When calling a DLL routine from TestComplete scripts, you perform a number of preparation actions by calling methods of the DLL program object. You define a DLL type, a routine type, types of routine parameters, load the DLL into memory, etc. (see Calling DLL Functions From Tests - Tutorial for details on this). In this topic we will consider how you can call DLL functions from keyword tests.
The easiest way to call a DLL routine from a keyword test is to create a helper script function that obtains needed parameters to be passed to the DLL routine, performs all needed preparation actions and calls the DLL routine with the specified parameter values and call this script function from the keyword test. Thus, in order to call a DLL routine from your keyword test, you need to perform the following steps:
-
Create a helper script function that defines the types of the needed dynamic library and the routine to be called, data types of routine parameters, loads the DLL into memory and calls the routine. In the parameters of this helper function, you should specify the values you need to pass from your keyword test to the DLL routine to be called. The script function should pass these values to the DLL routine and return the results of the routine to the keyword test.
JavaScript, JScript
function CallDLLRoutine(X, Y, TextToDraw)
{
var Def_DLL1, Def_DLL2, LpStr, Lib1, Lib2, dc;
// Defines the dll types
Def_DLL1 = DLL.DefineDLL("Gdi32");
Def_DLL2 = DLL.DefineDLL("USER32");
// Registering the function types in TestComplete
Def_DLL1.DefineProc("TextOutA",
vt_i4,
vt_i4,
vt_i4,
vt_lpstr,
vt_i4,
vt_i4);
Def_DLL2.DefineProc("GetDC", vt_i4, vt_i4);
Def_DLL2.DefineProc("ReleaseDC", vt_i4, vt_i4, vt_i4);
// Creates an alias for TextOutA
Def_DLL1.DefineAlias("TextOut", "TextOutA");
// Loads the dlls
Lib1 = DLL.Load("Gdi32");
Lib2 = DLL.Load("USER32");
// Creates the string parameter
LpStr = DLL.New("LPSTR", TextToDraw.length);
LpStr.Text = TextToDraw;
// Gets the device context for drawing
dc = Lib2.GetDC(0);
// Calls the TextOutA function from Gdi32.dll
// The function takes the values passed via the script routine parameters
res = Lib1.TextOut(dc, X, Y, LpStr, LpStr.Text.length);
// Releases the device context
Lib2.ReleaseDC(0, dc);
// Returns results of the TextOutA function
return res;
}Python
def CallDLLRoutine(X, Y, TextToDraw): # Defines the dll types Def_DLL1 = DLL.DefineDLL("Gdi32") Def_DLL2 = DLL.DefineDLL("USER32") # Registering the function types in TestComplete Def_DLL1.DefineProc("TextOutA", VT_I4, VT_I4, VT_I4, VT_LPSTR, VT_I4, VT_I4) Def_DLL2.DefineProc("GetDC", VT_I4, VT_I4) Def_DLL2.DefineProc("ReleaseDC", VT_I4, VT_I4, VT_I4) # Creates an alias for TextOutA Def_DLL1.DefineAlias("TextOut", "TextOutA") # Loads the dlls Lib1 = DLL.Load("Gdi32") Lib2 = DLL.Load("USER32") # Creates the string parameter LpStr = DLL.New("LPSTR", TextToDraw.length) LpStr.Text = TextToDraw # Gets the device context for drawing dc = Lib2.GetDC(0) # Calls the TextOutA function from Gdi32.dll # The function takes the values passed via the script routine parameters res = Lib1.TextOut(dc, X, Y, LpStr, LpStr.Text.length) # Releases the device context Lib2.ReleaseDC(0, dc) # Returns results of the TextOutA function return resVBScript
Function CallDLLRoutine(X, Y, TextToDraw)
' Defines the dll types
Set Def_DLL1 = DLL.DefineDLL("Gdi32")
Set Def_DLL2 = DLL.DefineDLL("USER32")
' Registering the function types in TestComplete
Call Def_DLL1.DefineProc("TextOutA", _
vt_i4, _
vt_i4, _
vt_i4, _
vt_lpstr, _
vt_i4, _
vt_i4)
Call Def_DLL2.DefineProc("GetDC", vt_i4, vt_i4)
Call Def_DLL2.DefineProc("ReleaseDC", vt_i4, vt_i4, vt_i4)
' Creates an alias for TextOutA
Call Def_DLL1.DefineAlias("TextOut", "TextOutA")
' Loads the dlls
Set Lib1 = DLL.Load("Gdi32")
Set Lib2 = DLL.Load("USER32")
' Creates a string parameter
Set LpStr = DLL.New("LPSTR", Len(TextToDraw))
LpStr.Text = TextToDraw
' Gets the device context for drawing
dc = Lib2.GetDC(0)
' Calls the TextOutA function from Gdi32.dll
