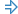1. Import Libraries
Before implementing test steps with TestLeft, you need to import the required classes:
Java
import org.junit.Assert;
import com.smartbear.testleft.LocalDriver;
import com.smartbear.testleft.Driver;
import com.smartbear.testleft.testobjects.*;
2. Create a Driver Object
You must create an instance of the Driver class as you do this in a regular TestLeft test. The way you do this, depends on your test. In our case, we create it in the first test step.
Since the LocalDriver method throws a number of exceptions, we also need to add the throws operator to the method declaration:
Java
@Given("I open Notepad")
@Pending
public void givenIOpenNotepad() throws Exception {
Driver driver = new LocalDriver();
}
We use the LocalDriver class. This way we access the TestLeft test engine on the local computer. To access the TestLeft test engine running on a remote computer, use the RemoteDriver class.
3. Run the Tested Application
-
Use the created driver object to run the tested application:
Java
@Given("I open Notepad")
@Pending
public void givenIOpenNotepad() throws Exception {
Driver driver = new LocalDriver();
TestProcess notepadProcess = driver.getApplications().run("notepad.exe");
}To learn more, see Running Applications From Tests.
-
Remove the
@Pendingannotation to command JBehave to execute the method. -
Run the test. TestLeft should run the Notepad application. After that, the test will stop because the next steps are not implemented yet.
Note: Do not close Notepad. You will use it to implement the next test steps.
4. Get Test Objects
When you create a test with TestLeft, you can inspect applications objects, their methods and properties by using TestLeft UI Spy and generate code to get them from the test.
-
Run the TestLeft UI Spy utility.
-
In IntelliJ IDEA, select Tools > TestLeft UI Spy to run the utility.
-- or --
-
Launch the <TestLeft>\Bin\SmartBear.TestLeft.UI.Spy.exe executable.
-
-
Configure the TestLeft UI Spy code generation settings. Click
 on the main toolbar and specify the following settings:
on the main toolbar and specify the following settings:-
In the Languages section, select Java.
-
In The first object section, select Main form / Page. The Process variable name box should specify the name of the variable that contains a reference to the testing process. In our case, it is
notepadProcess.
Click OK.
-
-
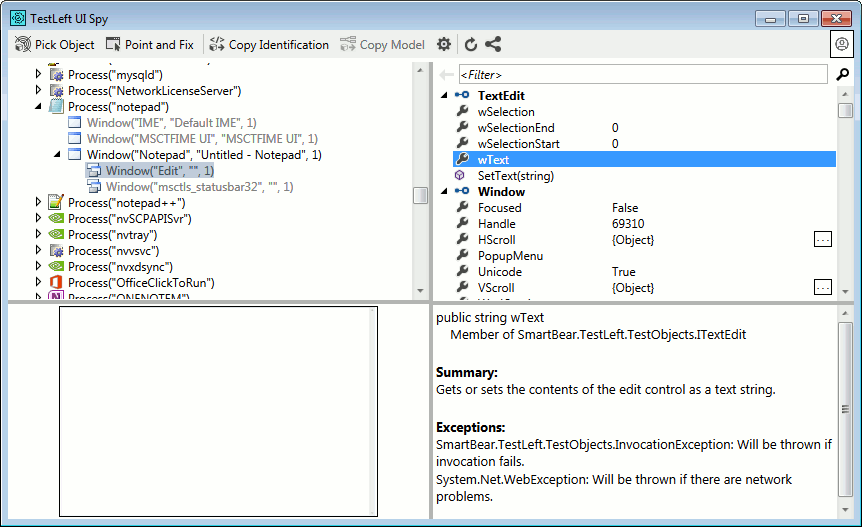
Hold the left mouse on the Pick Object button (the mouse cursor will turn into the target icon (
 ). Drug the cursor to the Notepad window and drop it once a red frame appears around the edit box:
