The easiest way to run ReadyAPI tests from Azure DevOps is to use the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps task. This topic describes how to do that.
Alternatively, you can run ReadyAPI tests by using command-line runners. See Command-Line Runners Specifics for details.
Also, you can run ReadyAPI tests in TestEngine. To learn about it, see Run ReadyAPI Tests in TestEngine from Azure DevOps.
Supported Azure DevOps versions
You can use the SoapUI Functional Testing extension with the following versions of Azure DevOps:
-
Azure DevOps Services (formerly Visual Studio Team Services)
-
Azure DevOps Server 2019
-
Team Foundation Server 2018
-
Team Foundation Server 2017
-
Team Foundation Server 2015 Update 4
There is no much difference between configuring Azure DevOps pipelines and Team Foundation Server build definitions. In this topic, we will show you how to configure only Azure DevOps pipeline.
Requirements for Azure DevOps agents
-
 Use self-hosted agents to run ReadyAPI tests. Running tests on Microsoft-hosted agents is not supported. (To learn more about agents, see the Build and Release Agents article in the MSDN Library.)
Use self-hosted agents to run ReadyAPI tests. Running tests on Microsoft-hosted agents is not supported. (To learn more about agents, see the Build and Release Agents article in the MSDN Library.) -
The agent must have activated Pro license to run ReadyAPI tests.
You can use either a Fixed or Floating license. We recommend that you use the Floating license: activate the license on some server in your network and configure the ReadyAPI instances on agents to consume a license from that server.
If you run an agent as a service and use a Fixed license, make sure you run the service as the user who activated the SoapUI license. To learn how to do it, see below.
Tip: You can use a trial license to try ReadyAPI out. To learn how to get it, see Online Activation of a Trial License Without ReadyAPI. For detailed information on how to install ReadyAPI, see Install Information. To learn how to activate ReadyAPI licenses, see License Activation.
-
The agent must have access to your team project and be registered in your agent pool. See Deploy an agent on Windows in Azure documentation.
