Your application may behave differently depending on the version of the device’s operating system. For example, different iOS versions may have different user interfaces, and so do applications for these iOS versions. Mobile applications can also have functions that are only supported since a specific iOS or Android version. To handle this in your tests, you can check the version of the device’s operating system and run tests created for this version.
To check the mobile OS version, use the following properties of the Device object:
-
OSInfo.VersionRelease- Android version -
OSInfo.ProductVersion- iOS version
Both of them return the OS version as a string, for example "6.0" or "11.0".
Checking the OS Version in Keyword Tests
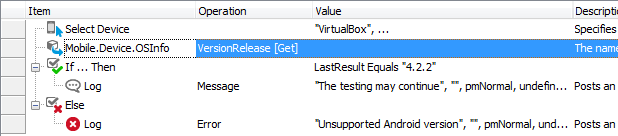
In keyword tests, use the Call Object Method operation to get the Android or iOS version. To configure this operation:
-
Add the Call Object Method operation to your keyword test. TestComplete will display the Operation Parameters wizard.
-
Enter one of the following as the object name:
-
Aliases.device.OSInfo- if you use Name Mapping, -
Mobile.Device.OSInfo- if you do not use Name Mapping, -
Mobile.Device("DeviceName").OSInfo- if you do not use Name Mapping and the device is not the current one.
Click Next.
-
-
Select one of the following properties:
-
The
VersionReleaseproperty for Android devices, -
The
ProductVersionproperty for iOS devices.
-
-
Press Finish.
Right after the Call Object Method operation, add an operation that will use the OS version. For example, the Log Message operation that will post the Last Operation Result value to the test log, or the Set Variable Value operation that will save the value to a variable for later use.
Checking the OS Version in Scripts
You may often need to learn the version of the device’s operating system to decide which tests to run next. For example (pseudocode):
if Android version > 6.0 then
do something
else
do something else
The device’s OSInfo.VersionRelease and OSInfo.ProductVersion properties return the version number as a string in the format major.minor.build.revision. You should parse version strings into numbers to work with them using comparison operators.
To learn only the major version, you can take the first character of the version string, convert it to a number and check it against the specified condition (for example, if it is greater than 5). The following example checks if an iOS device is running iOS 12:
JavaScript, JScript
function getiOSVersion()
{
Mobile.SetCurrent("John Smith's iPad");
// Get the iOS major version as a number
var version = Mobile.Device().OSInfo.ProductVersion;
var verMajor = parseInt(version);
if (verMajor = 12)
Log.Message("iOS 12");
else if (verMajor = 10)
Log.Message("iOS 11");
else
Log.Message("iOS 10");
}
Python
def getiOSVersion():
Mobile.SetCurrent("John Smith's iPad");
# Get the iOS major version as a number
version = Mobile.Device().OSInfo.ProductVersion;
verMajor = int(float(version));
if (verMajor >= 12):
Log.Message("iOS 12")
elif (verMajor == 11):
Log.Message("iOS 11")
else:
Log.Message("iOS 10");VBScript
Sub getiOSVersion
Dim version, verMajor
Call Mobile.SetCurrent("John Smith's iPad")
' Get the iOS major version as a number
version = Mobile.Device.OSInfo.ProductVersion
verMajor = CInt(Left(version, 2))
If verMajor = 12 Then
Call Log.Message("iOS 12")
ElseIf verMajor = 11 Then
Call Log.Message("iOS 11")
Else
Call Log.Message("iOS 10")
End If
End Sub
DelphiScript
procedure getiOSVersion;
var version, verMajor;
begin
Mobile.SetCurrent('John Smith''s iPad');
// Get the iOS major version as a number
version := Mobile.Device.OSInfo.ProductVersion;
verMajor := aqConvert.StrToInt(aqString.SubString(version, 0, 2));
case verMajor of
12: Log.Message('iOS 12');
11: Log.Message('iOS 11');
else Log.Message('iOS 10');
end;
end;
C++Script, C#Script
function getiOSVersion()
{
Mobile["SetCurrent"]("John Smith's iPad");
// Get the iOS major version as a number
var version = Mobile["Device"]()["OSInfo"]["ProductVersion"];
var verMajor = parseInt(version);
if (verMajor = 12)
Log["Message"]("iOS 12");
else if (verMajor = 11)
Log["Message"]("iOS 11");
else
Log["Message"]("iOS 10");
}
| Note: | You can run this script from keyword tests using the Run Code Snippet operation. |
If you need to learn the minor or build version number, you can use the .NET Version class that has version parsing and comparison methods. The example below checks whether the Android version is equal to or greater than 6.0:
JavaScript, JScript
function getAndroidVersion()
{
Mobile.SetCurrent("MyDevice");
var ver = Mobile.Device().OSInfo.VersionRelease;
if (GreaterOrEqual(ver, "6.0"))
Log.Message("Android version is 6.0 or later.")
else
Log.Message("Android version is earlier than 6.0.")
