The basic gestures supported by Android devices include (but not limited by) the following touch actions: Touch, Long press, Swipe, Drag, Double touch, Pinch open and Pinch close. (See Android Developer Guide: Gestures.)
This topic explains how to simulate actions over the Android device screen.
Basic Concepts
To access your mobile devices (real or virtual) from tests, you use the Device object. For the object, TestComplete provides a number of methods you can use to simulate various actions over your device:
-
Touch actions - Every object in Android applications can be touched (or “clicked”). You can perform a touch action at specific screen coordinates by calling the
Touchmethod. -
Long Press Actions - Long press actions enable the data selection mode. TestComplete provides a
TouchAndHoldmethod you can use to long press at specific screen coordinates. -
Swipe Actions - Swipe actions are used to scroll through the content or navigate between screens, windows and views. To perform a swipe action, you can call the
Swipemethod. -
Drag Actions - Drag actions are used to move items within containers. To perform a drag action, you can use the
Dragmethod. -
Other Touch Actions - The Double touch, Pinch close and Pinch open actions, as well as any other types of touch actions, can be recorded and simulated as gestures. For detailed information on recording gestures, see Recording Gestures (Multi-Touch Events).
Simulating Touch Actions in Keyword Tests
To simulate a touch at specific screen coordinates from keyword tests, use the Device Touch operation:
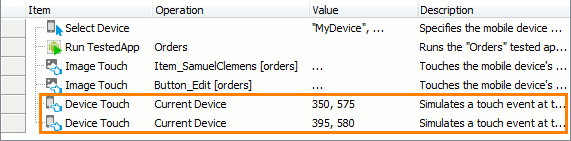
To simulate long press, swipe and drag actions in keyword tests, call the appropriate methods of the Device object by using the Call Object Method, Run Code Snippet or Run Script Routine operations.
| Note: | These operations are asynchronous. This means that TestComplete does not pause the test when they are executed. For more information, see Possible Issues. |
Simulating Touch Actions in Scripts
To touch at specific screen coordinates from scripts, use the Device.Touch method.
JavaScript, JScript
Mobile.Device().Touch(25, 70);
Python
Mobile.Device().Touch(25, 70);
VBScript
Call Mobile.Device.Touch(25, 70)
DelphiScript
Mobile.Device.Touch(25, 70);
C++Script, C#Script
Mobile["Device"]["Touch"](25, 70);
To perform a long press at specific screen coordinates for the specified period of time, use the Device.TouchAndHold method.
JavaScript, JScript
Mobile.Device().TouchAndHold(250, 270, 2500);
Python
Mobile.Device().TouchAndHold(250, 270, 2500);
VBScript
Call Mobile.Device.TouchAndHold(250, 270, 2500)
DelphiScript
Mobile.Device.TouchAndHold(250, 270, 2500);
C++Script, C#Script
Mobile["Device"]["TouchAndHold"](250, 270, 2500);
Use the Device.Swipe scripting method to simulate swipe actions from your scripts.
JavaScript, JScript
Mobile.Device().Swipe(650, 100, 600, 500, 10, 50);
Python
Mobile.Device().Swipe(650, 100, 600, 500, 10, 50);
VBScript
Call Mobile.Device.Swipe(650, 100, 600, 500, 10, 50)
DelphiScript
Mobile.Device.Swipe(650, 100, 600, 500, 10, 50);
C++Script, C#Script
Mobile["Device"]["Swipe"](650, 100, 600, 500, 10, 50);
Use the Device.Drag scripting method to simulate dragging in your scripts.
JavaScript, JScript
Mobile.Device().Drag(50, 70, 300, 150, 500);
Python
Mobile.Device().Drag(50, 70, 300, 150, 500);
VBScript
Call Mobile.Device.Drag(50, 70, 300, 150, 500)
DelphiScript
Mobile.Device.Drag(50, 70, 300, 150, 500);
C++Script, C#Script
Mobile["Device"]["Drag"](50, 70, 300, 150, 500);
| Note: | These methods are asynchronous. This means that TestComplete does not pause the test when they are executed. For more information, see Possible Issues. |
Simulating Custom Actions
In your tests, you may need to simulate arbitrary actions that cannot be performed with any of the methods and operations described above. For example, you may need to "draw" a custom shape on the device’s screen with a fingertip.
