About
Windows includes a built-in firewall controlling data transfers between your computer and other computers over the network or Internet. The firewall lets users specify trusted programs that are allowed to transfer information between the local computer and certain remote computers, while blocking requests that come from other programs and computers.
If you are using a Floating User license, TestComplete uses TCP and UDP protocols and port 1947 to communicate with the License Manager PC (the computer where your license is activated). These protocols and this port must not be blocked, otherwise, TestComplete will not be able to access the License Manager PC and exchange the licensing data.
TestComplete and TestComplete Service also exchange data with computers during distributed testing, so you need to allow these programs through the firewall to run distributed tests.
See below for detailed instructions on allowing TestComplete, its licensing systems and TestComplete Service through Windows Firewall.
Notes
-
For the Floating User license, configure the firewall settings both on your License Manager PC and on your TestComplete workstation.
-
For distributed testing, configure the firewall settings on all the computers that participate in distributed testing and where Windows Firewall runs.
-
 You may be unable to change some of the firewall settings if your computer is connected to a domain and the settings are controlled by your system administrator. In this case, ask your system administrator to allow TestComplete and its utilities through the firewall.
You may be unable to change some of the firewall settings if your computer is connected to a domain and the settings are controlled by your system administrator. In this case, ask your system administrator to allow TestComplete and its utilities through the firewall.
Checking if Firewall Is Running
To find out whether Windows Firewall is running:
-
In your Windows operating system, open Control Panel by clicking Start and then clicking Control Panel.
-
In the search box, type Firewall and then select the Windows Firewall applet. The Windows Firewall window will open.
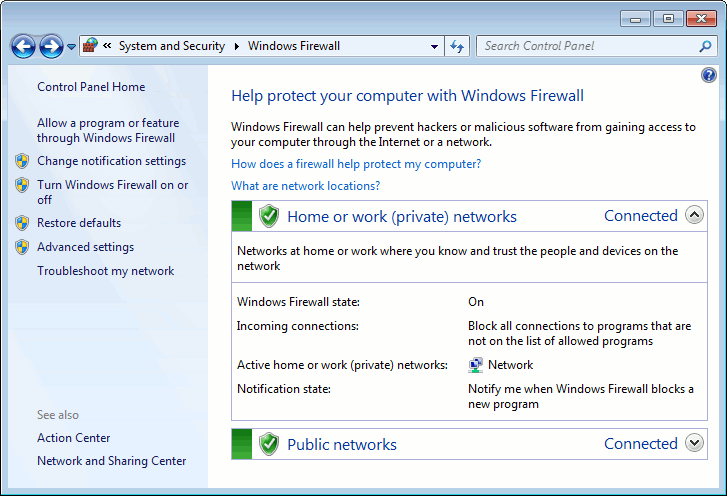
If a green check mark is displayed next to the network location that includes your License Manager PC (if you use the Floating User license) or the computers participating in distributed testing, it means that Windows Firewall is running and controlling data transfers. In this case, configure your Firewall to allow TestComplete network activities (see below).
If there is no green check mark, Windows Firewall is disabled and it does not block any network requests. In this case, there is no need to change the firewall settings.
Configuring Firewall Settings
If Windows Firewall is on for network locations where your License Manager PC is located, make sure that TCP and UDP traffic through port 1947 is allowed:
-
In the left part of the Windows Firewall window, click Advanced settings.
-
In the resulting Windows Firewall and Advanced Security window, select Inbound Rules and then click New Rule.
-
In the resulting wizard, click Port and then click Next.
-
Click TCP. Then click Specific local ports and enter 1947. Click Next.
-
Click Allow the connection and then click Next.
-
Select the needed scope and click Next.
-
Enter a name for the rule and click Finish.
Repeat the steps for the UPD protocol. Then repeat the steps to create outbound rules that will allow TCP and UDP traffic through port 1947.
If Windows Firewall is on for a network location that includes your distributed testing workstations, add TestComplete and its utilities to the firewall’s list of exceptions:
-
On the left of the Windows Firewall window, click Allow a program through Windows Firewall. The Allowed Programs panel will appear.
-
Locate SmartBear TestComplete 14 in the list of programs and tick the check box for each network location where you need TestComplete to have access through the firewall.
If TestComplete is not in the list:
-
Click the Add another program button. The Add a Program dialog will open.
-
Select TestComplete 14 in the Programs list.
If it is not in the list, click Browse and browse for the TestComplete executable -- TestComplete.exe.
-
Click the Network location types button and check the network locations for which you want to allow TestComplete activities.
-
Click Add to close the dialog and add TestComplete to the firewall’s list of exceptions.
-
-
Repeat previous step to add TestComplete Service’s executable -- TestCompleteService14.exe (<TestComplete>\Bin\TestCompleteService14.exe) to the firewall’s list of exceptions.
-
Press OK to close the Allowed Programs panel.
Also, you need to create firewall rules that will open ports used by TestComplete and TestComplete Service to exchange data with projects participating in distributed testing.
The ports used by TestComplete and TestComplete Service are specified by the TCP ports for remote connections option. By default, ports 6095 - 6097 are used.
-
On the left of the Windows Firewall window, click Advanced settings. The Windows Firewall with Advanced Settings window will open.
-
In the tree on the left of the window, click Inbound Rules.
-
Create a new rule:
-
In the Actions panel of the window, click New Rule. The New Inbound Rule Wizard will appear.
-
On the Rule Type page of the wizard, select Port. Click Next.
-
On the Protocol and Ports page of the wizard, select Port. In the Specific local ports edit box specify the port number. Click Next.
-
On the Action page of the wizard, select Allow the connection and click Next.
-
On the Profile page of the wizard, select the network location for which you want to open a port and click Next.
-
On the Name page of the wizard, in the Name field, specify the rule name and press Finish.
-
-
In the tree on the left of the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security window, select Outbound Rules.
-
Repeat step 3 to open the same port for outbound connections.
-
Repeat steps 1-4 to open other ports.
Once you are done, close the Windows Firewall window.
TestComplete 32-bit executable is located in the <TestComplete>\Bin folder.
TestComplete 64-bit executable is located in the <TestComplete>\x64\Bin folder.
See Also
Configuring Your System
TestComplete and Antiviruses
Distributed Testing - Basic Concepts