' The function takes the values passed via the script routine parameters
res = Lib1.TextOut(dc, X, Y, LpStr, Len(LpStr.Text))
' Releases the device context
Call Lib2.ReleaseDC(0, dc)
' Returns results of the TextOutA function
CallDLLRoutine = res
End FunctionDelphiScript
function CallDLLRoutine(X, Y, TextToDraw);
var Def_DLL1, Def_DLL2, LpStr, Lib1, Lib2, dc, res;
begin
// Defines the dll types
Def_DLL1 := DLL.DefineDLL('Gdi32');
Def_DLL2 := DLL.DefineDLL('USER32');
// Registering the function types in TestComplete
Def_DLL1.DefineProc('TextOutA',
vt_i4,
vt_i4,
vt_i4,
vt_lpstr,
vt_i4,
vt_i4);
Def_DLL2.DefineProc('GetDC', vt_i4, vt_i4);
Def_DLL2.DefineProc('ReleaseDC', vt_i4, vt_i4, vt_i4);
// Creates an alias for TextOutA
Def_DLL1.DefineAlias('TextOut', 'TextOutA');
// Loads the dlls
Lib1 := DLL.Load('Gdi32');
Lib2 := DLL.Load('USER32');
// Creates a string parameter
LpStr := DLL.New('LPSTR', Length(TextToDraw));
LpStr.Text := TextToDraw;
// Gets the device context for drawing
dc := Lib2.GetDC(0);
// Calls the TextOutA function from Gdi32.dll
// The function takes the values passed via the script routine parameters
res := Lib1.TextOut(dc, X, Y, LpStr, Length(LpStr.Text));
// Releases the device context
Lib2.ReleaseDC(0, dc);
// Returns results of the TextOutA function
result := res;
end;C++Script, C#Script
function CallDLLRoutine(X, Y, TextToDraw)
{
var Def_DLL1, Def_DLL2, LpStr, Lib1, Lib2, dc;
// Defines the dll types
Def_DLL1 = DLL["DefineDLL"]("Gdi32");
Def_DLL2 = DLL["DefineDLL"]("USER32");
// Registering the function types in TestComplete
Def_DLL1["DefineProc"]("TextOutA",
vt_i4,
vt_i4,
vt_i4,
vt_lpstr,
vt_i4,
vt_i4);
Def_DLL2["DefineProc"]("GetDC", vt_i4, vt_i4);
Def_DLL2["DefineProc"]("ReleaseDC", vt_i4, vt_i4, vt_i4);
// Creates an alias for TextOutA
Def_DLL1["DefineAlias"]("TextOut", "TextOutA");
// Loads the dlls
Lib1 = DLL["Load"]("Gdi32");
Lib2 = DLL["Load"]("USER32");
// Creates a string parameter
LpStr = DLL["New"]("LPSTR", TextToDraw["length"]);
LpStr["Text"] = TextToDraw;
// Gets the device context for drawing
dc = Lib2["GetDC"](0);
// Calls the TextOutA function from Gdi32.dll
// The function takes the values passed via the script routine parameters
res = Lib1["TextOut"](dc, X, Y, LpStr, LpStr["Text"]["length"]);
// Releases the device context
Lib2["ReleaseDC"](0, dc);
// Returns results of the TextOutA function
return res;
}Note: If the DLL routine you are going to call gets some complex parameters like structures, you need to create appropriate variables in the helper script routine and initialize their members by the values passed via the script routine parameters. For more information, see Using Custom Data Structures in DLL Function Calls. For more instructions on calling DLL routines from scripts, see Calling DLL Functions From Tests - Tutorial.
-
Add the Run Script Routine operation to your keyword test and specify the created helper script routine in its parameters to call the routine from the test.
-
In the Run Script Routine operation’s parameters, specify values you need to pass via the helper script routine’s parameters:
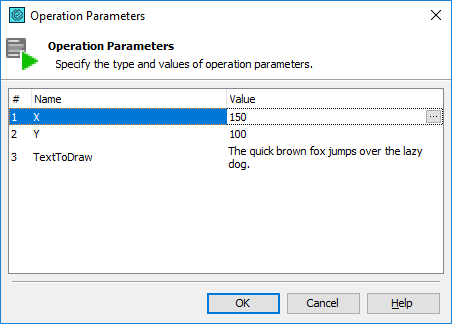
The helper script function gets these parameters and then passes them to the called DLL routine.
-
The result of the DLL function call is returned by the helper script function. To obtain the result in your keyword test, you can insert the Set Variable Value keyword test operation after the Run Script Routine operation and assign the result of the Run Script Routine operation (that is, the last operation result) to some variable. This can be a keyword test variable, a project or project suite variable. Then you can use the value of this variable in your test. For instance, you can post it to the test log:
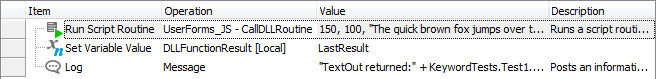
Although the approach described above requires scripting, it allows calling DLL routines from keyword tests and using the returned values in tests.
See Also
Calling DLL Functions From Tests
Calling DLL Functions From Tests - Overview
Calling DLL Functions From Tests - Tutorial