). Drug the cursor to the Notepad window and drop it once a red frame appears around the edit box:TestLeft UI Spy will select the object in the object tree. The panel on the right shows the methods and properties of the selected object:
-
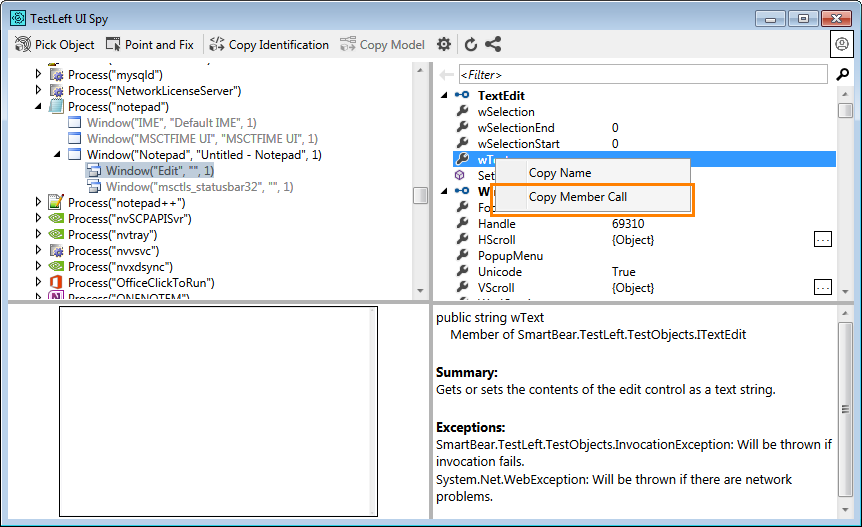
To verify that the Notepad window contains no text, use the
wTextproperty. Right-click thewTextproperty and select Copy Member Call from the context menu:TestLeft will copy the required code to the clipboard.
-
Paste the generated code to the method of the next test step:
Java
@Given("there is no text in Notepad")
@Pending
public void givenThereIsNoTextInNotepad() {
TextEdit edit = (TextEdit) notepadProcess.find(TopLevelWindow.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Notepad";
}}).find(TextEdit.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Edit";
}});
String wTextValue = edit.getwText();
} -
The
findandgetwTextmethods throw a number of exceptions, so you need to add thethrowsoperator to the method declaration:Java
@Given("there is no text in Notepad")
@Pending
public void givenThereIsNoTextInNotepad() throws Exception {
...
} -
You can see that this code cannot find the
notepadProcessobject. To fix that, you need to make the corresponding object visible for this method. Declare the notepadProcess variable at the beginning of the class:Java
public class UndoTypingSteps {
private TestProcess notepadProcess;
@Given("I open Notepad")
public void givenIOpenNotepad() throws Exception {
Driver driver = new LocalDriver();
notepadProcess = driver.getApplications().run("notepad.exe");
}
} -
Use the
Assert.assertEqualsmethod to verify that the property contains an empty string:Java
@Given("there is no text in Notepad")
@Pending
public void givenThereIsNoTextInNotepad() throws Exception {
TextEdit edit = (TextEdit) notepadProcess.find(TopLevelWindow.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Notepad";
}}).find(TextEdit.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Edit";
}});
String wTextValue = edit.getwText();
Assert.assertEquals("", wTextValue);
}
5. Simulate User Actions
-
To implement the next test steps, you need to interact with the edit box. Therefore, you need to make it visible for other methods. Declare the corresponding variable at the beginning of the class:
Java
public class UndoTypingSteps {
private TestProcess notepadProcess;
private TextEdit edit;
...
@Given("there is no text in Notepad")
@Pending
public void givenThereIsNoTextInNotepad() throws Exception {
edit = (TextEdit) notepadProcess.find(TopLevelWindow.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Notepad";
}}).find(TextEdit.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Edit";
}});
...
