This topic explains how to compile Visual C++ (unmanaged) and Qt applications in Microsoft Visual Studio 2002 and 2003 to prepare them for testing.
-
Open your Visual C++ 7.x project in Microsoft Visual Studio .NET 2002 (7.0) or 2003 (7.1), depending on which version of Visual Studio the project was created in.
-
(Optional). To keep your release configuration intact, choose Build | Configuration Manager and select another configuration, say, Debug, as active for the project.
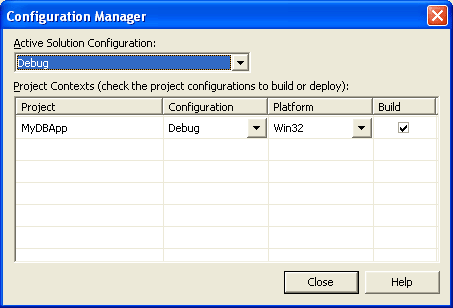
If you need to test the Release configuration, you can skip this step, but remember to restore the compiler settings after the testing is over.
-
Open the project properties. To do this, right-click the project in the Solution Explorer and select Properties from the context menu.
-
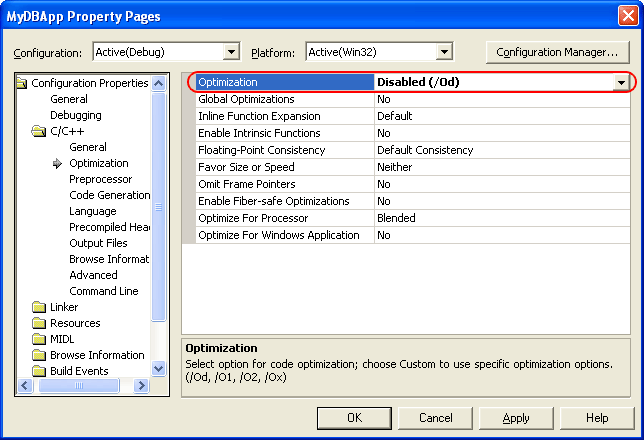
In the Project Properties dialog, select the Configuration Properties | C/C++ | Optimization category and set the Optimization option to Disabled (/Od).
-
To access the internal methods and properties of MFC objects, compile the application with run-time type information (RTTI):
-
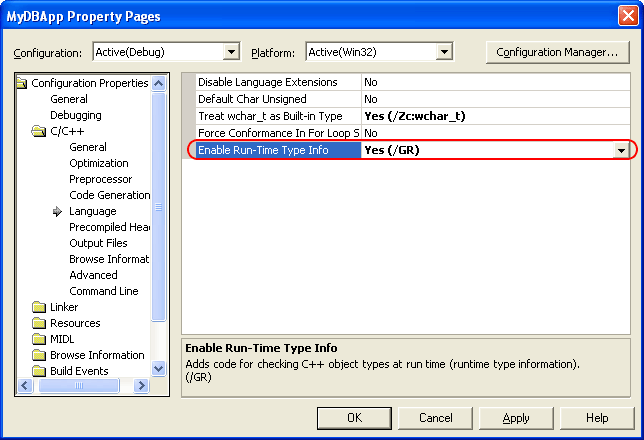
In the Project Properties dialog, select the Configuration Properties | C/C++ | Language category.
-
Set the Enable Run-Time Type Info option to Yes (/GR):
-
-
To access the private, protected, and public internals of the application, compile your application with run-time type information (RTTI) and debug information:
-
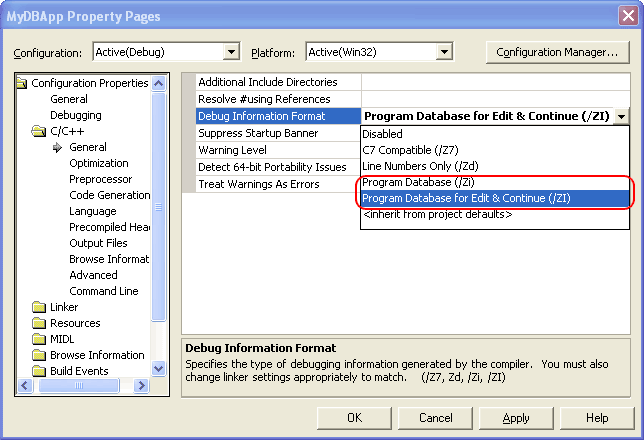
In the Project Properties dialog, select the Configuration Properties | C/C++ | General node and set the Debug Information Format option to either Program Database (/Zi) or Program Database for Edit and Continue (/ZI).
