About
When testing, you may need to use data from external storages. Microsoft Excel files are among the most popular data storages. TestComplete allows you to retrieve data from Excel files and use them in your tests. Also, you can add data to existing Excel files or create new ones.
Video Tutorial
In Keyword Tests
Note: To work with Excel files in your tests, you do not need to have Microsoft Office Excel installed on your computer.
Use special operations grouped into the Excel section to read data from Excel cells and write data to them.
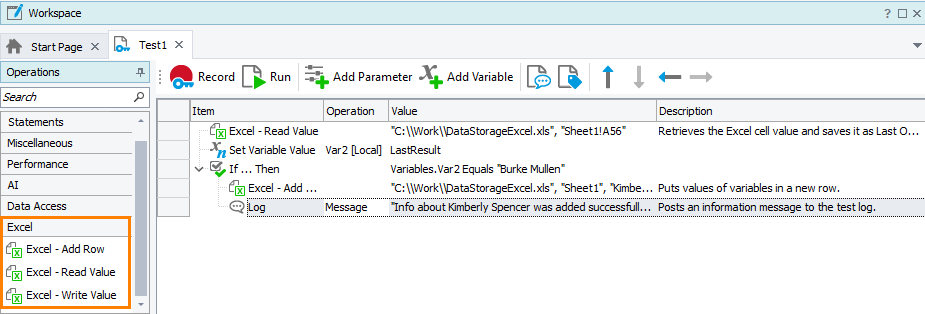
When you write data via these operations, you do not need to add additional operations to save changed data. Excel operations will do it automatically.
In Script Tests
If you work with Excel files in script tests, use the Excel object. The following script illustrates how to read data from Excel cells and write it into a new row:
JavaScript, JScript
function ExcelExample()
{
// Get the sheet of the Excel file
var excelFile = Excel.Open("C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel.xlsx");
var excelSheet = excelFile.SheetByTitle("Sheet1");
// Read data from the Excel file
var valueA = excelSheet.Cell("A", 3).Value;
var valueB = excelSheet.Cell(2, 3).Value;
var valueC = excelSheet.CellByName("C3").Value;
// Write the obtained data into a new row of the file
var rowIndex = excelSheet.RowCount + 1;
excelSheet.Cell("A", rowIndex).Value = valueA;
excelSheet.Cell(2, rowIndex).Value = valueB;
excelSheet.Cell("C", rowIndex).Value = valueC;
// Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save();
// Save the file with another name
// excelFile.SaveAs("C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel_new.xlsx");
}
Python
def ExcelExample():
# Get the sheet of the Excel file
excelFile = Excel.Open("C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel.xlsx")
excelSheet = excelFile.SheetByTitle["Sheet1"]
# Read data from the Excel file
valueA = excelSheet.Cell["A", 3].Value
valueB = excelSheet.Cell[2, 3].Value
valueC = excelSheet.CellByName["C3"].Value
# Write the obtained data into a new row of the file
rowIndex = excelSheet.RowCount + 1
excelSheet.Cell["A", rowIndex].Value = valueA
excelSheet.Cell[2, rowIndex].Value = valueB
excelSheet.Cell("C", rowIndex).Value = valueC
# Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save()
# Save the file with another name
# excelFile.SaveAs("C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel_new.xlsx")VBScript
Sub ExcelExample
Dim excelFile, excelSheet, valueA, valueB, valueC, rowIndex
' Get the sheet of the Excel file
Set excelFile = Excel.Open("C:\temp\DataStorageExcel.xlsx")
Set excelSheet = excelFile.SheetByTitle("Sheet1")
' Read data from the Excel file
valueA = excelSheet.Cell("A", 3).Value
valueB = excelSheet.Cell(2, 3).Value
valueС = excelSheet.CellByName("C3").Value
' Write the obtained data into a new row of the file
rowIndex = excelSheet.RowCount + 1
excelSheet.Cell("A", rowIndex).Value = valueA
excelSheet.Cell(2, rowIndex).Value = valueB
excelSheet.Cell("C", rowIndex).Value = valueC
' Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save()
' Save the file with another name
' excelFile.SaveAs("C:\temp\DataStorageExcel_new.xlsx")
End Sub
DelphiScript
procedure ExcelExample;
var
excelFile, excelSheet, valueA, valueB, valueC, rowIndex;
begin
// Get the sheet of the Excel file
excelFile := Excel.Open('C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel.xlsx');
excelSheet := excelFile.SheetByTitle('Sheet1');
// Read data from the Excel file
valueA := excelSheet.Cell('A', 3).Value;
valueB := excelSheet.Cell(2, 3).Value;
valueC := excelSheet.CellByName('C3').Value;
// Write the obtained data into a new row of the file
rowIndex := excelSheet.RowCount + 1;
excelSheet.Cell('A', rowIndex).Value := valueA;
excelSheet.Cell(2, rowIndex).Value := valueB;
excelSheet.Cell('C', rowIndex).Value := valueC;
// Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile.Save();
// Save the file with another name
// excelFile.SaveAs('C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel_new.xlsx');
end;
C++Script, C#Script
function ExcelExample()
{
// Get the sheet of the Excel file
var excelFile = Excel["Open"]("C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel.xlsx");
var excelSheet = excelFile["SheetByTitle"]("Sheet1");
// Read data from the Excel file
var valueA = excelSheet["Cell"]("A", 3)["Value"];
var valueB = excelSheet["Cell"](2, 3)["Value"];
var valueC = excelSheet["CellByName"]("C3")["Value"];
// Write the obtained data into a new row of the file
var rowIndex = excelSheet["RowCount + 1"];
excelSheet["Cell"]("A", rowIndex)["Value"] = valueA;
excelSheet["Cell"](2, rowIndex)["Value"] = valueB;
excelSheet["Cell"]("C", rowIndex)["Value"] = valueC;
// Save the file to apply the changes
excelFile["Save"]();
// Save the file with another name
// excelFile["SaveAs"]("C:\\temp\\DataStorageExcel.xlsx");
}
Checkpoints
To validate data in Excel files, you can use the Excel checkpoint. It allows you to compare an entire Excel file or a selected sheet with the baseline Excel file.
For this purpose, use the Excel Checkpoint operation or the Files.Excel_File_Name.CheckExcelWorkbook method in your keyword or script tests, respectively.
Alternatively, you can iterate through your Excel file and compare the desired data via if � then � else statements and comparison operators.
Common Tasks
Typically, in TestComplete, you need to do the following tasks with Excel files:
Remarks
- Excel files secured with passwords are not supported.
- Target Excel files must not be open in third-party programs during test executions.
Alternatives
 All these approaches require Microsoft Office Excel installed on your computer.
All these approaches require Microsoft Office Excel installed on your computer.
DB Table Variables
In data-driven keyword tests, use a DB Table variable to store the link of the Excel file and then iterate through its data, for example, by using the Data-Driven Loop operation.
DB Table variables do not allow writing data to Excel files.
For more information, see Using DB Table Variables.
DDTDriver Object
If you create data-driven script tests and use Excel files as data storages, the good way is using the DDTDriver object to read data from a file, iterate through its rows, and use obtained values.
The DDTDriver object does not allow writing data to Excel files.
For more information, see Using the DDTDriver Object.
COM Object
There may be a case, when you need to work with ranges of cells or change cell formats in Excel files, you can use the Excel.Application COM object.
For more information, see Working With Excel Files via COM.
See Also
Data-Driven Testing
Data-Driven Testing - Retrieving Input Data From Storage
Working With COM Objects

 Creating and Opening files
Creating and Opening files