Note: You cannot use the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps extension on agents deployed on Linux or macOS. To run ReadyAPI tests on such agents, use command-line runners.
-
In addition, if you are going to export test logs, make sure your build agent has access to the folder to which the logs will be exported.
1. Prepare ReadyAPI project
-
Make your ReadyAPI project available to the agents.
Typically, you store your project in a source control system (like Git or Team Foundation Version Control) and then configure your build to get the project from source control and place it to the needed folder on the computer where tests will run.
As an alternative, you can place your project in a shared network folder. Make sure your agent has access to that folder.
-
In addition, if your project uses external files as data sources for your tests (see Data Sources and Data-Driven Testing), make sure your build agent has access to these files.
2. Install SoapUI Pro Functional Testing extension
-
Go to the Visual Studio Marketplace.
Tip: You can open the marketplace directly from Azure DevOps by selecting Browse Marketplace in the top right corner: 
-
Search for the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps extension.
-
The way you install the extension depends on the Azure DevOps version you use:
3. Configure build definition
To run ReadyAPI tests from Azure DevOps, perform the following steps:
 3.1. Create a build definition
3.1. Create a build definition
 3.2. Configure pipeline to run tests
3.2. Configure pipeline to run tests
 3.3. (Optional) Get the test results
3.3. (Optional) Get the test results
3.1. Create a build definition
-
Open your Azure DevOps project’s web portal and navigate to the Pipeline hub.
-
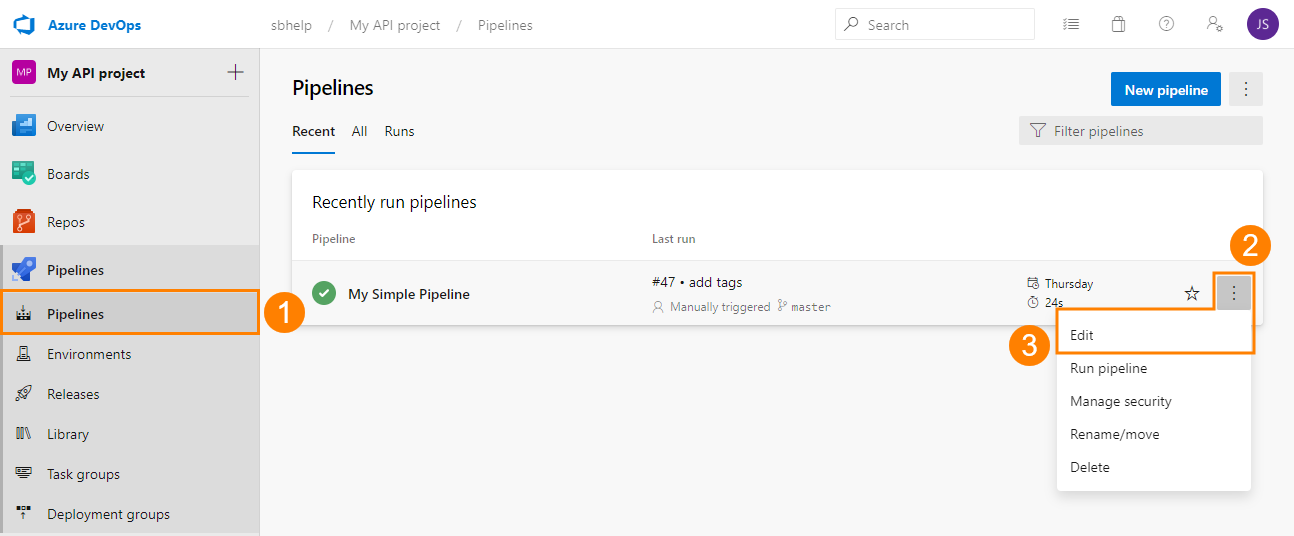
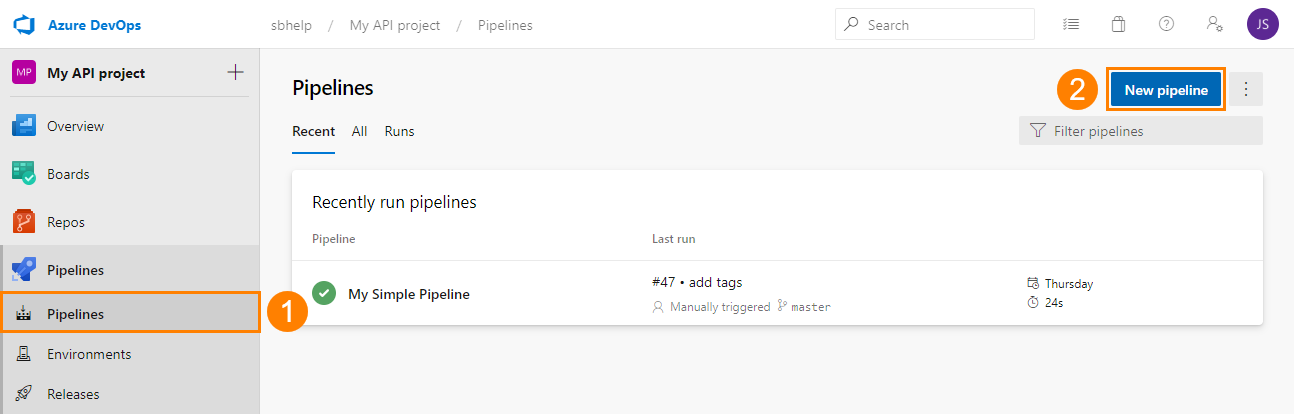
Open an existing pipeline:
– or –
Create a new one:
-
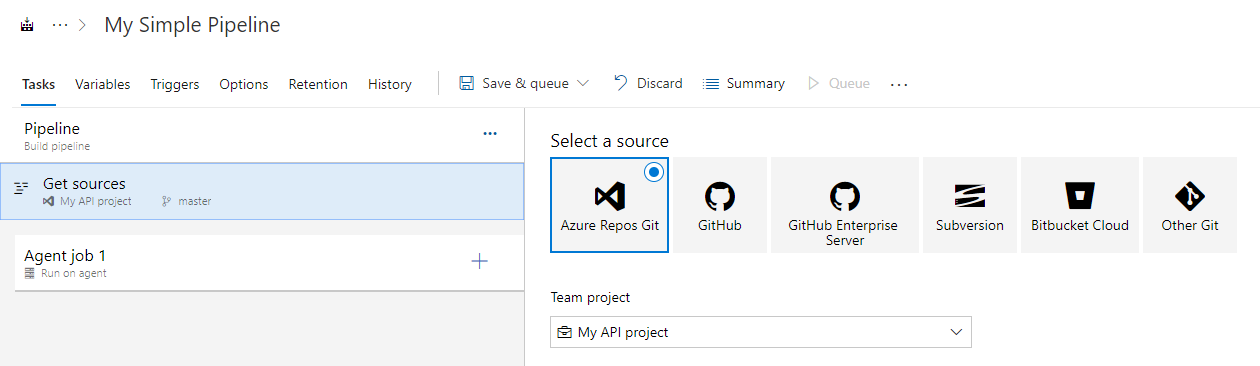
If your ReadyAPI project is stored in a source control system, configure your build definition to copy it to the folder to which an agent has access:
3.2. Configure pipeline to run tests
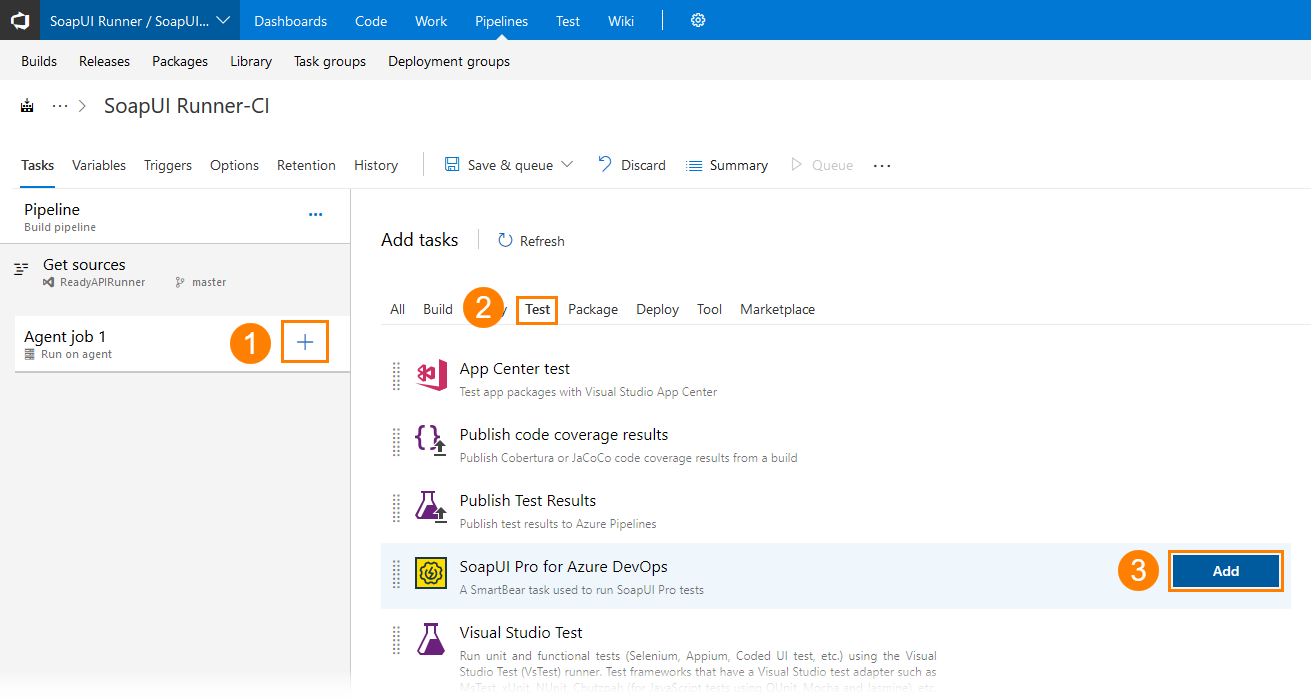
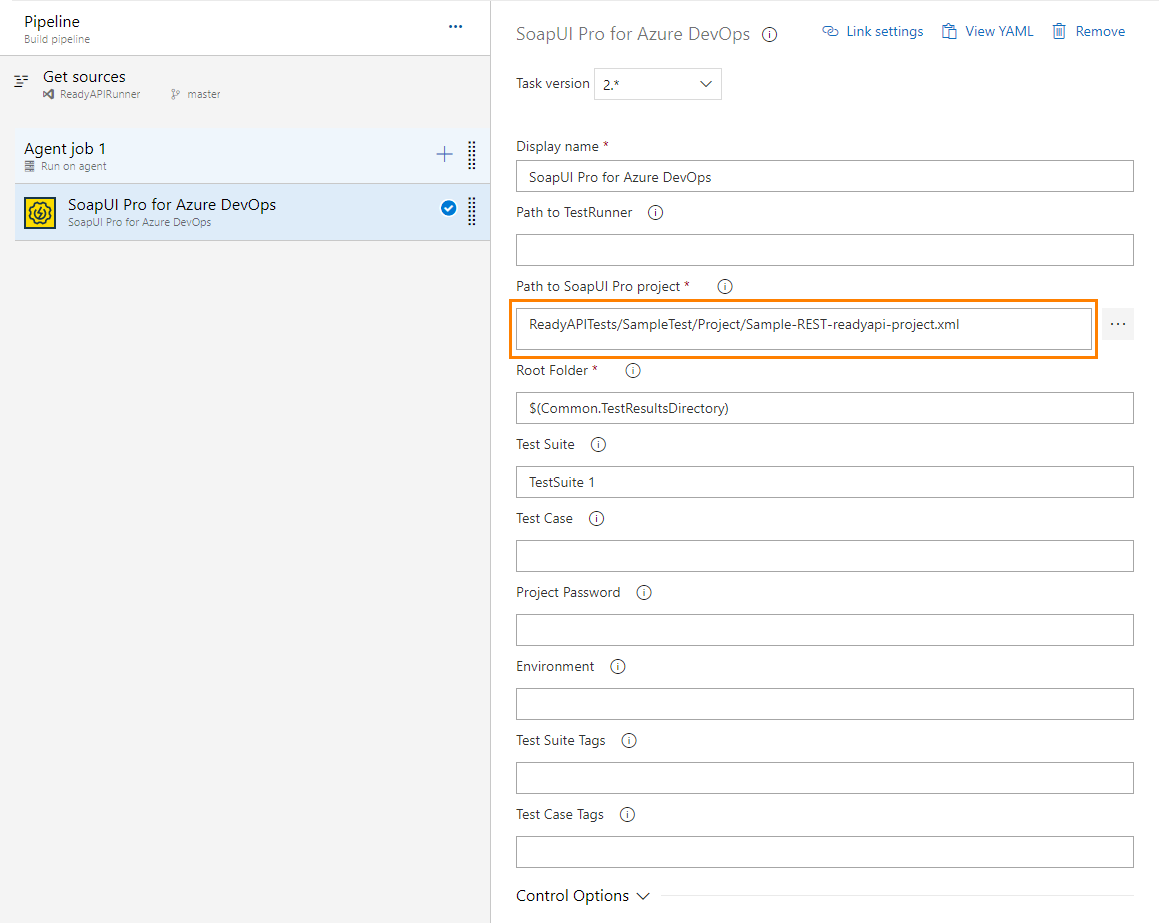