-
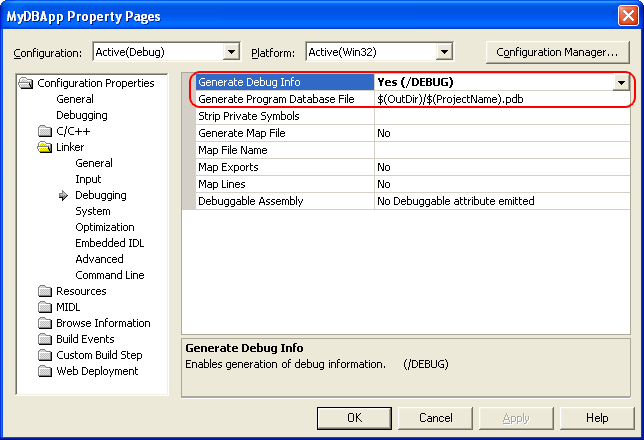
Select the Configuration Properties | Linker | Debugging category and set the Generate Debug Info option to Yes (/DEBUG). Also, make sure the Generate Program Database File option on this page specifies a valid path to the file that will hold debug information.
-
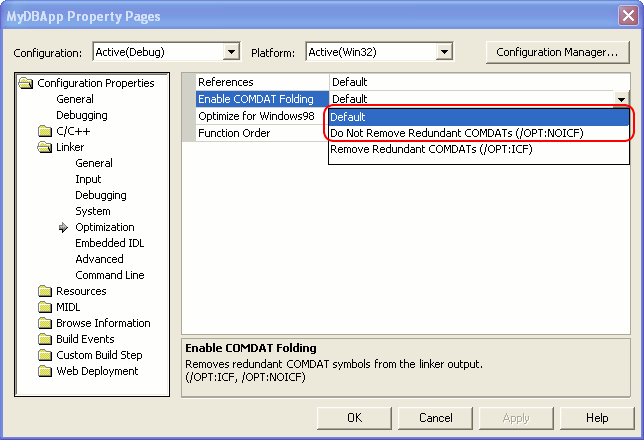
Select the Configuration Properties | Linker | Optimization category and set the Enable COMDAT Folding option to either Default or Do Not Remove Redundant COMDATs (/OPT:NOICF).
-
-
If your application uses MFC classes, select the Configuration Properties | General category and specify whether you want to use MFC in static or shared DLLs in the Project defaults | Use of MFC combo box:
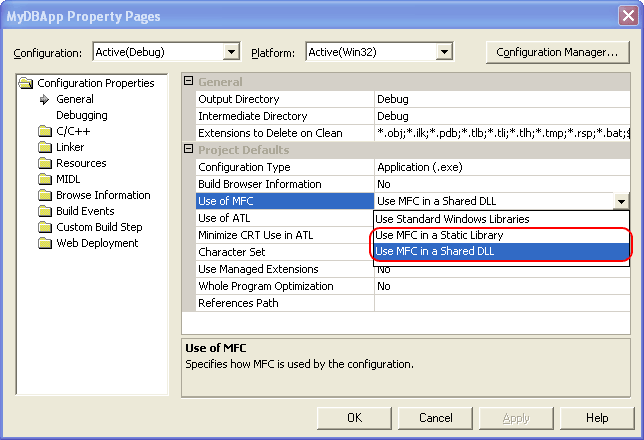

If you use the Use MFC in a Shared DLL option, Copy MFC debug information files to the compiled application’s folder. For instructions, see Downloading MFC Debug Information. -
Re-compile your application.
When your application is ready for the final delivery, remember to compile it without debug information and RTTI to reduce the application size.