}
// Uses the .NET Version class to compare two version strings.
// Returns True if the first version string is greater than or equal to the second version.
// Otherwise, it returns False.
function GreaterOrEqual(VersionStr1, VersionStr2)
{
var clsVersion = dotNET.System.Version;
var ver1 = clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr1);
var ver2 = clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr2);
return clsVersion.op_GreaterThanOrEqual(ver1, ver2);
}
Python
def getAndroidVersion():
Mobile.SetCurrent("MyDevice");
ver = Mobile.Device().OSInfo.VersionRelease;
if (GreaterOrEqual(ver, "6.0")):
Log.Message("Android version is 6.0 or later.")
else:
Log.Message("Android version is earlier than 6.0.")
# Uses the .NET Version class to compare two version strings.
# Returns True if the first version string is greater than or equal to the second version.
# Otherwise, it returns False.
def GreaterOrEqual(VersionStr1, VersionStr2):
clsVersion = dotNET.System.Version;
ver1 = clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr1);
ver2 = clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr2);
return clsVersion.op_GreaterThanOrEqual(ver1, ver2);VBScript
Sub getAndroidVersion
Dim ver
Mobile.SetCurrent("MyDevice")
ver = Mobile.Device.OSInfo.VersionRelease
If GreaterOrEqual(ver, "6.0") Then
Log.Message("Android version is 6.0 or later.")
Else
Log.Message("Android version is earlier than 6.0.")
End If
End Sub
' Uses the .NET Version class to compare two version strings.
' Returns True if the first version string is greater than or equal to the second version.
' Otherwise, it returns False.
Function GreaterOrEqual(VersionStr1, VersionStr2)
Dim clsVersion, ver1, ver2
Set clsVersion = dotNET.System.Version
Set ver1 = clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr1)
Set ver2 = clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr2)
GreaterOrEqual = clsVersion.op_GreaterThanOrEqual(ver1, ver2)
End Function
DelphiScript
// Uses the .NET Version class to compare two version strings.
// Returns True if the first version string is greater than or equal to the second version.
// Otherwise, it returns False.
function GreaterOrEqual(VersionStr1, VersionStr2);
var clsVersion, ver1, ver2;
begin
clsVersion := dotNET.System.Version;
ver1 := clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr1);
ver2 := clsVersion.zctor_4(VersionStr2);
Result := clsVersion.op_GreaterThanOrEqual(ver1, ver2);
end;
procedure getAndroidVersion;
var ver;
begin
Mobile.SetCurrent('MyDevice');
ver := Mobile.Device.OSInfo.VersionRelease;
if GreaterOrEqual(ver, '6.0') then
Log.Message('Android version is 6.0 or later.')
else
Log.Message('Android version is earlier than 6.0.');
end;
C++Script, C#Script
function getAndroidVersion()
{
Mobile["SetCurrent"]("MyDevice");
var ver = Mobile["Device"].OSInfo["VersionRelease"];
if (GreaterOrEqual(ver, "6.0"))
Log["Message"]("Android version is 6.0 or later.")
else
Log["Message"]("Android version is earlier than 6.0")
}
// Uses the .NET Version class to compare two version strings.
// Returns True if the first version string is greater than or equal to the second version
// Otherwise, it returns False.
function GreaterOrEqual(VersionStr1, VersionStr2)
{
var clsVersion = dotNET["System"].Version;
var ver1 = clsVersion["zctor_4"](VersionStr1);
var ver2 = clsVersion["zctor_4"](VersionStr2);
return clsVersion["op_GreaterThanOrEqual"](ver1, ver2);
}
| Note: | You can run this script from keyword tests using the Run Script Routine operation. |

 Checking the OS Version in Keyword Tests
Checking the OS Version in Keyword Tests