To run ReadyAPI tests, use the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps task. It allows you to easily configure your pipeline to run SoapUI tests.
Alternatively, you can run ReadyAPI tests by using command-line runners. In this case, you must add one of the built-in tasks and specify command-line arguments. To learn more, see Command-Line Runners Specifics.
Add the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps task and specify its parameters:
| Tip: |
By default, Azure DevOps adds version 2 of the extension. If you want to use version 1, select it from the Version drop-down list. |
| Option | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Path to SoapUI Pro Project | Required. The path to your ReadyAPI project.
Note: Specify a dot ( |
||
| Path to TestRunner | Fully-qualified path to the particular version of TestRunner. Leave the field blank to use the recent version of ReadyAPI installed on an agent. | ||
| Root Folder | Required. Fully-qualified path to the directory on the agent where ReadyAPI will store test reports. The default value is $(Common.TestResultsDirectory). |
||
| Test Suite | A test suite to run. To run all the test suites in the project, leave the field blank. | ||
| Test Case | A test case to run. Leave the field blank to run all the test cases of the specified test suite, or, if you have not specified a test suite, all the test cases of your project. | ||
| Password | The encryption password. It is required if your project is encrypted. | ||
| Environment | The environment configuration that the task will use for the test run. See Environments. | ||
| Test Suite Tags | The tags of the test suites you want to run.
|
||
| Test Case Tags | The tags of the test cases you want to run.
|
3.3. (Optional) Get the test results
 Skip this step if you use the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps extension version 2.0. This version of the extension publishes test results automatically.
Skip this step if you use the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps extension version 2.0. This version of the extension publishes test results automatically.
After the test run is over, the SoapUI Pro for Azure DevOps extension exports the test results in a JUnit-style format, so you can publish the test results to your team project.
