Prerequisites
You can start a Jenkins job directly from CucumberStudio. There are two prerequisites to do so:
-
You need an account on the Jenkins server that is able to start jobs.
-
The Jenkins server must be accessible for CucumberStudio. If your server is hosted in a private network, you have two options:
-
Install and use CucumberStudio Enterprise.
– or –
-
Configure the proxies and firewalls running in your network to allow traffic between your Jenkins server and the following server that CucumberStudio Cloud uses:
Fully qualified domain name (FQDN) IP address egress.osc-fr1.scalingo.com171.33.105.206
(at the moment of writing)We’d recommend specifying the server URL (FQDN) rather than its IP, because the IP address can change.
You can check the IP address matching the specified FQDN at any time by running a command like
nslookup egress.osc-fr1.scalingo.com.
-
1. Enable Jenkins
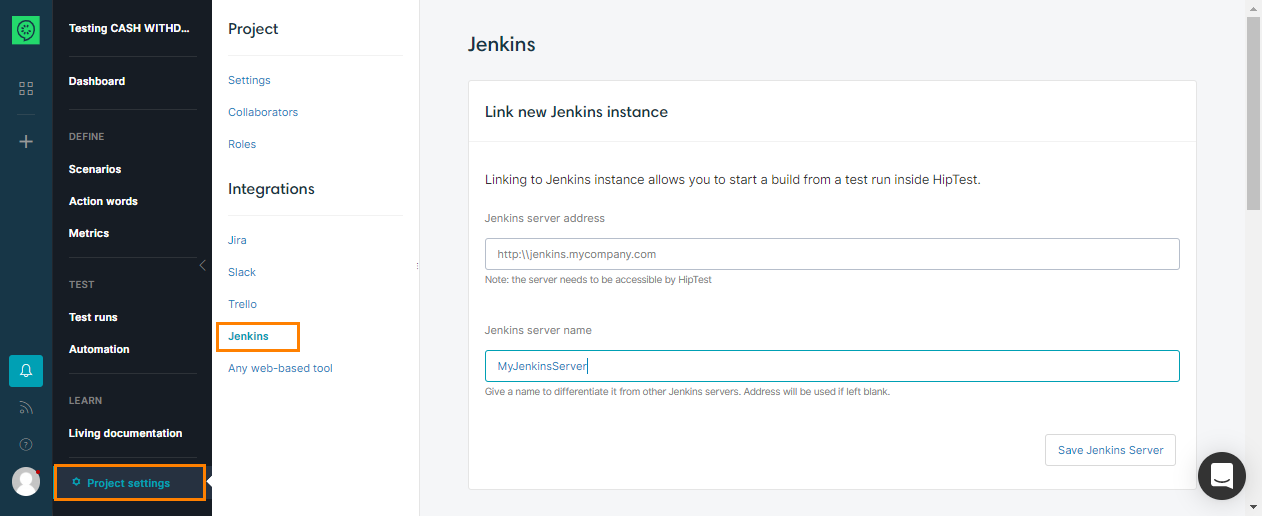
Go to your project settings and look for the Jenkins settings panel. Enter the URL of the Jenkins server and save:
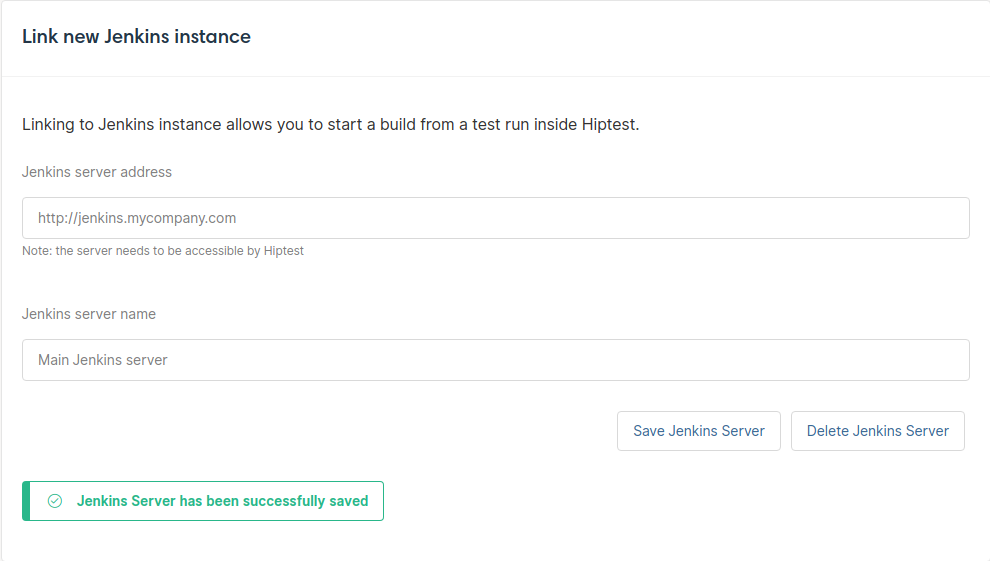
Several Jenkins servers may be added here. Feel free to assign them identifiable names:
| Note: | The Delete Jenkins Server button won’t be available if the server is referenced in a test run. |
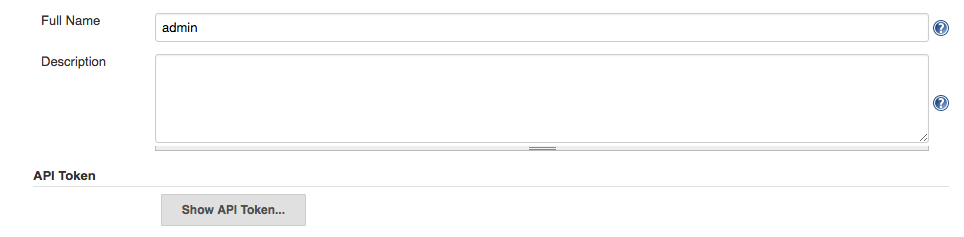
Saving a Jenkins URL allows you to store the credentials used to connect to that Jenkins server. We strongly recommend you to use the API token instead of the password. To find it, login to Jenkins, open your profile and click on the Configure link.
You will find the API token sub-section, click on the Show API token button and use the API token as the password in CucumberStudio:
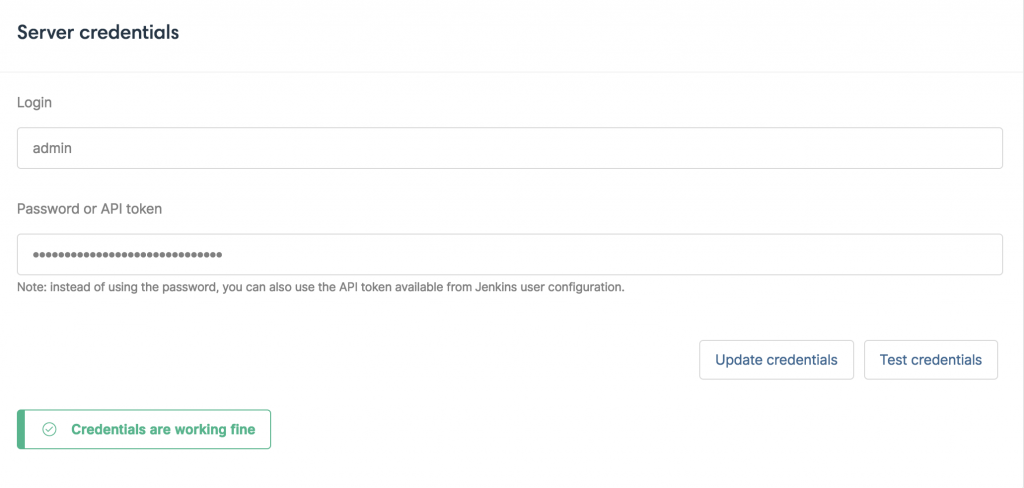
Once the credentials have been saved, you can click on Test credentials to ensure that the connection between CucumberStudio and Jenkins is working as expected:
2. Select the jobs to start
To be able to start a Jenkins job, you will need a test run from which the job will be started. In the test run, you will see the Jenkins jobs section. It will list all jobs linked to this project:
Normally, you have no job linked to the test run for now, so let’s add one. Click on the Add new job button:
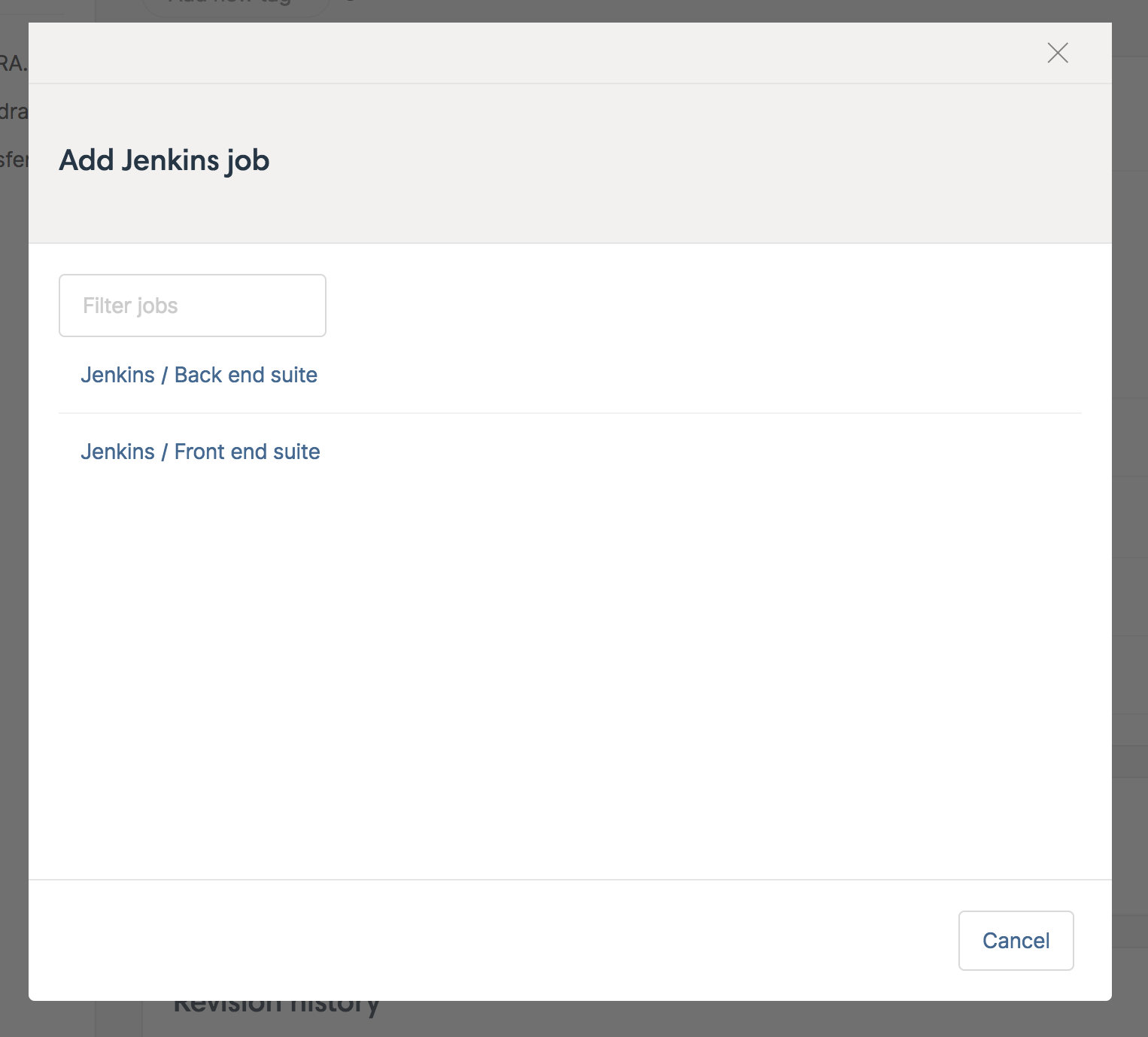
Click on the name of the job you want to link to this project and it will appear in the Jenkins panel:
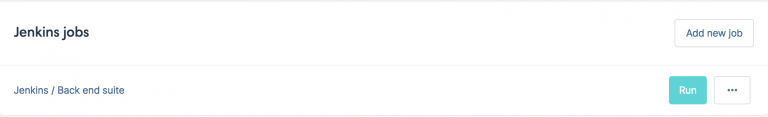
Now click on the button Run to start it:
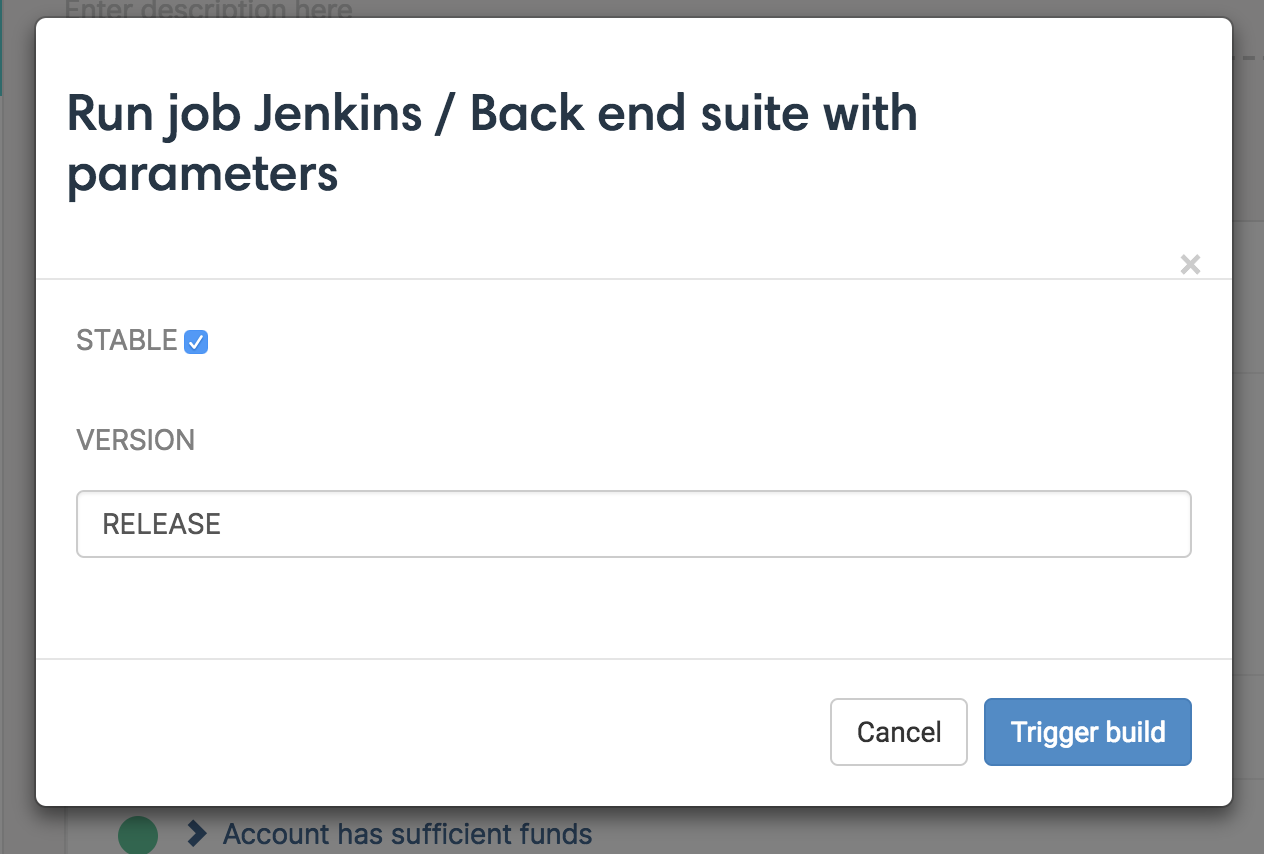
For parametrized jobs, after clicking on Run button, a modal will appear with the Jenkins parameters pre-filled. You can check or modify them before to trigger the build:
| Note: | Credentials, File and Custom parameters are not supported by CucumberStudio. If the job linked to your test run contains some of them, a warning message will appear to notify that they will be ignored. |
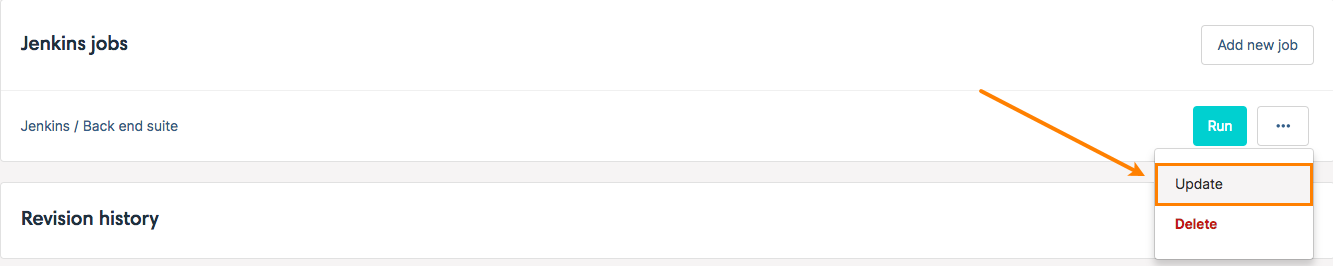
3. Refreshing job
If your job is modified in Jenkins (default value changes, adding/deleting parameters, …), you may refresh your linked job in CucumberStudio. There is nothing more simple! All you have to do is to click on Update before filling your parameters and triggering your build.
That’s it, you Jenkins job is now started. You can link multiple jobs to a single test run.
