There can be different error messages during the test run. You may need to check the error type to handle errors in the desired manner. For example, you may want not to stop test run on some errors and stop them on others. To see which error occurred, check the text of the error message. This topic contains detailed description of how you can do this.
-
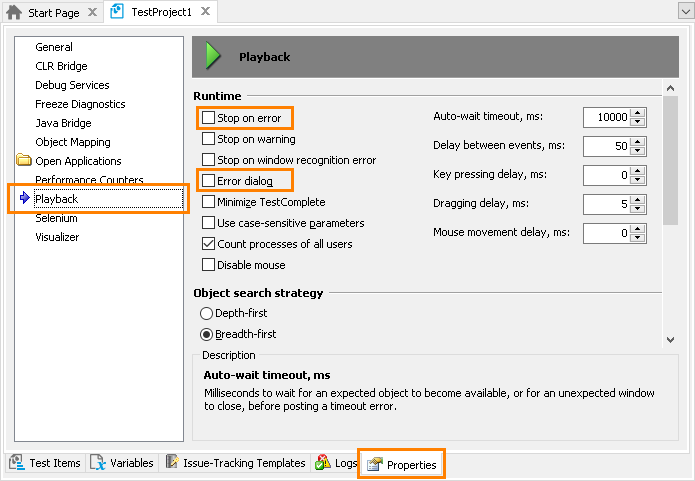
Open the project properties and select Playback on the list on the left of the page. Disable the Stop on error and Error dialog options. Otherwise, TestComplete stops the entire test run right after the first error or exception occurs.
-
Create an event handler for the OnLogError event. See Creating Event Handlers for TestComplete Events.
This event occurs every time TestComplete posts an error message to the test log. The event handler receives the
LogParamsobject as a parameter. You can use itsMessageTextproperty of thisLogParamsobject to get the text of the error message that is being posted to the log. Once you get the text, you can determine what error occurred. -
In the event handler, create test commands that will get the error message text and perform the desired actions. For instance, you may stop the test. To do this, you can use the
Runner.Stopscript method that stops either the current test item, or the entire test run depending on the parameters.The following code snippet checks the text of the error message and performs specific actions depending on the result of the check:
JavaScript
function GeneralEvents_OnLogError(Sender, LogParams)
{
if (equal(LogParams.MessageText, "Object not found"))
{
// It is an expected error.
// Perform actions that handle this error in the special way
}
else
{
// If another error occurs,
// Stop the current test item.
Runner.Stop(true);
}
}JScript
function GeneralEvents_OnLogError(Sender, LogParams)
{
if (LogParams.MessageText == "Object not found")
{
// It is an expected error.
// Perform actions that handle this error in the special way
}
else
{
// If another error occurs,
// Stop the current test item.
Runner.Stop(true);
}
}Python
def GeneralEvents_OnLogError(Sender, LogParams): if (LogParams.MessageText == "Object not found") : #It is an expected error. # Perform actions that handle this error in the special way ... else: # If another error occurs, # Stop the current test item. Runner.Stop(True)VBScript
Sub GeneralEvents_OnLogError(Sender, LogParams)
If (LogParams.MessageText = "Object not found") then
' It is an expected error.
' Perform actions that handle this error in the special way
else
' If another error occurs,
' Stop the current test item.
Runner.Stop(true)
End If
End SubDelphiScript
procedure GeneralEvents_OnLogError(Sender; LogParams);
begin
if (LogParams.MessageText = 'Object not found') then
begin
// It is an expected error.
// Perform actions that handle this error in the special way
end
else
begin
// If another error occurs,
// Stop the current test item.
Runner.Stop(true);
end;
end;C++Script, C#Script
function GeneralEvents_OnLogError(Sender, LogParams)
{
if (LogParams["MessageText"] == "Object not found")
{
// It is an expected error.
// Perform actions that handle this error in the special way
}
else
{
// If another error occurs,
// Stop the current test item.
Runner["Stop"](true);
}
}Note that you can perform similar actions in a handling keyword test by using keyword test operations. For instance, you can simply run the above script code from your event handling keyword test by using the Run Script Routine operation.
-
Change the Stop on Error properties of the project suite’s and project’s test items to customize the further behavior of the test engine. To learn more about it, see Stopping Tests on Errors and Exceptions - Overview.
See Also
Controlling Test Execution Flow
Stopping Tests on Errors and Exceptions - Overview
OnLogError Event
Runner.Stop Method
Stop Execution Operation