| Note: | If you use command-line runners, the way you export test results depends on the arguments you pass to the runner. If you export test results in a format different from a JUnit-style report, you can use the Copy Files or Publish Artifacts task to fetch the exported files and place them in the desired folder (for example, in your build’s drop folder). |
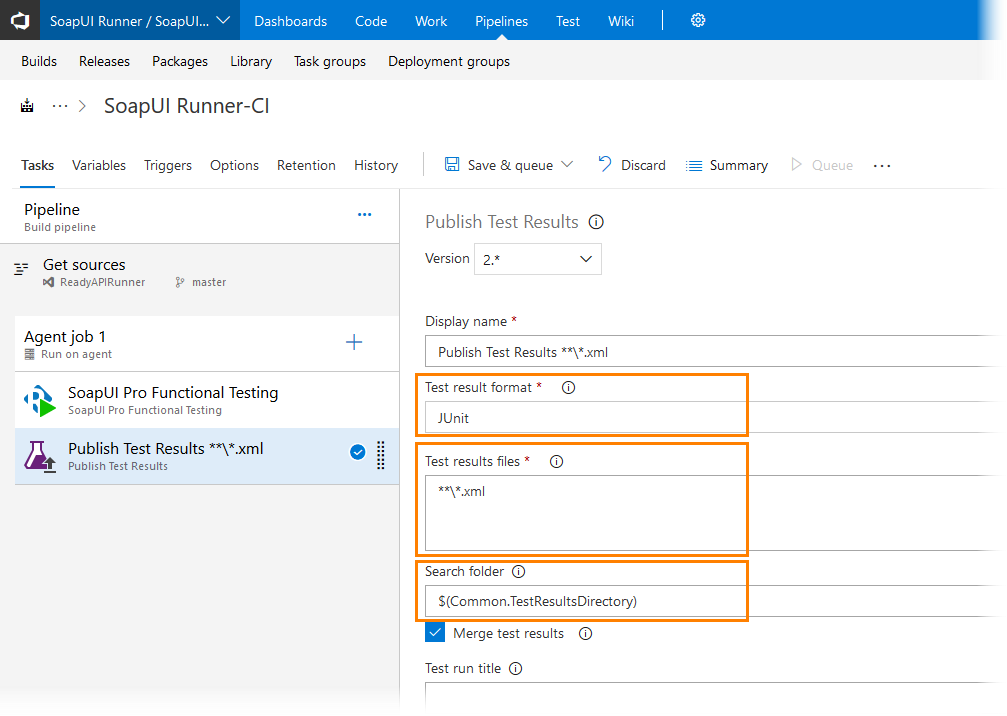
To publish test results to your team project:
-
Add the Publish Test Results task to your pipeline.
-
In the Test result format drop-down list, select JUnit.
-
In the Test results files text box, specify the
**\*.xmlminimatch pattern to search for the exported JUnit-style report files. -
In the Search Folder text box, specify the folder in which your ReadyAPI test results are stored.
-
To merge several reports into a single test result, select the Merge test results check box.
-
In the Test run title text box, enter the name of the test run that will be assigned to the test results. This name will be used in the test run statistics (you can view it in the Test hub).
3.4. (Optional) Select agents to run
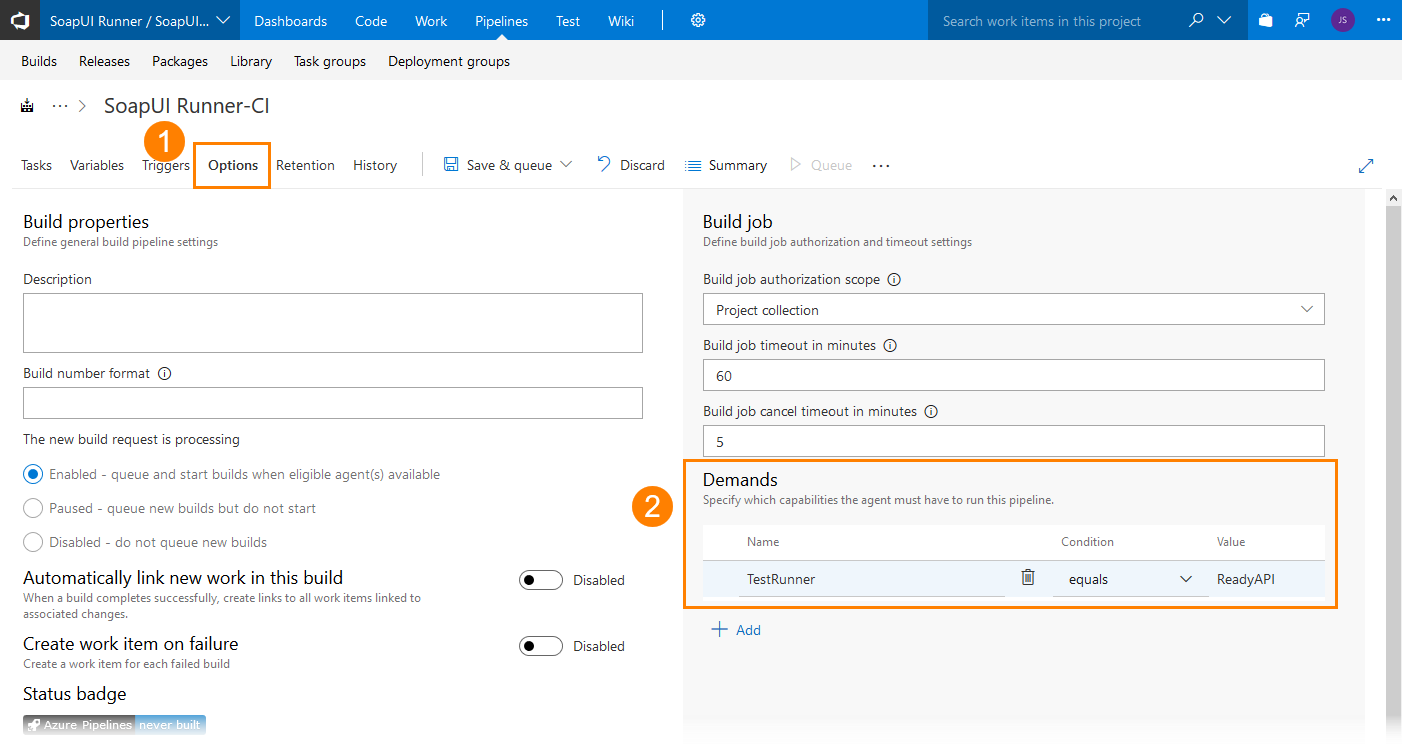
If you have multiple Azure DevOps agents, you can configure your pipeline to run ReadyAPI tests only on those agents that have ReadyAPI installed. To do this, for the needed agents, register custom capabilities that will specify that the agents have ReadyAPI installed, and then specify demands for your pipelines to run only on the needed agents:
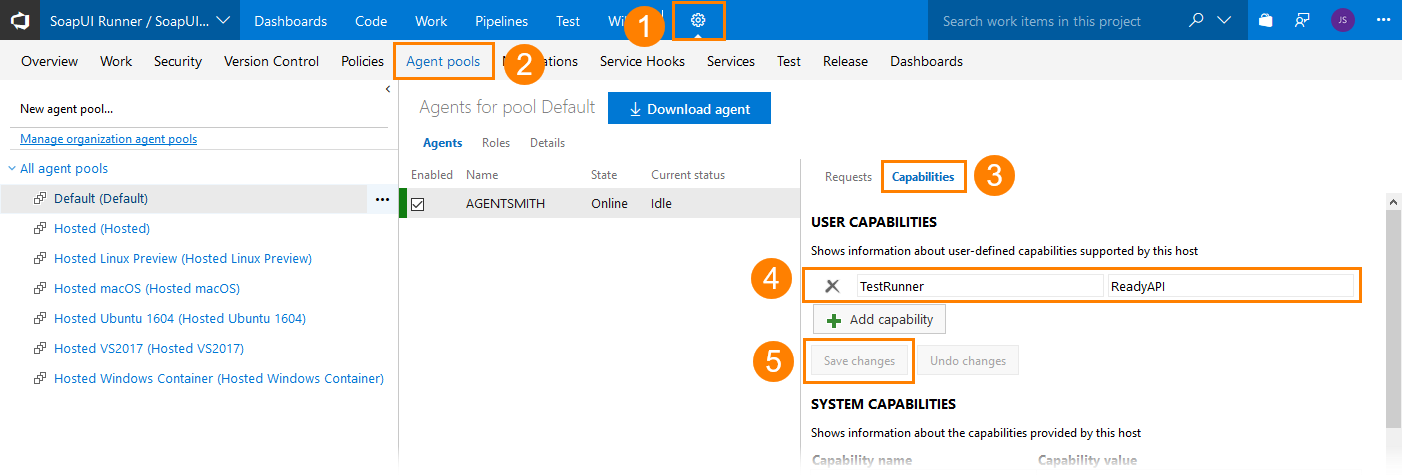
1. Define custom capacities for your agents
-
Open your Azure DevOps project’s web portal. Navigate to the Agents Pool page (you must have an appropriate permission to access the page and manage agent queues):
For Azure DevOps Services:
 https://<Your_VSO_Account_Name>.visualstudio.com/_admin/_AgentPool
https://<Your_VSO_Account_Name>.visualstudio.com/_admin/_AgentPoolFor On-Premises Azure DevOps Server:
 https://<Your_Server_Name>/tfs/<Collection_Name>/_admin/_AgentPool
https://<Your_Server_Name>/tfs/<Collection_Name>/_admin/_AgentPool -
Select the queue to which your agent belongs and then select the needed agent.
-
Switch to the Capabilities page.
-
Click
 Add Capability and create a custom capability that will specify whether ReadyAPI is installed on the agent:
Add Capability and create a custom capability that will specify whether ReadyAPI is installed on the agent: -
Click Save Changes to apply the changes.
2. Specify build and release demands
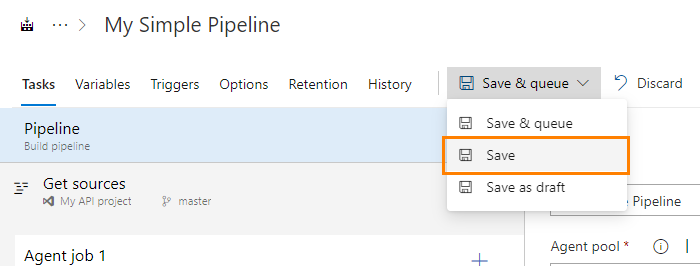
3.5. Save build definition
4. Run build and view test result
To run the build:
-
Select it on the Builds page of the Pipelines hub and then click
 Queue.
Queue.
– or –
-
Click
 Queue on the Edit Build Definition page.
Queue on the Edit Build Definition page.
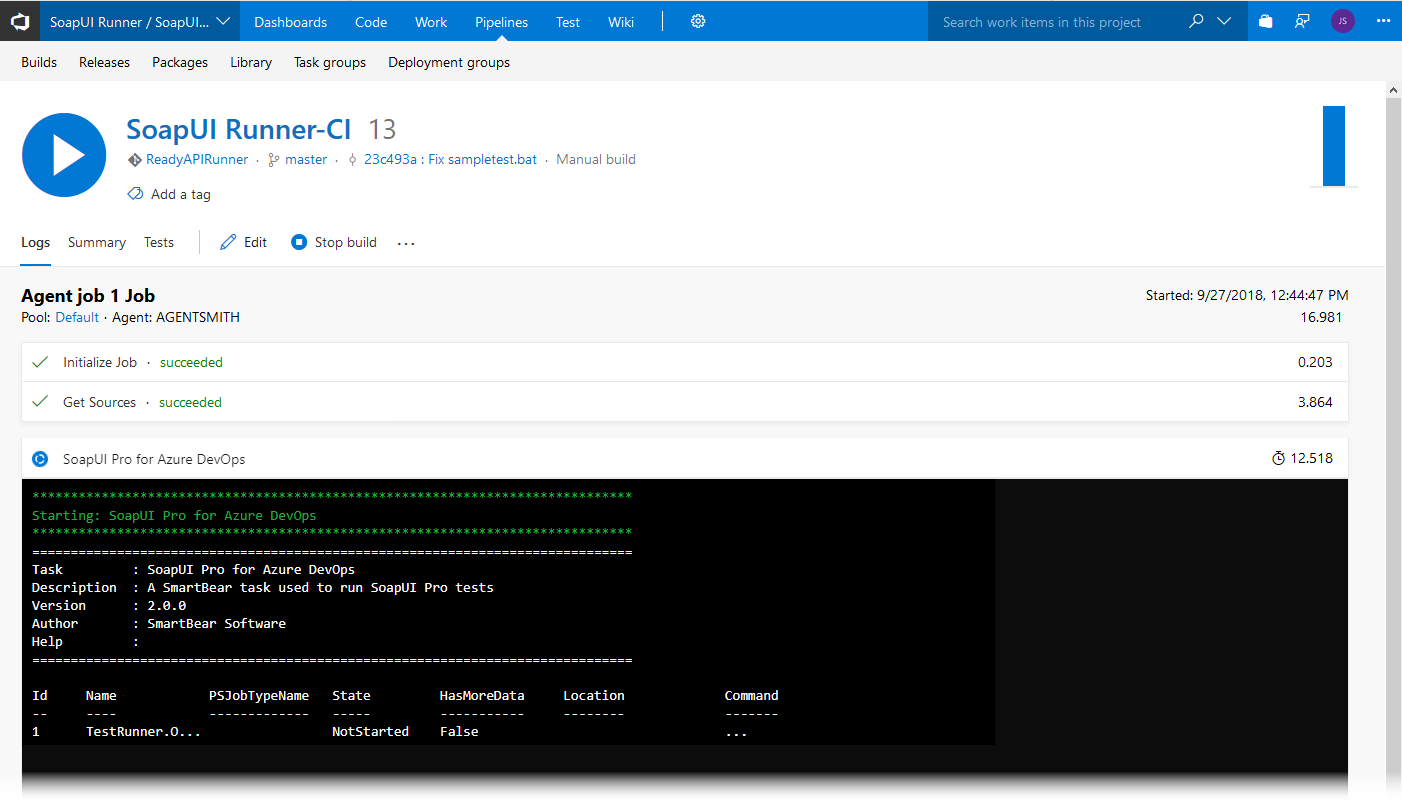
Switch to the Build page to view the build progress:
The build will run the task that executes your ReadyAPI tests. It will also fetch and publish the test results if configured.