You can simulate custom actions using the following TestComplete scripting methods:
Using these methods, you can create custom actions or simulate standard actions, such as Drag, Touch, Long Press and others.
Below are some script examples that demonstrate how to use these methods to simulate Android actions. If you want to simulate these actions from keyword tests, use the Run Code Snippet operation or create several Call Object Method operations that invoke the needed methods one after another.
-
Example 1
To simulate a custom drag action, call the
Device.TouchPressandDevice.TouchReleasemethods one after another. Emulate thePressevent at the current position of the item to be dragged, and then call theReleaseevent at the destination coordinates.JavaScript, JScript
Mobile.Device().TouchPress(50, 70);
Mobile.Device().TouchRelease(300, 150);Python
Mobile.Device().TouchPress(50, 70);
Mobile.Device().TouchRelease(300, 150);VBScript
Call Mobile.Device.TouchPress(50, 70)
Call Mobile.Device.TouchRelease(300, 150)DelphiScript
Mobile.Device.TouchPress(50, 70);
Mobile.Device.TouchRelease(300, 150);C++Script, C#Script
Mobile["Device"]["TouchPress"](50, 70);
Mobile["Device"]["TouchRelease"](300, 150);Note that the X and Y parameters of the
TouchPressandTouchReleasemethods are dissimilar. -
Example 2
To simulate custom long press actions, call the
Device.TouchPress,DelayandDevice.TouchReleasescripting methods one after another.JavaScript, JScript
Mobile.Device().TouchPress(250, 270);
Delay(200);
Mobile.Device().TouchRelease(250, 270);Python
Mobile.Device().TouchPress(250, 270);
Delay(200);
Mobile.Device().TouchRelease(250, 270);VBScript
Call Mobile.Device.TouchPress(250, 270)
Call Delay(200)
Call Mobile.Device.TouchRelease(250, 270)DelphiScript
Mobile.Device.TouchPress(250, 270);
Delay(200);
Mobile.Device.TouchRelease(250, 270);C++Script, C#Script
Mobile["Device"]["TouchPress"](250, 270);
Delay(200);
Mobile["Device"]["TouchRelease"](250, 270);Note that the
TouchPress()andTouchRelease()methods should have the same values of the X and Y parameters. -
Example 3
To simulate custom shape actions, call
Device.TouchPress, severalDevice.Movemethods and thenDevice.TouchRelease.JavaScript, JScript
Mobile.Device().TouchPress(250, 270);
Mobile.Device().Move(270, 270);
Mobile.Device().Move(290, 290);
Mobile.Device().Move(240, 240);
Mobile.Device().TouchRelease(240, 240);Python
Mobile.Device().TouchPress(250, 270);
Mobile.Device().Move(270, 270);
Mobile.Device().Move(290, 290);
Mobile.Device().Move(240, 240);
Mobile.Device().TouchRelease(240, 240);VBScript
Call Mobile.Device.TouchPress(250, 270)
Call Mobile.Device.Move(270, 270)
Call Mobile.Device.Move(290, 290)
Call Mobile.Device.Move(240, 240)
Call Mobile.Device.TouchRelease(240, 240)DelphiScript
Mobile.Device.TouchPress(250, 270);
Mobile.Device.Move(270, 270);
Mobile.Device.Move(290, 290);
Mobile.Device.Move(240, 240);
Mobile.Device.TouchRelease(240, 240);C++Script, C#Script
Mobile["Device"]["TouchPress"](250, 270);
Mobile["Device"]["Move"](270, 270);
Mobile["Device"]["Move"](290, 290);
Mobile["Device"]["Move"](240, 240);
Mobile["Device"]["TouchRelease"](240, 240);
See Also
Simulating User Actions Over Android Devices
Simulating Text Input on Android Devices
Simulating Basic Touch Actions Over Android Open Applications
Simulating Basic User Actions in Image-Based Tests

 Basic Concepts
Basic Concepts