This topic describes the possible entries for outgoing WS-Security messages.
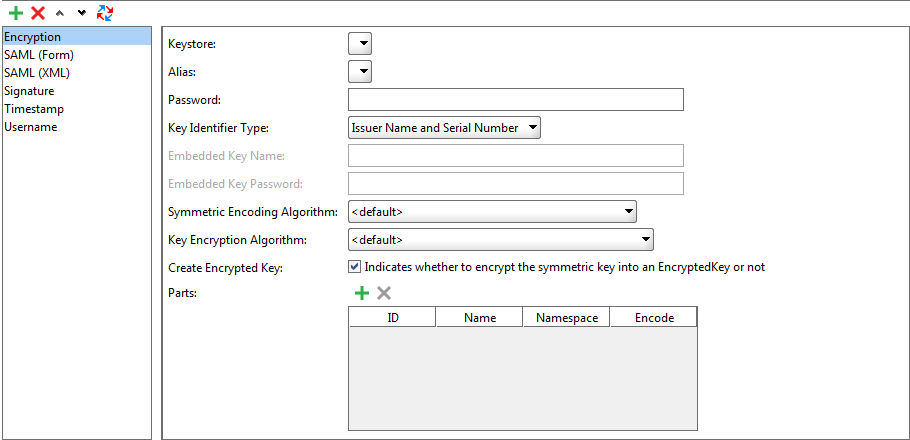
Encryption Entries
You use encryption entries to encrypt a message content before request sending.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Keystore |
The keystore to use when encrypting the message. Must be specified on the keystore tab. |
| Alias |
The alias to use when encrypting the message. |
| Password |
The password used along with this alias. |
| Key Identifier Type |
The type of the key to use. |
| Embedded Key Name |
The name of the Embedded KeyInfo key identifier. |
| Embedded Key Password |
The password of the Embedded KeyInfo key identifier. |
| Symmetric Encryption Algorithms / Key Encryption Algorithm |
The encryption algorithm to use. |
| Create Encrypted Key |
If selected, the message will contain an encrypted key. |
| Parts |
A table containing the parts of the message to encrypt. You can specify an element by its ID, name, or namespace. |
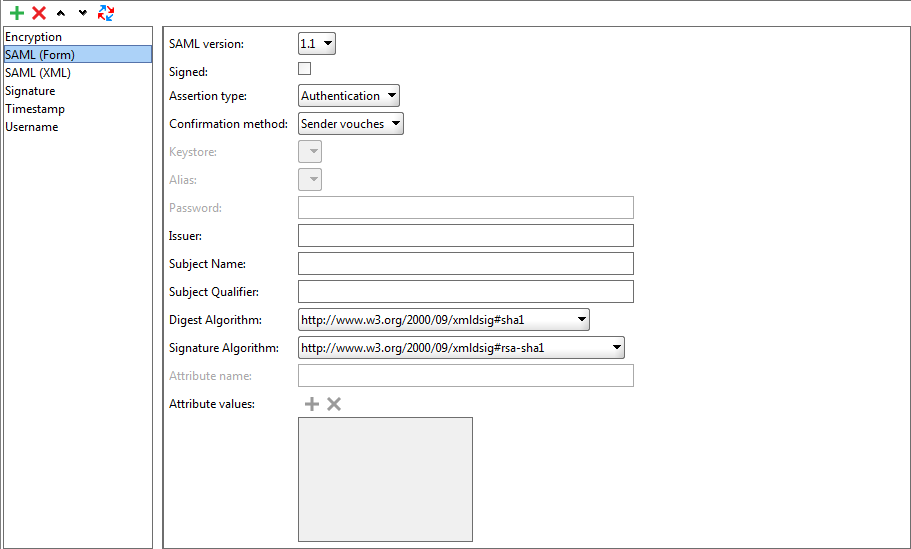
SAML (Form) Entries
You use SAML (Form) entries to configure the Security Assertion Markup Language in an outgoing request.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| SAML version |
The SAML version. |
| Signed |
If selected, the assertion will be signed by using a keystore. |
| Assertion type |
The type of the assertion. |
| Keystore |
The keystore used to sign the assertion. |
| Password |
The password used by the keystore. |
| Issuer |
The name of the assertion issuer. |
| Subject name |
The subject tested by the assertion. |
| Subject Qualifier |
The conditions checked by the assertion. |
| Digest Algorithm / Signature Algorithm |
The algorithms used to verify the conditions. |
| Attribute name |
The name of the attribute to be checked by the assertion. Available only for Attribute assertions. |
| Attribute values |
A list of values that should belong to the attribute specified above. |
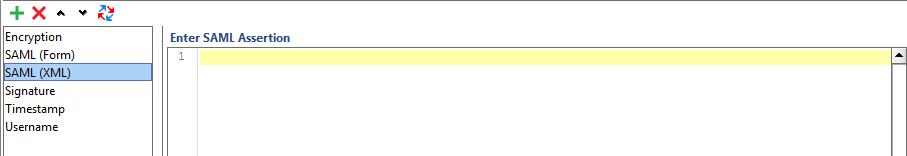
SAML (XML) Entries
You can use a SAML (XML) entry to add a SAML assertion that you cannot generate by using a SAML (Form) entry or to enter an assertion yourself. You enter a SAML assertion directly. The assertion will be validated, and then applied to the WSS header. You can enter both SAML 1 and SAML 2 assertions.
