AQTime is a COM server and it can be controlled from other applications like any other COM server. Other SmartBear applications, for example, TestComplete, use much of it to integrate AQTime tests and results. This topic provides a step-by-step explanation of how you can control AQTime via COM from Visual Basic and Visual C++ applications. For information on automating AQTime from managed code (for instance, C#), see Working With AQTime From Managed Code.
In this topic:
 |
Three notes before we proceed:
|
Setting up Visual Basic
To work with AQTime in your VB application, add a reference to the AQTime object library to your application that will use AQTime as a COM server. The following steps explain how you can do this. Note that this step is optional. It is not required if you will work with AQTime via IntegrationManager (see below).
-
Open your COM client application in Microsoft Visual Basic.
-
Select Project > References from Visual Basic menu. This will call the References dialog.
-
In the dialog, check SmartBear AQTime Library and press OK. This will add a reference to the AQTime object library to your COM client application:
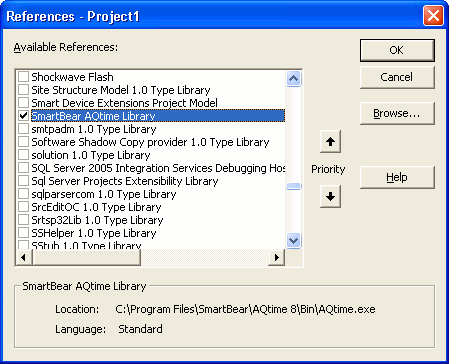
If AQTime library is not present in the dialog, you can add it directly by pressing Browse and selecting the <AQTime>\Bin\AQTime.exe file in the ensuing Open File dialog.
Setting Up Visual C++
To automate AQTime from a Visual C++ application, you need to include the AQtimeConstants.h header file in your project. This file contains the CLSID of the AQTime COM object and imports the AQTime type library information. It is shipped with AQTime SDK and is located in the <AQTime SDK>\CPP\Common folder.
In order for the compiler to be able to find this header file, you need to add the <AQTime SDK>\CPP\Common folder to your project’s search directories. To do this:
-
From the Visual C++ menu, select Project > Properties. The Property Pages dialog box will open.
-
In the tree on the left of the dialog, select the Configuration Properties > C\C++ > General property page.
-
In the Additional Include Directories property value, specify the fully-qualified path to the <AQTime SDK>\CPP\Common folder.
Then add the following line to the precompiled header file (usually stdafx.h) or the source file that will contain the AQTime automation code:
Visual C++
#include <AQtimeConstants.h>
Connecting to AQTime via COM
The first step in using AQTime as a COM server is connecting to it. To create a connection, you have to create reference to AQTime object. This object implements methods and properties to connect and work with AQTime.
In Visual Basic, you can create the AQTime COM object by calling the CreateObject function with the AQtime.AQtime or AQtime.AQtime.8 ProgID as a parameter:
Visual Basic
Set AQtimeObject = CreateObject("AQtime.AQtime")
In Visual C++, you can create the AQTime COM object either by using the CoCreateInstance function or the ATL smart pointer class CComPtr and its CComPtr::CoCreateInstance method (recommended). The CLSID is specified via the CProductAQtime constant from the AQTime SDK’s AQtimeConstants.h file:
Visual C++
CComPtr<IAQtimeManager> aqTimeManager;
HRESULT hr = aqTimeManager.CoCreateInstance(CProductAQtime);
The code above will connect your COM client application to the currently running instance of AQTime. If AQTime has not been launched yet, this code will launch it.
The AQtime object contains the following methods and properties:
| Property (Method) | Description |
|---|---|
Quit |
Method. Use it to exit AQTime. |
Manager |
Property. Returns a reference to the IaqBaseManager object that provides access to internal AQTime interfaces. These are the same interfaces that different components of AQTime use to connect and work with each other. Using these interfaces you can perform almost any action that you can do via AQTime’s user interface. |
IntegrationManager |
Property. Returns a reference to the IaqTimeIntegrationSupportManager object (hereinafter we will call it IntegrationManager for short). It provides access to a subset of higher-level functions specifically engineered to let users perform most typical actions over AQTime with ease. For a list of these functions, see IaqTimeIntegrationSupportManager Object. |
Functionality provided by IntegrationManager is less than what you could do if you would decide to use Manager. However, use of IntegrationManager is much more easier. For instance, you can start the profiler run and save results by calling only one IntegrationManager’s method. If you used Manager, you would have to write more complex code.
If you will work with AQTime via the IntegrationManager property, you may skip the Setting up Visual Basic step (see above).
Using IntegrationManager to Automate AQTime
The IntegrationManager includes methods and properties that let you easily perform typical tasks over AQTime: open a project, select and run a profiler and save profiling results to a file. For detailed information, see IaqTimeIntegrationSupportManager Object.
Using the IntegrationManager is the easiest way to automate AQTime. Let’s create sample code that will:
- Connect to AQTime via COM.
- Open a project.
- Select a profiler.
- Start profiling and save results to an .xml file.
To perform these tasks, we will use only three methods and one property of the IntegrationManager object: OpenProject, SelectProfiler, Start and ProfilingStarted. The code snippet below also demonstrates how you can specify run parameters:
Two notes:
-
Both
StartandAttachmethods returns immediately after profiling is started. If you try to close AQTime when it is profiling an application (this happens, for example, when you callQuitright afterStart), AQTime displays a message that asks you whether you want to close application and terminate profiling. To avoid this message, we used a loop that waits until the profiling is over. -
Settings of profiling areas and triggers, selected profiling mode (Normal, ASP.NET, IIS, Service or COM Server), currently selected profiler, and others, are stored in AQTime project files. When you profile your application using the
StartorAttachmethods of theIntegrationManagerobject, AQTime uses profiling mode and area and trigger settings stored in your AQTime project.Therefore, we recommend to prepare your project in AQTime before you profile that project with AQTime via COM.
Working With Profiling Areas
Using AQTime COM interfaces, you can create, remove and modify profiling areas of your projects. For complete information on how to do this, see Managing Profiling Areas via COM.
See Also
Working With AQTime via COM
Working With AQTime From Managed Code
COM Type Reference
Automating AQTime

 Setting up Visual Basic
Setting up Visual Basic View Sample Code
View Sample Code