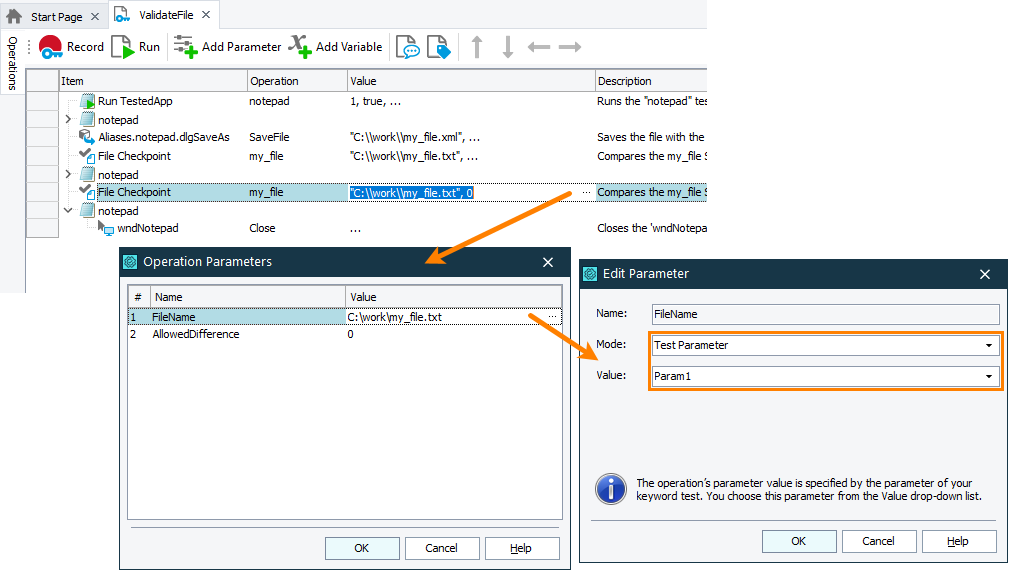
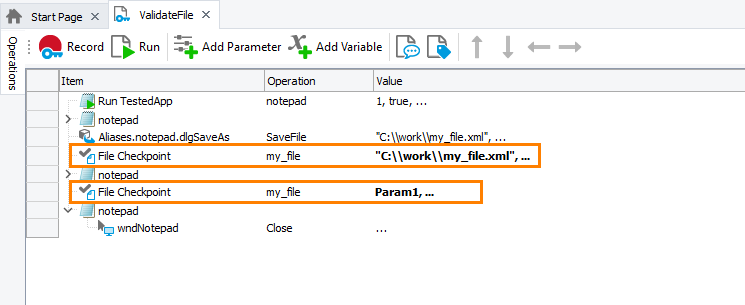
The image below demonstrates two file checkpoints. One of them verifies a file specified by its hard-coded name, the other verifies a file whose path is stored in the keyword test Param1 parameter:
The sections below describe how to parameterize your file checkpoints:
In keyword tests
-
Create a parameter that will pass the needed value to the checkpoint. It can be:
-
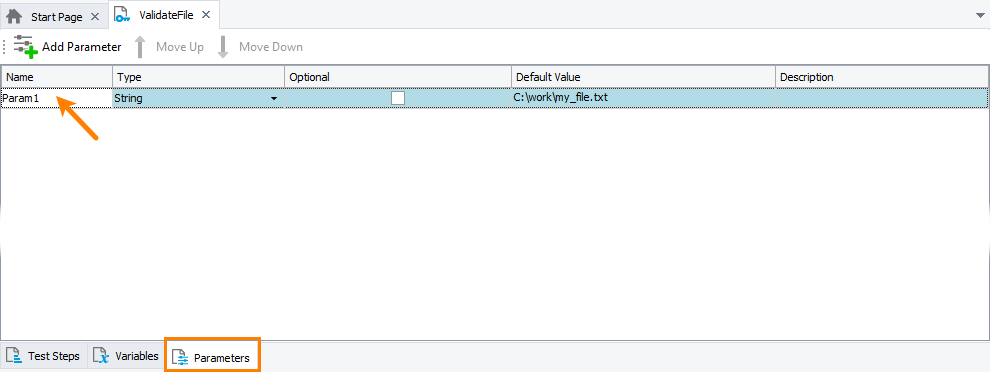
A test parameter. You create it on the Parameters page of your test.
