You can use the built-in browser to record requests to the web site, filter the needed ones, and create an API definition from them. To define this process, ReadyAPI uses the Discovery term.
1. Start Browser Discovery
You can discover the API for an existing project or create a new project.
-
To create a new project:
-
Select File > New Project.
-
In the follow-up dialog, select the REST Discovery tab.
-
Select the Use the built-in browser option.
-
Click OK.
-
-
To add an API to an existing project:
-
Right-click the project you need.
-
Select Discover APIs.
-
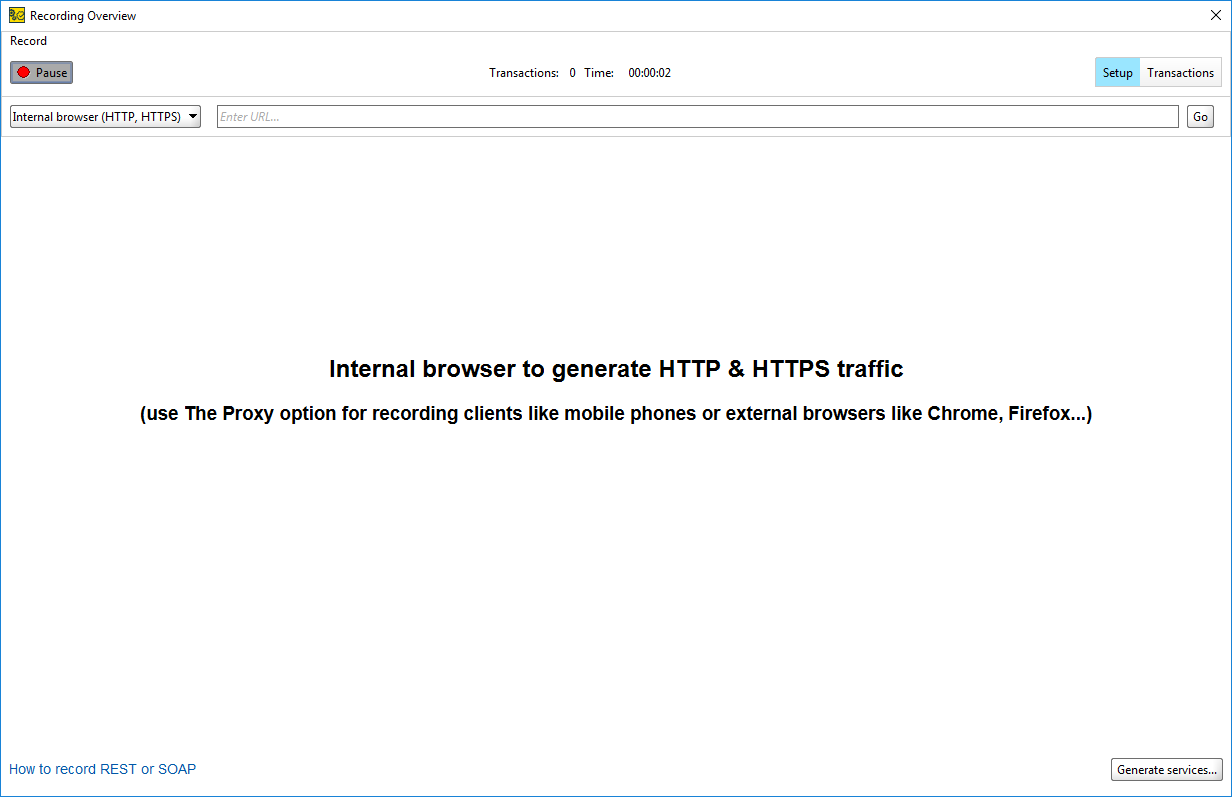
In either case, ReadyAPI will open the Recording Overview dialog. Make sure to select the Internal browser (HTTP, HTTPS) option in the drop-down list. You can enter the URL and start recording a request to the target service.
2. Record Requests
Use the built-in ReadyAPI browser to navigate to your service. ReadyAPI sends requests in the same way a browser would and records all API calls it performs.
If your service uses many API calls, click ![]() to disable recording until you get to the web page with the API you need. Then, click
to disable recording until you get to the web page with the API you need. Then, click ![]() again to re-enable recording.
again to re-enable recording.