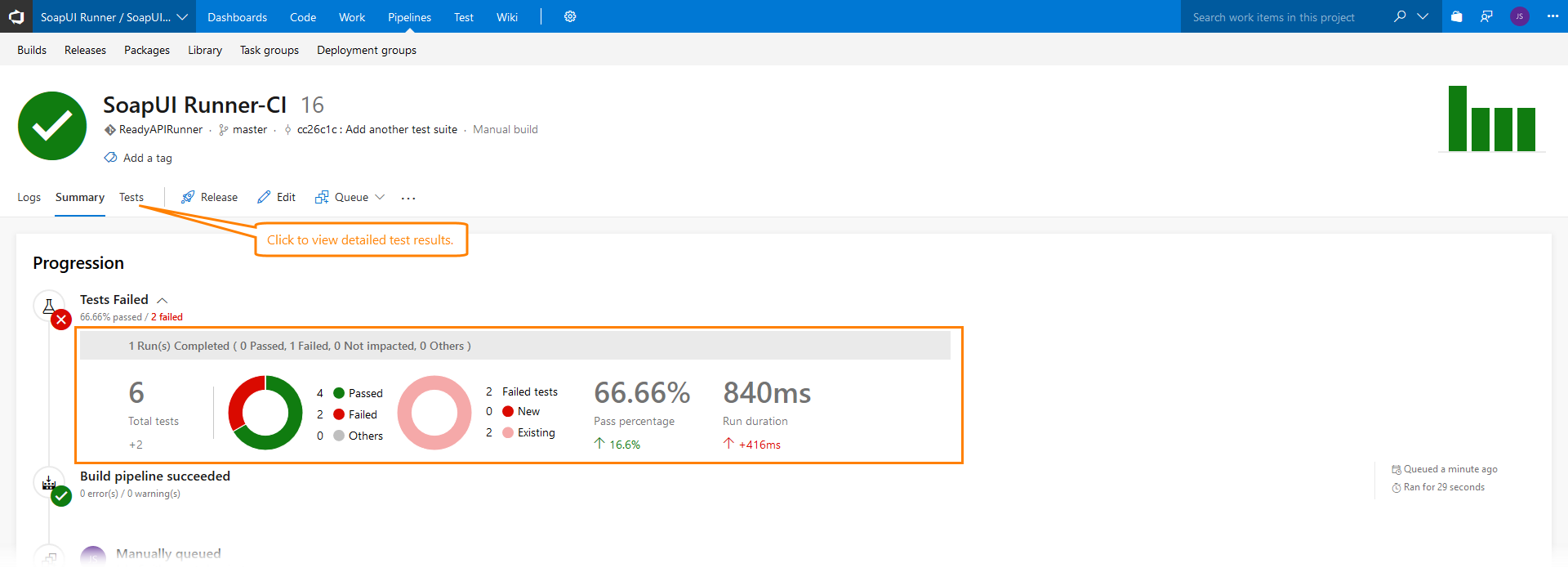
After the build is over, you can view the test results. On the Summary page of the build report, view the Test Results section. It shows the number of failed and passed tests:
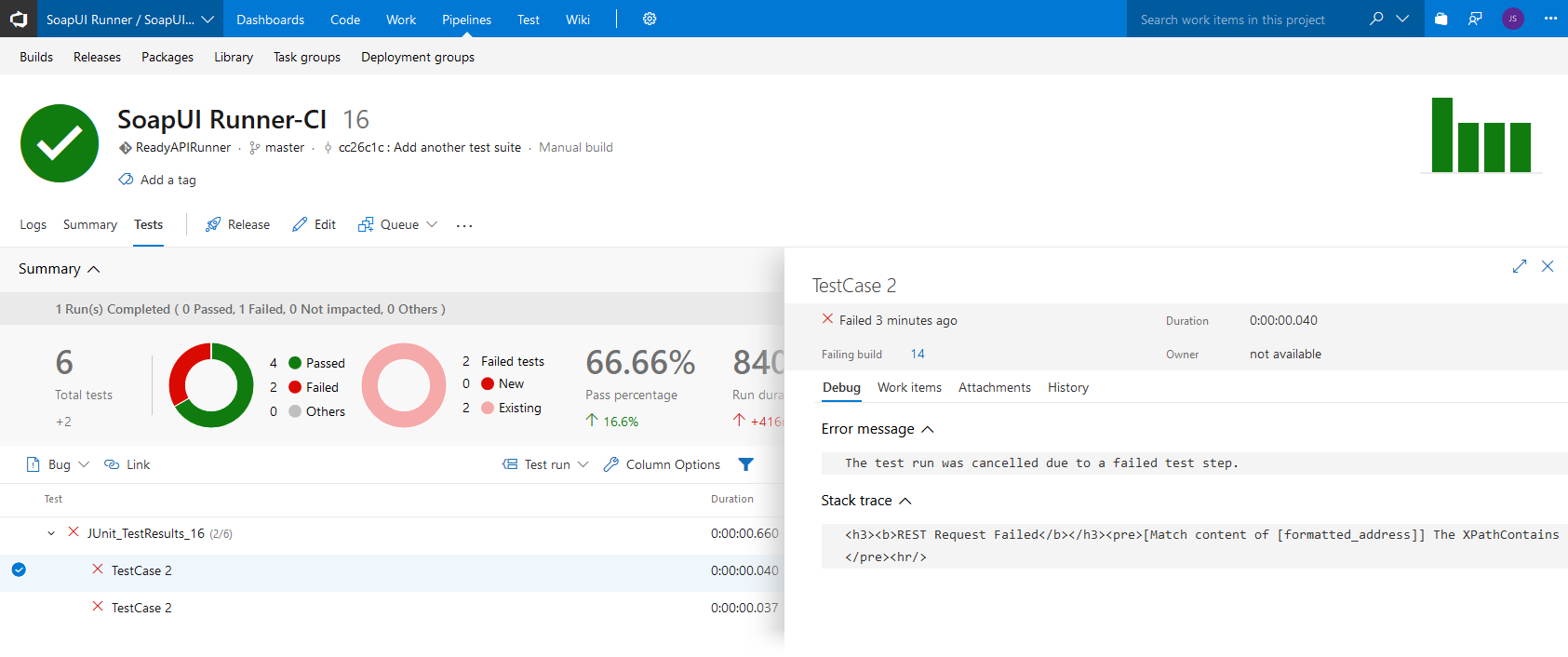