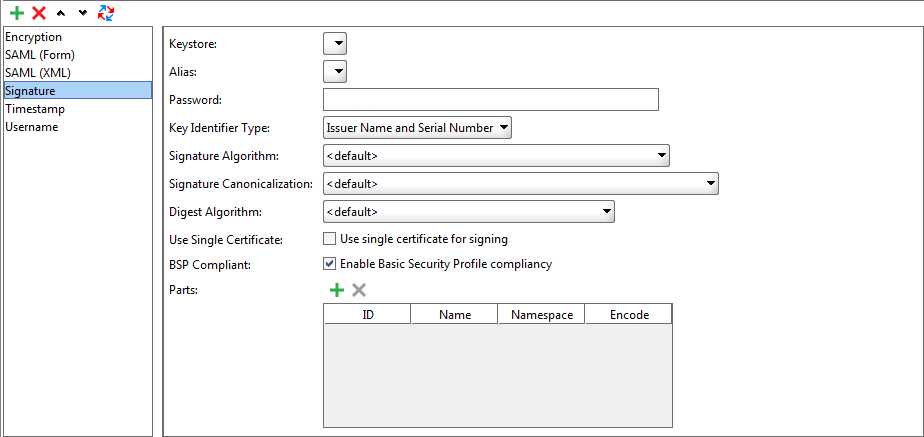
Signature Entries
You use signature entries to sign requests.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Keystore |
The keystore to use when signing the message. |
| Alias |
The alias to use when signing the message. |
| Password |
The password used along with the alias. |
| Key Identifier Type |
The type of the key to use. |
| Signature Algorithm |
The XML message signature algorithm. |
| Signature Canonicalization |
The set of rules to use for XML signature formatting. |
| Digest Algorithm |
The set of rules used to create a message hash code. This code can be used to verify message integrity. |
| Use Single Certificate |
If selected, the signature will use a single certificate. |
| Parts |
A table containing the parts of the message to encrypt. You can specify an element by its ID, name, or namespace. |
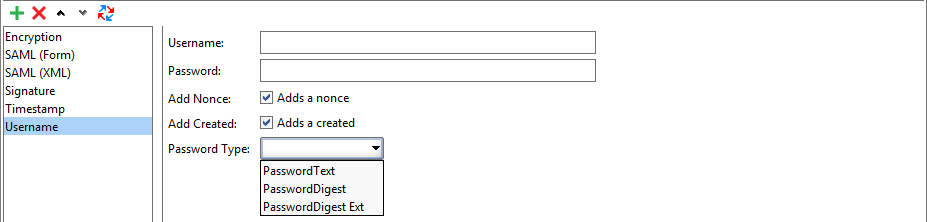
Username Entries
You use username entries to add a UsernameToken item to a message. This token is most commonly used to pass the caller credentials.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Username |
The user’s login. |
| Password |
The user’s password used along with the specified login. |
| Add Nonce |
If selected, the message includes a random value to prevent an attacker from replaying the request. |
| Add Created |
If selected, a timestamp is added to the message. |
| Password Type |
Specifies how the password should be serialized. |
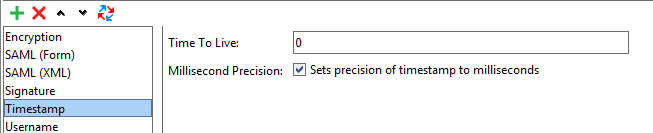
Timestamp Entries
You use timestamp entries to add the Timestamp header to the message. This header specifies the time frame during which the message is valid.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Time to Live |
Indicates how long the message is valid, in seconds. |
| Millisecond Precision |
Select to specify the Time to Live value in milliseconds. |