4. Going a bit further
If needed, you can get some extra data from CucumberStudio when starting the build. There are three available parameters:
-
test_run_data: is the link to the XML export of the test run from which the job was started. This can be used for example to filter the tests you want to run.
-
project_token: is the project secret token. You can use it to push the results of the execution back to CucumberStudio.
-
test_run_id: is the ID of the test run used to start the build. Again, it can be used to push the results back to CucumberStudio.
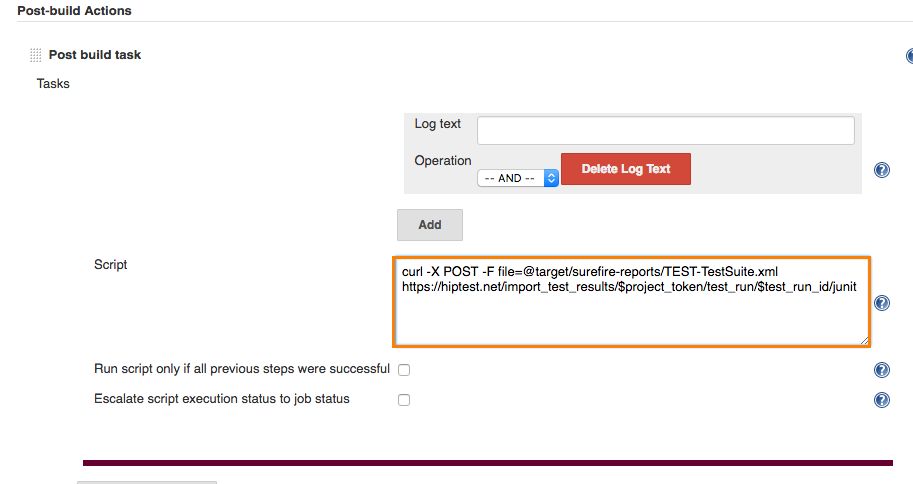
Here is an example of a post-build action that pushes the results back to CucumberStudio, based on those parameters:
| Note: | Post build task is an optional Post-build Action available as a Jenkins plugin Hudson Post build task. |