Click Detailed report or switch to the Tests page to view detailed test results:
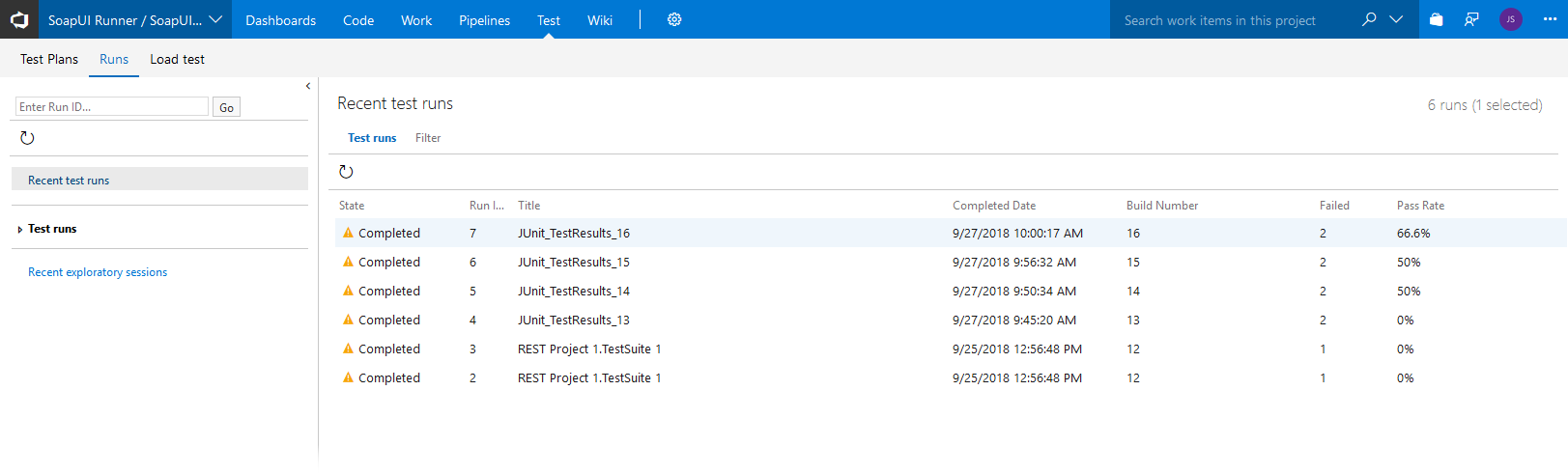
On the Test hub, you can view the test run statistics for your team project:
Click a test run to view detailed information.