}
} -
JBehave can pass text of a test step to the corresponding method as an argument. To do that, put the name of the argument with a leading dollar sign (
$) to the regular expression. For example, to extract the text in quotes from the third test step, modify the corresponding regular expression in the following way:Java
@When("I type \"$arg1\"")
@Pending
public void whenITypeSomeText(String arg1) {
} -
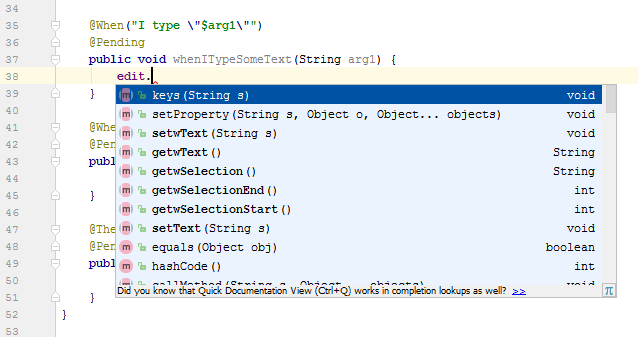
On the next test step, you need to enter text in the Notepad window. If your IDE supports the autocomplete feature, examine the list of methods available to the object:
To simulate typing text, we will use the
keysmethod:Java
@When("I type \"$arg1\"")
@Pending
public void whenITypeSomeText(String arg1) {
edit.keys(arg1);
} -
The
keysmethod throws a number of exceptions, so you need to add thethrowsoperator to the method declaration:Java
@When("I type \"$arg1\"")
@Pending
public void whenITypeSomeText(String arg1) throws Exception {
edit.keys(arg1);
} -
To simulate pressing hotkeys, we also use the
keysmethod:Java
@When("I press [Ctrl + z]")
@Pending
public void whenIPressCtrlZ() throws Exception {
edit.keys("^z");
} -
Finally, you can check that Notepad does not contain any text. Use the
Assert.assertEqualmethod, as we did it earlier:Java
@Then("I should see no text in Notepad")
@Pending
public void thenIShouldSeeNoTextInNotepad()throws Throwable {
Assert.assertEquals("", edit.getwText());
} -
Remove the
@Pendingannotations from the methods to command JBehave to execute them. -
Run the test and check if it works. TestLeft will run Notepad, enter text, undo the action and check if the Notepad window is empty.
6. Refactor the Test
In behavior-driven development, it is a good practice to refactor the code after the test passes.
In our example, the Notepad application is still running after the test run is over. It means that when another scenario starts, it will run another instance of the application. This may cause errors and performance issues. To fix that, you must close the application when the scenario finishes. To do that, use the @AfterScenario annotation. JBehave will run a method with this annotation at the end of each test scenario. Add the following method to the test class:
Java
import org.jbehave.core.annotations.AfterScenario;
...
public class UndoTypingSteps {
...
@AfterScenario
public void cleanUp() throws Exception {
if (notepadProcess != null)
notepadProcess.close();
}
}
Final Code
The final test code is as follows:
Java
import org.jbehave.core.annotations.Given;
import org.jbehave.core.annotations.When;
import org.jbehave.core.annotations.Then;
import org.jbehave.core.annotations.AfterScenario;
import org.junit.Assert;
import com.smartbear.testleft.Driver;
import com.smartbear.testleft.LocalDriver;
import com.smartbear.testleft.testobjects.*;
public class UndoTypingSteps {
private TestProcess notepadProcess;
private TextEdit edit;
@Given("I open Notepad")
public void givenIOpenNotepad() throws Exception {
Driver driver = new LocalDriver();
// Run the application
notepadProcess = driver.getApplications().run("notepad.exe");
}
@Given("there is no text in Notepad")
public void givenThereIsNoTextInNotepad() throws Exception{
// Obtain the edit box object
edit = (TextEdit) notepadProcess.find(TopLevelWindow.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Notepad";
}}).find(TextEdit.class, new WindowPattern(){{
WndClass = "Edit";
}});
// Get the value of the wText property
String wTextValue = edit.getwText();
// Verify that the edit box does not contain any text
Assert.assertEquals("", wTextValue);
}
@When("I type \"$arg1\"")
public void whenITypeSomeText(String arg1) throws Exception {
// Type the specified text
edit.keys(arg1);
}
@When("I press [Ctrl + z]")
public void whenIPressCtrlZ() throws Exception {
// Press hotkeys
edit.keys("^z");
}
@Then("I should see no text in Notepad")
public void thenIShouldSeeNoTextInNotepad() throws Exception {
// Verify that the edit box is empty
Assert.assertEquals("", edit.getwText());
}
@AfterScenario
public void cleanUp() throws Exception {
// Close the application
if (notepadProcess != null)
notepadProcess.close();
}
}
See Also
Behavior-Driven Development
About Behavior-Driven Development
 Prev
Prev