-
A keyword test variable. You create it on the Variables page of your test.
-
A project or project suite variable. You can create them on the Variables page of your project or project suite respectively.
For example, the image below shows the Param1 parameter of a keyword test:
-
-
In your keyword test, replace the hard-coded value of the checkpoint operation with the created parameter or variable:
-
Assign the needed value to the created parameter or variable:
-
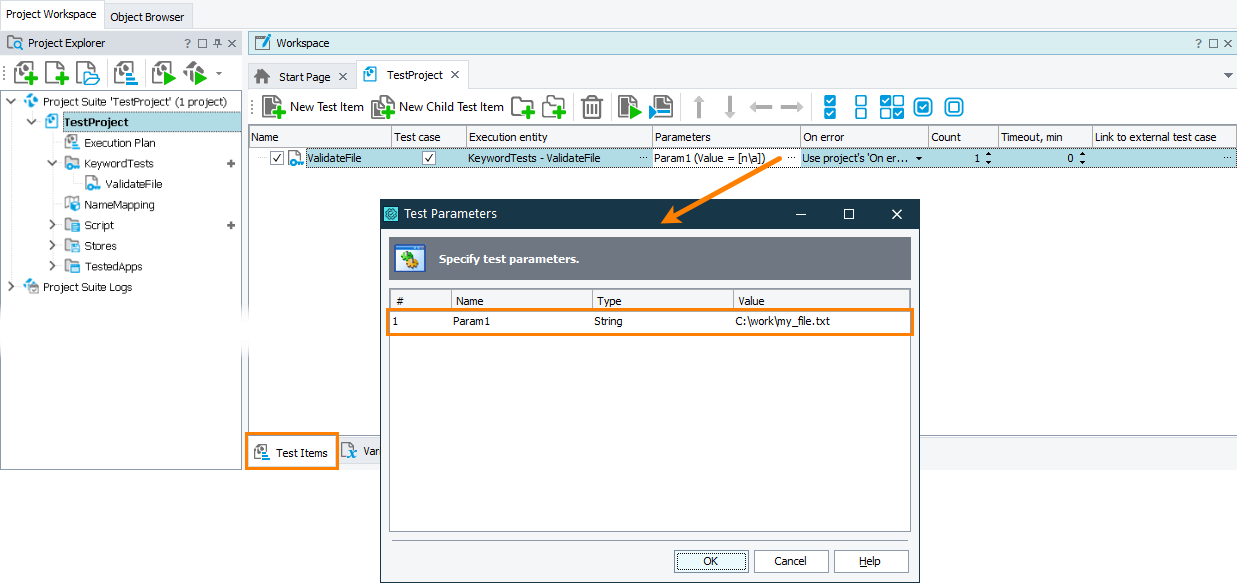
If you use a test parameter, set its value when you run your test:
-
If you run it as part of the project’s test items sequence, set the test parameter in the Execution Plan editor of your project:
-
If you run your test from another test, set the parameter value when calling your test.
-
-
To set a variable value, you can use the Set Variable Value operation.
-
-
Run the test with the needed parameter value assigned.
In scripts
-
Define a parameter or variable that will pass the needed value to the checkpoint. It can be:
-
A script routine parameter.
-
A script variable.
