This topic provides an overview of testing applications based on Chromium Embedded Framework (CEF).
 About Automated Testing of CEF-Based Applications
About Automated Testing of CEF-Based Applications
 Exposing CEF-Based Applications
Exposing CEF-Based Applications
| Note: | To learn how to test Electron-based applications, see About Testing Electron Applications. |
About Automated Testing of CEF-Based Applications
With TestComplete, you can test web pages in applications that use the Chromium Embedded Framework. TestComplete supports CEF3 versions of the framework. You can test 32-bit and 64-bit applications created with the following programming languages and frameworks:
| Language / Framework | CEF Project |
|---|---|
| C, C++ | generic Chromium Embedded Framework |
| Delphi | DCEF3 |
| .NET | CefSharp (including WPF projects of CEFSharp) |
| Java | JavaChromiumEmbedded JavaCEF |
Currently, the supported versions of CEF3 builds are 3.3282.1741 and earlier. If you use, NuGet or some other package manager to add CEF libraries to your application, make sure that the version of the CEF build within the package conforms to the version of CEF builds supported by TestComplete.
You need to add your CEF-based application to the Tested Applications collection as a generic Windows application. See Adding Tested Applications. In this case, TestComplete may try to expose the application automatically (see below).
Requirements
-
An active license for the TestComplete Web Module.
-
The following plugins must be enabled in TestComplete:
-
Web Testing
-
Chromium Embedded Framework Support
These plugins are installed and enabled automatically as part of the TestComplete Web module. You can check if these plugins are active in File | Install Extensions.
-
Exposing CEF-Based Applications
There are two ways to gain access to web pages and elements of CEF-based applications: automatic (recommended) and manual.
Automatic
In order to expose a CEF-based application, you need to add it to the Tested Applications collection and then launch it in Simple run mode, while one of the following conditions is met:
- The application's executable imports the libcef.dll library.
-- or --
- The libcef.dll library and the application's executable are located in the same folder.
-- or --
- The application has the
injectCefHookcommand-line argument (in any letter case and with any prefix).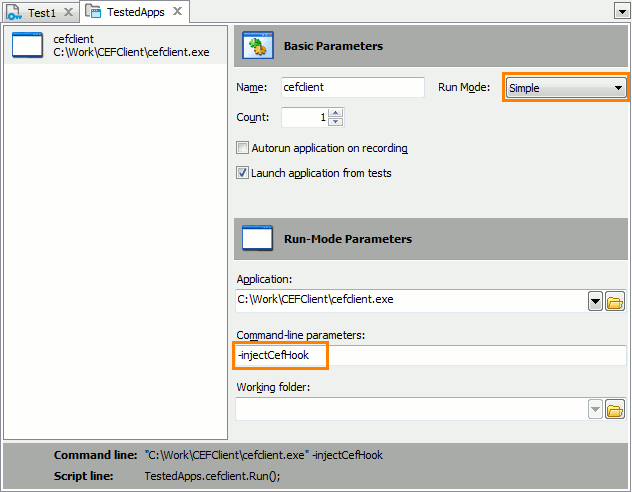
Manual
If you start a CEF-based application in some other way, or launch it in another run mode (RunAs, Debug or Profile), then you need to prepare the application manually. See Preparing CEF-Based Applications for Testing for instructions on how to do this.
After the application is exposed (either automatically or manually), TestComplete will be able to access web pages and elements in the application’s embedded Chromium browser. You can test these web pages as you normally do this in a regular browser.
Specifics of Testing CEF-Based Applications
Web testing in embedded browsers, like CEF-based applications, differs from testing in regular web browsers. The main difference is that TestComplete identifies CEF-based applications as Process test objects rather than Browser test objects. Also, Page objects are nested under the browser hosted window, they are not direct child objects of the application’s process.
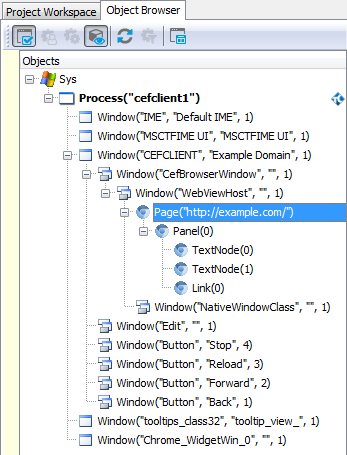
To get a Page object for an embedded web page, you can use the following code:
JavaScript, JScript
function Test()
{
// Search for the Page object
var p = Sys.Process("cefclient1");
var page = p.FindChild("ObjectType", "Page", 5);
if (page.Exists)
{
// Work with the Page object
page.ToUrl("www.example.com");
}
else
{
Log.Error("The Page object was not found.");
}
}
Python
def Test():
# Search for the Page object
p = Sys.Process("cefclient1");
page = p.FindChild("ObjectType", "Page", 5);
if page.Exists:
# Work with the Page object
page.ToUrl("www.example.com");
else:
Log.Error("The Page object was not found.");VBScript
Sub Test
Dim p, page
' Search for the Page object
Set p = Sys.Process("cefclient1")
Set page = p.FindChild("ObjectType", "Page", 5)
If page.Exists Then
' Work with the Page object
page.ToUrl("www.example.com")
Else
Log.Error("The Page object was not found.")
End If
End Sub
DelphiScript
procedure Test;
var p, page;
begin
// Search for the Page object
p := Sys.Process('cefclient1');
page := p.FindChild('ObjectType', 'Page', 5);
if page.Exists then
begin
// Work with the Page object
page.ToUrl('www.example.com');
end
else
Log.Error('The Page object was not found.');
end;
C++Script, C#Script
function Test()
{
// Search for the Page object
var p = Sys["Process"]("cefclient1");
var page = p["FindChild"]("ObjectType", "Page", 5);
if (page["Exists"])
{
// Work with the Page object
page["ToUrl"]("www.example.com");
}
else
{
Log["Error"]("The Page object was not found.");
}
}
For more differences between regular and embedded browsers, see the Specifics of Web Testing in Embedded Browsers section in the Considerations for Web Testing topic.
Known Issues and Limitations
-
.NET applications created with CefGlue are not supported.
-
Windowless (offscreen) rendering mode is supported only for WPF controls of CefSharp applications. Other applications that use offscreeen rendering are not supported.
-
TestComplete cannot perform
ClickItemactions on ListBox controls in applications based on CEF3 builds 1650 and 1750. This behavior is caused by an issue in the Chromium engine and was fixed in CEF build 1916. As a workaround, you can select items of ListBox controls by calling theKeysaction:aListBox.Keys("[Down][Down]") // Select the second item in the list
aListBox.Keys("myItem") // Input the desired value -
If you face issues when accessing GUI objects in your CEF application, make sure the
LifespanHandlerandLoadHandlerinterfaces are implemented in your application.
See Also
Support for Chromium Embedded Framework
Preparing CEF-Based Applications for Testing
Considerations for Web Testing