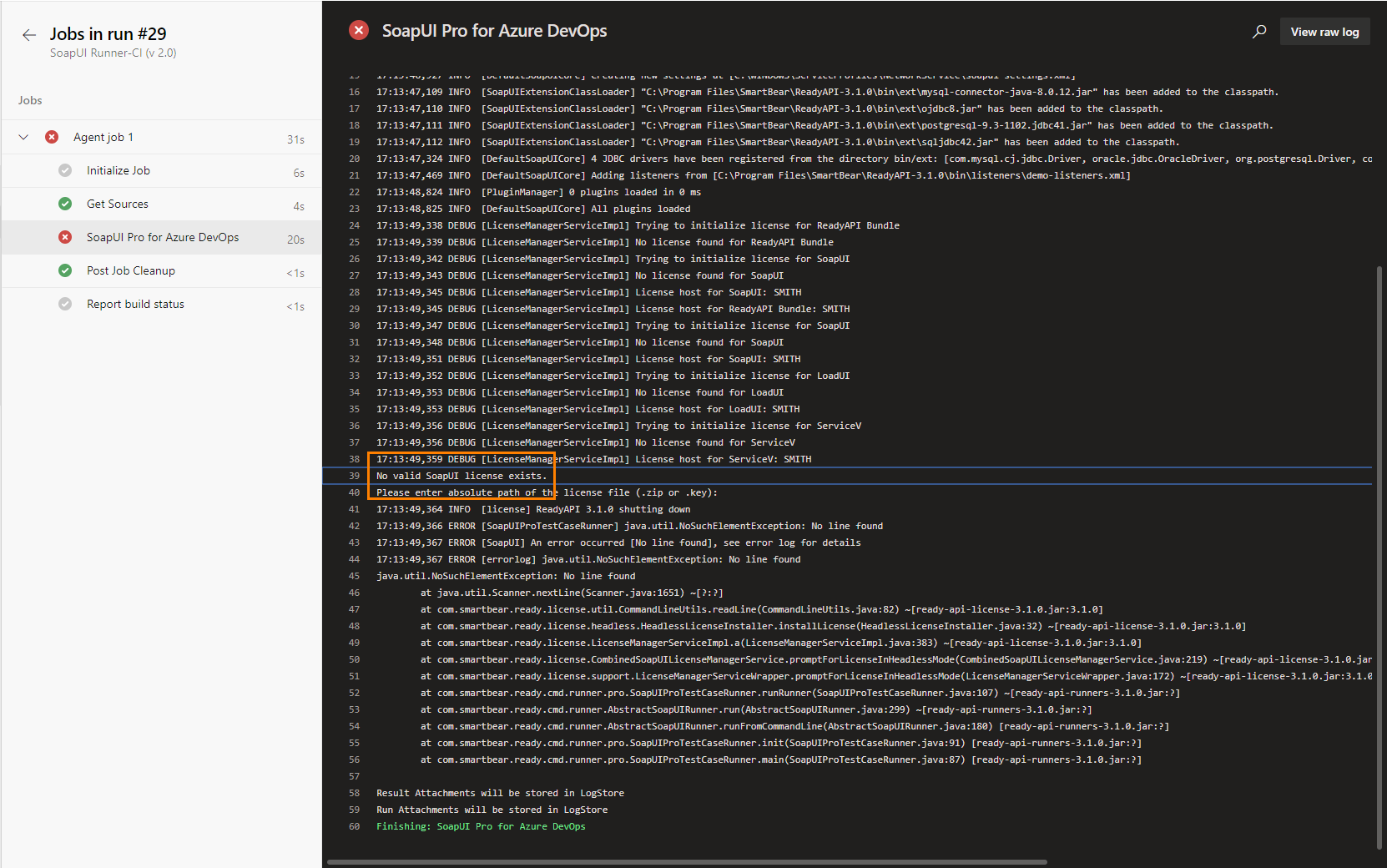
Possible issues
When you configure an Azure agent to run as a service, you need to run the service as the same user who activated the SoapUI license. Otherwise, ReadyAPI will not be able to find it:
You can do it both when configuring an agent and when the agent service is already created:
Specify a user while configuring an agent
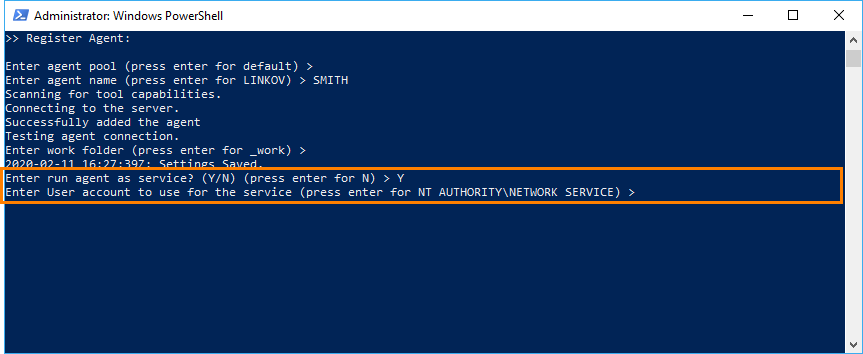
When you create an agent, you need to configure it by using the utility shipped with the agent binaries. See the Microsoft documentation. You can specify the needed user during this process. To do this:
-
After you specify that you are going to run the agent as a service, the utility asks you which user account you want to use:
-
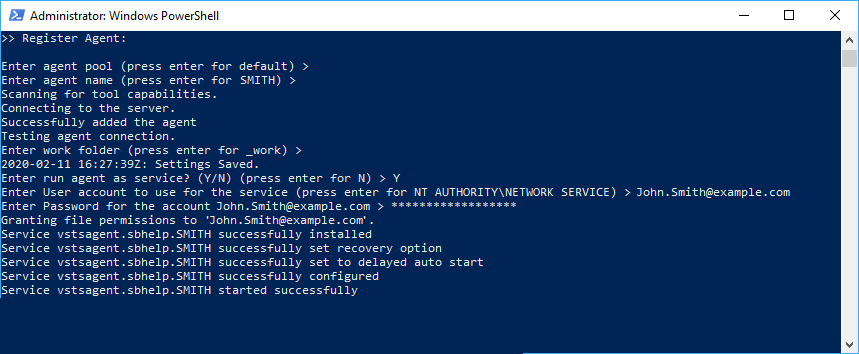
Specify the user account that you used to activate the SoapUI license and enter its password:
Specify a user when a service exists
-
Make sure you have a valid license activated. If you do not have a valid license, activate a SoapUI license (see License Activation).
-
Open the Control Panel.
-
Select System and Security and then Administrative Tools.
-
Run the Services utility.
-
Search for the agent service. Its name looks something like
VSTS Agent (<agent name>). -
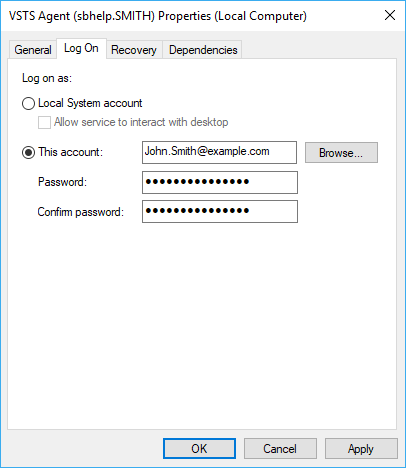
Right-click the service and select Properties.
-
On the Log On tab, select This account and enter the credentials of the Windows user account you will use to run SoapUI.
Note: This is the account that you used when activating the SoapUI license. -
Restart the service to apply the changes.
See Also
Azure DevOps (formerly VSTS) Integration
Command-Line Runners Specifics
ReadyAPI Documentation

 Azure DevOps Services
Azure DevOps Services