In TestComplete tests, you can create Excel files or access already existing ones.
In Script Tests
The following steps are required:
-
Get access to a file. To create a new file, use the
Excel.Createmethod. To access an existing file, use theExcel.Openmethod. -
Get access to a worksheet. You can specify the worksheet by its title or index. For this purpose, use the
SheetByTitleorSheetByIndexmethods respectively.
JavaScript, JScript
function ExcelExample()
{
// Get the data that will be written into an Excel file
var curTime = aqDateTime.Now();
var cpu = Sys.CPUUsage;
var fileName = "c:\\temp\\MyFile.xlsx";
var excelFile;
var excelSheet;
if (aqFile.Exists(fileName))
{
// Open the existing Excel file
excelFile = Excel.Open(fileName);
excelSheet = excelFile.SheetByIndex(0);
// Write the data into a new row of the existing file
var rowIndex = excelSheet.RowCount + 1;
excelSheet.Cell("A", rowIndex).Value = curTime;
excelSheet.Cell(2, rowIndex).Value = cpu;
}
else
{
// Create a new Excel file
excelFile = Excel.Create(fileName);
excelSheet = excelFile.AddSheet("Sheet1");
// Write the data into the first row of the created file
excelSheet.Cell("A", 1).Value = curTime;
excelSheet.Cell(2, 1).Value = cpu;
}
// Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save();
}
Python
def ExcelExample():
# Get the data that will be written into an Excel file
curTime = aqDateTime.Now()
cpu = Sys.CPUUsage
fileName = "c:\\temp\\MyFile.xlsx"
if (aqFile.Exists(fileName)):
# Open the existing Excel file
excelFile = Excel.Open(fileName)
excelSheet = excelFile.SheetByIndex[0]
# Write the data into a new row of the existing file
rowIndex = excelSheet.RowCount + 1
excelSheet.Cell["A", rowIndex].Value = curTime
excelSheet.Cell[2, rowIndex].Value = cpu
else:
# Create a new Excel file
excelFile = Excel.Create(fileName)
excelSheet = excelFile.AddSheet("Sheet1")
# Write the data into the first row of the created file
excelSheet.Cell["A", 1].Value = curTime
excelSheet.Cell[2, 1].Value = cpu
# Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save()VBScript
Sub ExcelExample
Dim curTime, cpu, fileName, excelFile, excelSheet, rowIndex
' Get the data that will be written into an Excel file
curTime = aqDateTime.Now()
cpu = Sys.CPUUsage
fileName = "c:\temp\MyFile.xlsx"
If aqFile.Exists(fileName) Then
' Open the existing Excel file
Set excelFile = Excel.Open(fileName)
Set excelSheet = excelFile.SheetByIndex(0)
' Write the data into a new row of the existing file
rowIndex = excelSheet.RowCount + 1
excelSheet.Cell("A", rowIndex).Value = curTime
excelSheet.Cell(2, rowIndex).Value = cpu
Else
' Create a new Excel file
Set excelFile = Excel.Create(fileName)
Set excelSheet = excelFile.AddSheet("Sheet1")
' Write the data into the first row of the created file
excelSheet.Cell("A", 1).Value = curTime
excelSheet.Cell(2, 1).Value = cpu
End If
' Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save()
End Sub
DelphiScript
procedure ExcelExample;
var
curTime, cpu, fileName, excelFile, excelSheet, rowIndex;
begin
// Get the data that will be written into an Excel file
curTime := aqDateTime.Now();
cpu := Sys.CPUUsage;
fileName := 'c:\\temp\\MyFile.xlsx';
if (aqFile.Exists(fileName)) then
begin
// Open the existing Excel file
excelFile := Excel.Open(fileName);
excelSheet := excelFile.SheetByIndex(0);
// Write the data into a new row of the existing file
rowIndex := excelSheet.RowCount + 1;
excelSheet.Cell('A', rowIndex).Value := curTime;
excelSheet.Cell(2, rowIndex).Value := cpu;
end
else
begin
// Create a new Excel file
excelFile := Excel.Create(fileName);
excelSheet := excelFile.AddSheet('Sheet1');
// Write the data into the first row of the created file
excelSheet.Cell('A', 1).Value := curTime;
excelSheet.Cell(2, 1).Value := cpu;
end;
// Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save();
end;
C++Script, C#Script
function ExcelExample()
{
// Get the data that will be written into an Excel file
var curTime = aqDateTime["Now"]();
var cpu = Sys["CPUUsage"];
var fileName = "c:\\temp\\MyFile.xlsx";
var excelFile;
var excelSheet;
if (aqFile["Exists"](fileName))
{
// Open the existing Excel file
excelFile = Excel["Open"](fileName);
excelSheet = excelFile["SheetByIndex"](0);
// Write the data into a new row of the existing file
var rowIndex = excelSheet["RowCount"] + 1;
excelSheet["Cell"]("A", rowIndex)["Value"] = curTime;
excelSheet["Cell"](2, rowIndex)["Value"] = cpu;
}
else
{
// Create a new Excel file
excelFile = Excel["Create"](fileName);
excelSheet = excelFile["AddSheet"]("Sheet1");
// Write the data into the first row of the created file
excelSheet["Cell"]("A", 1)["Value"] = curTime;
excelSheet["Cell"](2, 1)["Value"] = cpu;
}
// Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile["Save"]();
}
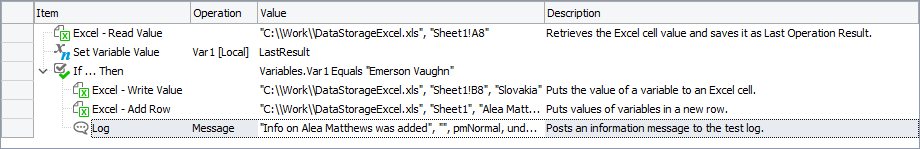
In Keyword Tests
You do not have to add any additional operations to create or open Excel files. TestComplete automatically accesses the file when you start reading data from or writing it to this file.
Related Tasks
See the following topics to continue working with Excel files:

 Reading data
Reading data