 |
Some websites perform API calls for extra data after the page is loaded. ReadyAPI will track these calls and record them, as well. |
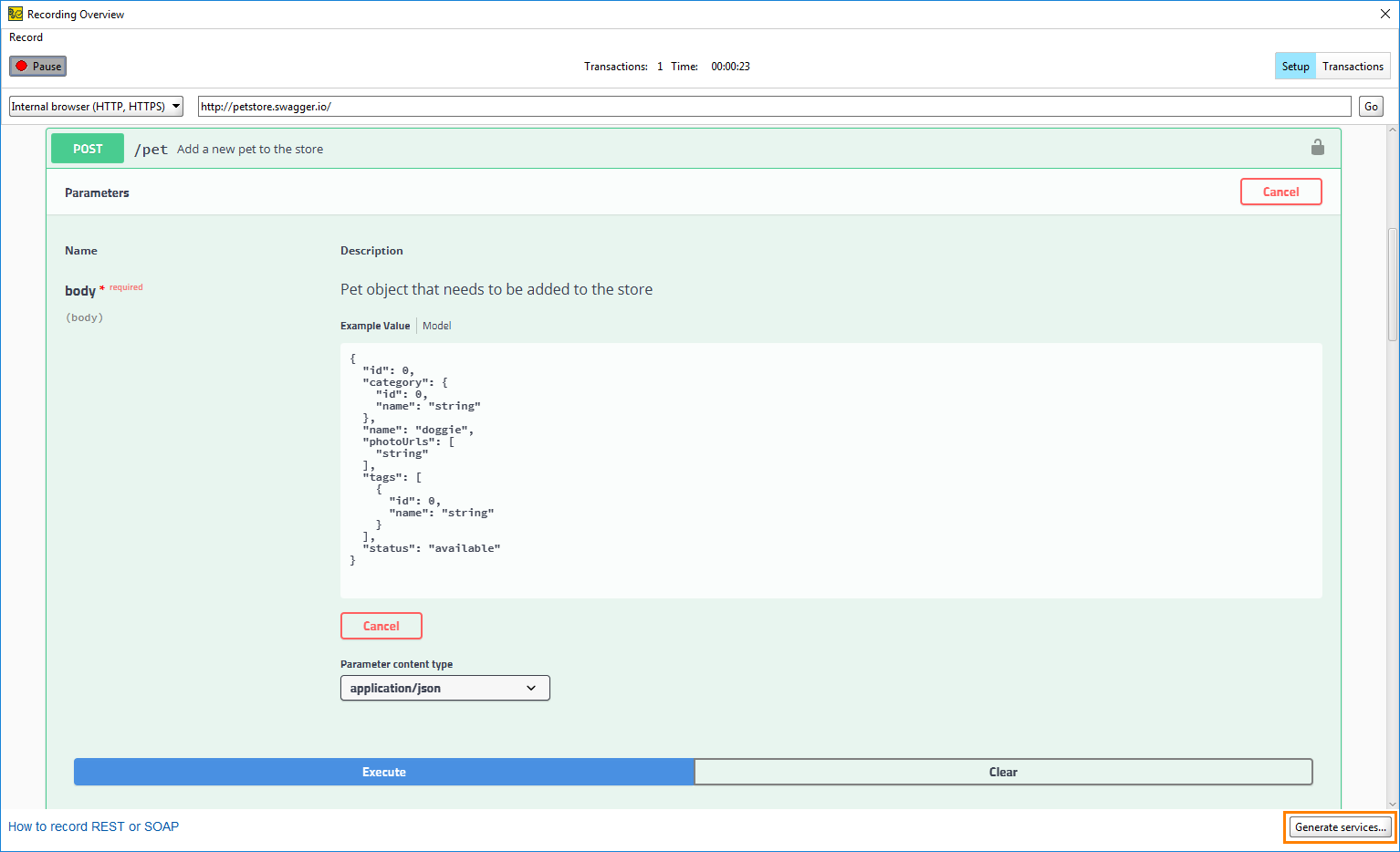
To view the recorded requests and responses, switch to the Transactions page.
3. Generate Service Definitions
To generate a service definition for the requests ReadyAPI has recorded:
-
Make sure to select only the requests you need on the Transactions page. Otherwise, ReadyAPI will create API definitions for all available requests.
-
Click Generate services.
-
In the Generate Services dialog, select Generate Test Case or Generate LoadUI Test to create a simple SoapUI or LoadUI test.
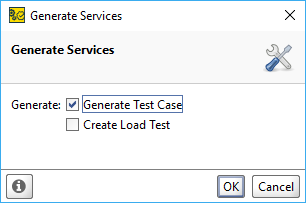
-
Click OK.
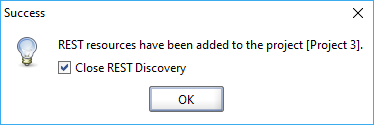
ReadyAPI will generate service definitions and, if selected, ask you to name the SoapUI test suite and LoadUI test respectively. Then, it will inform you of the success and offer to close the Recording Overview dialog.
 |
Make sure to deselect the Close REST Discovery option if you want to create more API definitions from requests ReadyAPI has recorded. |
HTTPS Service Specifics
When you discover a service by using an HTTPS connection, the browser first creates a secure connection. During this process, the server sends a certificate and the browser verifies if the certificate can be trusted. If the certificate is trusted, a connection is established. If it is not, the browser displays a warning and stops creating the connection.
Internal services that are used for testing often use self-signed certificates that are not trusted by default. To work with them, enable the Self-signed certificate option in the Internal Browser properties.
Additionally, the browser can verify the hostname against the hostname provided in the certificate by using SNI and prevent connections if the certificate is issued to a different host. To disable verification, deselect the Hostname verification option in the Internal Browser properties.
 |
These options pose a security risk when working with untrusted websites. |
See Also
Discovering APIs
Using ReadyAPI as Proxy
Discovery Tutorial
Discovering APIs
Internal Browser
Creating Your First Functional Test
Tutorials and Samples