 |
Information in this topic applies to desktop applications only. |
Environment variables store information that can be used by different applications in Windows. Some environment variables store Windows system paths, such as the Program Files folder, Windows folder, user profile folder and so on. These paths can be different on different computers and in different versions of Windows. If you need to use system paths in your automated tests, you can evaluate the corresponding environment variables instead of hard-coding the paths.
 |
On 64-bit systems, the WOW64 subsystem may redirect paths to some system directories and libraries when working with 32-bit applications. If you experience problems when using environment variables, use strict values to avoid redirection. |
Getting Environment Variable Values
To get an environment variable value on the current computer, use the aqEnvironment.GetEnvironmentVariable method:
JavaScript, JScript
// Get user profile path
Log.Message(aqEnvironment.GetEnvironmentVariable("USERPROFILE"));
Python
# Get user profile path
Log.Message(aqEnvironment.GetEnvironmentVariable("USERPROFILE"))VBScript
' Get user profile path
Call Log.Message(aqEnvironment.GetEnvironmentVariable("USERPROFILE"))
DelphiScript
// Get user profile path
Log.Message(aqEnvironment.GetEnvironmentVariable('USERPROFILE'));
C++Script, C#Script
// Get user profile path
Log["Message"](aqEnvironment["GetEnvironmentVariable"]("USERPROFILE"));
To get an environment variable value from a remote computer, use the WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable method:
JavaScript, JScript
WMI.ConnectToComputer("computername", "DOMAIN\\User", "password");
Log.Message(WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable("WINDIR"));
Python
WMI.ConnectToComputer("computername", "DOMAIN\\User", "password")
Log.Message(WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable("WINDIR"))VBScript
Call WMI.ConnectToComputer("computername", "DOMAIN\User", "password")
Call Log.Message(WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable("WINDIR"))
DelphiScript
WMI.ConnectToComputer('computername', 'DOMAIN\User', 'password');
Log.Message(WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable("WINDIR"));
C++Script, C#Script
WMI["ConnectToComputer"]("computername", "DOMAIN\\User", "password");
Log["Message"](WMI["GetEnvironmentVariable"]("WINDIR"));
| Note: | WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable returns the local variable if you do not specify the computer to connect to. |
In keyword tests, you can use the aqEnvironment.GetEnvironmentVariable and WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable methods directly in operation parameters using the Code Expression mode:
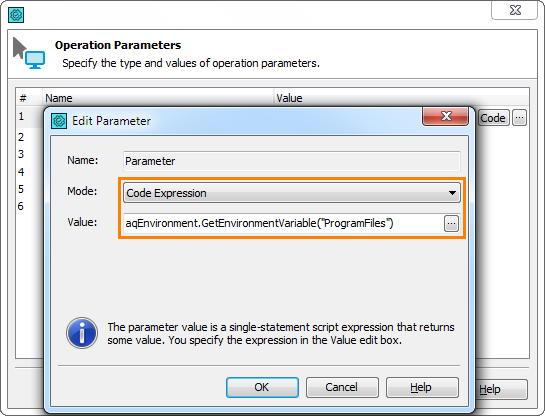
System vs User Variables
Windows has system environment variables and user environment variables. System variables apply to all users on the computer, while user variables are only for the currently logged on user.
If you have a system variable and a user variable with the same name:
-
To get the user variable, use
aqEnvironment.GetEnvironmentVariable. -
To get the system variable, use
WMI.GetEnvironmentVariable.
TestComplete Constants for Environment Variables
TestComplete has built-in constants for some environment variables. Use these constants in your tests instead of getting the corresponding environment variables:
| Environment Variable | Description | TestComplete Constant |
|---|---|---|
COMPUTERNAME |
The computer name. | Sys.HostName |
NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS |
The number of processors installed on the computer. | Sys.CPUCount |
SystemRoot,
WINDIR |
The path to the Windows directory. | Sys.OSInfo.WindowsDirectory |
TEMP, TMP |
The user’s temporary directory. | Sys.OSInfo.TempDirectory |
USERDOMAIN |
The domain of the user account. | Sys.DomainName |
USERNAME |
The user name. | Sys.UserName |
Using Environment Variables in Tested Application Paths
TestComplete lets you use environment variables such as %PROGRAMFILES% to specify where your tested application is installed. For more information, see Using Variables in Tested Application Paths.
See Also
Advanced Tasks
Avoiding Computer-Specific Settings
Running Tests on Multiple Operating Systems
Using Variables in Tested Application Paths

 Getting Environment Variable Values
Getting Environment Variable Values