For example, the code snippet below shows how to declare the Param1 parameter of a script routine:
JavaScript, JScript
function ValidateFile(Param1)
{
…
…
}Python
def ValidateFile(Param1):
…VBScript
Sub ValidateFile(Param1)
…
End SubDelphiScript
procedure ValidateFile(Param1);
begin
…
end;C++Script, C#Script
function ValidateFile(Param1)
{
…
} -
-
Replace the hard-coded parameter of the
Files.File_Checkpoint_Name.Checkmethod with the created variable or parameter:JavaScript, JScript
function ValidateFile(Param1)
{
…
// Validate the file
Files.my_file.Check(Param1);
…
}Python
def ValidateFile(Param1):
…
# Validate the file
Files.my_file.Check(Param1)
…VBScript
Sub ValidateFile(Param1)
…
' Validate the file
Call Files.my_file.Check(Param1)
…
End SubDelphiScript
procedure ValidateFile(Param1);
begin
…
// Validate the file
Files.my_file.Check(Param1);
…
end;C++Script, C#Script
function ValidateFile(Param1)
{
…
// Validate the file
Files["my_file"]["Check"](Param1);
…
} -
Assign the needed value to the parameter or variable:
-
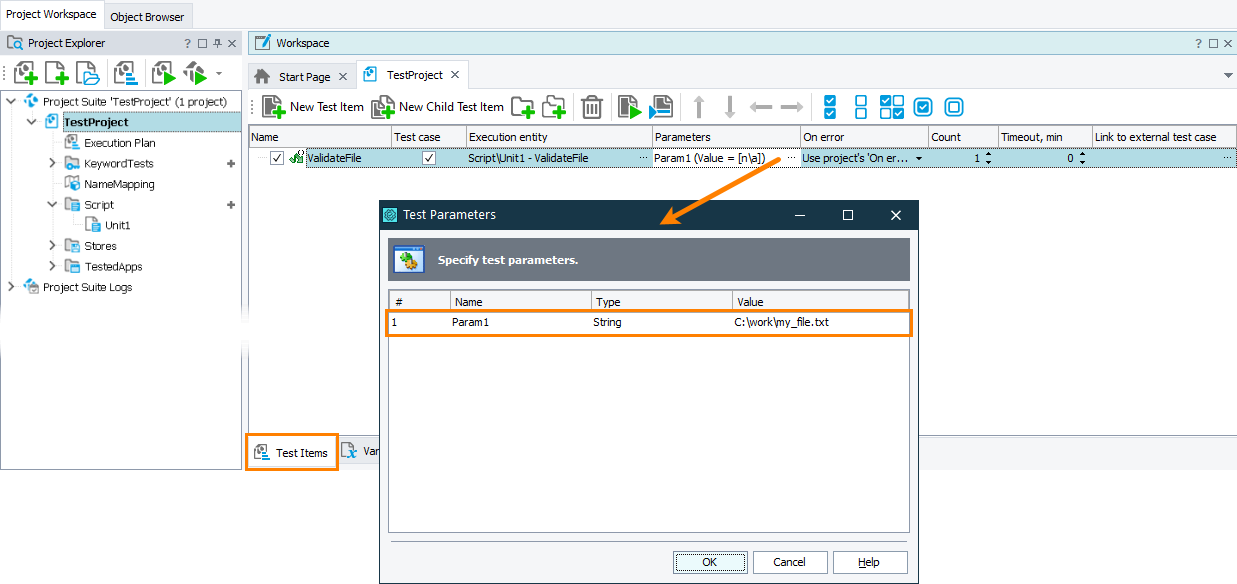
If you use a script parameter, you set the parameter value when you call the script, either from another script routine or as the project’s test item.
The image below shows how to set the parameter value when running the script routine as a project’s test item:
-
If you use a variable, set its value in the script before the script executes the checkpoint.
-
-
Run the script with the needed parameter value assigned.
See Also
File Checkpoints
About File Checkpoints
Creating File Checkpoints
Parameterizing Keyword Tests
Parameterizing Script Routines

 In keyword tests
In keyword tests